mirror of
https://github.com/pyecharts/pyecharts.git
synced 2026-02-01 17:46:01 +00:00
English documents update (#719)
* update docs/en-us/, add 7 md files, 2 have finished translation. fix and add some contents in docs/zh-cn/ * finish translating api.md update api.md, advanced.md * finished docs/en_us/charts_configure.md * finished themes.md translation work * finished charts_configure.md translation work * temp commit * [漏斗图] 标签外部显示需要补图 * Finish charts_base.md translation work * Finish charts_base.md translation work * fix ![funnel-1] url mistake * 1. charts_base.md, unitified use ![xxx-demo] url tag; 2. Delete zh_cn donate.md English content; 3. _sidebar.md correct some mistake; 4. donors.md unitified use zh-cn/donors
This commit is contained in:
parent
94d2995393
commit
cb1888ba0f
@ -1,9 +1,16 @@
|
||||
pyecharts is a class library for generating ECharts charts. ECharts is a data visualization JS library of Baidu Open Source. The graphics generated with ECharts are very visual, and pyecharts is designed to interface with Python, making it easy to use data generation diagrams directly in Python.
|
||||
|
||||
- Basic Usage
|
||||
- [Chart Render](en-us/prepare)
|
||||
- [Chart Options](en-us/charts)
|
||||
- [Chart Configuration](en-us/charts_configure)
|
||||
- [Chart Basic](en-us/charts_base)
|
||||
- [Chart Customization](en-us/charts_custom)
|
||||
- Advance Topics
|
||||
- [Chart API](en-us/api)
|
||||
- [Custom Map](en-us/customize_map)
|
||||
- [Themes Customization](en-us/themes)
|
||||
- [Map Customization](en-us/customize_map)
|
||||
- [Callback Function & Event Handler](en-us/advanced)
|
||||
- [Language Translator Extension](en-us/translator)
|
||||
- Platform Support
|
||||
- [Jupyter Notebook](en-us/jupyter_notebook)
|
||||
- [Flask](en-us/flask)
|
||||
@ -12,9 +19,11 @@
|
||||
- Other Resources
|
||||
- [Demo Projects](https://github.com/pyecharts/pyecharts-users-cases)
|
||||
- [Geography & Map](en-us/datasets)
|
||||
|
||||
- Development
|
||||
- Project Release
|
||||
- [Changelog](zh-cn/changelog)
|
||||
- [Release Note](zh-cn/release-note)
|
||||
- [Release Note](zh-cn/release-note/)
|
||||
- Project Development
|
||||
- [Technical Documents](en-us/technical)
|
||||
- [Team](en-us/team)
|
||||
- [Donors List](zh-cn/donors)
|
||||
- [FAQ](en-us/faq)
|
||||
|
||||
285
docs/en-us/advanced.md
Normal file
285
docs/en-us/advanced.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,285 @@
|
||||
> Advanced Usage: This document describes advanced usage of the pyecharts library.
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Starting with v0.5.0, pyecharts supports the *javascript callback function* and the *echarts event handler*, further covering the [ECharts](http://echarts.baidu.com/) related features. Inject new vitality into the development of the project.
|
||||
|
||||
In the field of Python-To-Javascript language translation, [javascripthon](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/javascripthon) is a simple Python 3.5+ to Javascript language translator; [dukpy](https:/ /github.com/amol-/dukpy) Supports language translation for Python 2.7 and Python 3.4.
|
||||
|
||||
Based above, the pyecharts team developed [pyecharts-javascripthon] (https://github.com/pyecharts/pyecharts-javascripthon) as the underlying Python-To-Javascript language translation library, which encapsulated the above two different translators. Several Javascript data type adaptation modules are also available. For more on the translator, please go to [Translator] (en-us/translator).
|
||||
|
||||
pyecharts currently only uses and encapsulates some of Javascripthon's translation rules, mainly **Function Translate**. Use pseudo code to indicate the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
input:a Python function objection
|
||||
output:a multi-line unicode string
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For example, input the following Python functions:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def add(x, y):
|
||||
return x + y
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Translated into the following Javascript functions.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
function add(x, y) {
|
||||
return (x + y);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For pyecharts users, there is no need to understand how the translator works.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic installation
|
||||
|
||||
pyecharts has pyecharts-javascripthon installed by default and can also be installed via pip.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ pip install pyecharts-javascripthon
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment restrictions
|
||||
|
||||
Since Javascripthon requires a version of Python of at least 3.5+ and pyecharts users of python 2.7, 3.4, 3.5 and 3.6, pyecharts-javascripthon uses a two-track system: python 3.5+ users directly use Javascripthon; python 2.7 and 3.4 users call network translation services (software as a service). At the same time, I hope that everyone will support the operating expenses of this network service.
|
||||
|
||||
> Note: Make sure the system is networked when using Python 2.7-3.4 users.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## JavaScript callback function
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic usage
|
||||
|
||||
pyecharts has encapsulated the underlying related logic and is transparent to the user. So you can use it as before. The callback function is assigned to the echarts configuration dictionary via the `add` method. The callback function here must satisfy one of the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
- Defined function with `def`
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the `lambda` expression is currently not supported.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def label_formatter(params):
|
||||
return params.value + ' [Good!]'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
attr = ["Jan", "Feb"]
|
||||
v1 = [2.0, 4.9]
|
||||
bar = Bar("Bar chart", "precipitation and evaporation one year")
|
||||
bar.add("precipitation", attr, v1, is_label_show=True, label_formatter=label_formatter)
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> Callback function format reference [series[i]-bar.label.formatter](http://echarts.baidu.com/option.html#series-bar.label.formatter) 。
|
||||
|
||||
Rendering
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Tooltip example
|
||||
|
||||
For example, pyecharts users often ask questions in the Geo diagram how to display only the map coordinate names and values in the tooltip without the latitude and longitude.
|
||||
|
||||
Like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def test_geo_shantou_city():
|
||||
data = [('澄海区', 30), ('南澳县', 40), ('龙湖区', 50), ('金平区', 60)]
|
||||
geo = Geo("汕头市地图示例", **style.init_style)
|
||||
attr, value = geo.cast(data)
|
||||
geo.add(
|
||||
"",
|
||||
attr,
|
||||
value,
|
||||
maptype="汕头",
|
||||
is_visualmap=True,
|
||||
is_legend_show=False,
|
||||
label_emphasis_textsize=15,
|
||||
label_emphasis_pos='right',
|
||||
)
|
||||
geo.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, you can do this by defining a `geo_formatter` function firstly.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def geo_formatter(params):
|
||||
return params.name + ' : ' + params.value[2]
|
||||
|
||||
def test_geo_shantou_city():
|
||||
data = [('澄海区', 30), ('南澳县', 40), ('龙湖区', 50), ('金平区', 60)]
|
||||
geo = Geo("汕头市地图示例", **style.init_style)
|
||||
attr, value = geo.cast(data)
|
||||
geo.add(
|
||||
"",
|
||||
attr,
|
||||
value,
|
||||
maptype="汕头",
|
||||
is_visualmap=True,
|
||||
is_legend_show=False,
|
||||
tooltip_formatter=geo_formatter, # The point is here to pass the function directly as a parameter.
|
||||
label_emphasis_textsize=15,
|
||||
label_emphasis_pos='right',
|
||||
)
|
||||
geo.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Label example
|
||||
|
||||
Use the callback function to set float type
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts_javascripthon.dom import window
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar, Grid
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def custom_formatter(params):
|
||||
return window.parseFloat(params.value).toFixed(2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
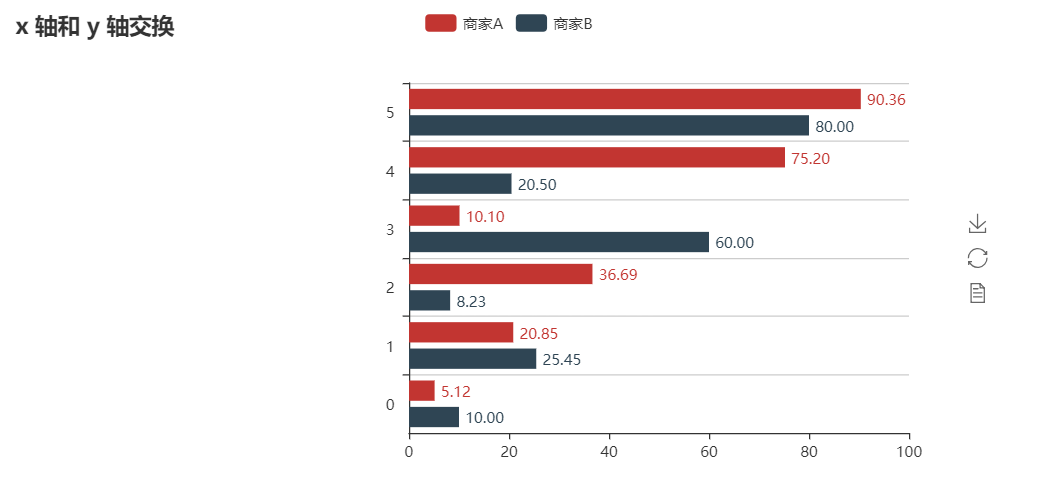
attr = ["aa", "bb", "Diabetes Mellitus Requiring Medication", "d", "e", "fff"]
|
||||
v1 = [5.12, 20.85, 36.69, 10.10, 75.20, 90.36]
|
||||
v2 = [10.00, 25.45, 8.23, 60.00, 20.50, 80.00]
|
||||
bar = Bar("x 轴和 y 轴交换")
|
||||
bar.add(
|
||||
"商家A",
|
||||
attr,
|
||||
v1,
|
||||
is_label_show=True,
|
||||
label_pos="right",
|
||||
label_formatter=custom_formatter,
|
||||
)
|
||||
bar.add(
|
||||
"商家B",
|
||||
attr,
|
||||
v2,
|
||||
is_convert=True,
|
||||
is_label_show=True,
|
||||
label_pos="right",
|
||||
label_formatter=custom_formatter,
|
||||
)
|
||||
grid = Grid()
|
||||
grid.add(bar, grid_left="40%")
|
||||
grid.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## JavaScript event handlers
|
||||
|
||||
Echarts provides [api/events](http://echarts.baidu.com/api.html#events) event handlers, mainly via 'on' method.
|
||||
|
||||
pyecharts provides the following global event name variables based on the official list of events. Located in the `pyecharts.echarts.events` module.
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
# Mouse Events
|
||||
MOUSE_CLICK = "click"
|
||||
MOUSE_DBCLICK = "dbclick"
|
||||
MOUSE_DOWN = "mousedown"
|
||||
MOUSE_OVER = "mouseover"
|
||||
MOUSE_GLOBALOUT = "globalout"
|
||||
|
||||
# Other Events
|
||||
LEGEND_SELECT_CHANGED = "legendselectchanged"
|
||||
LEGEND_SELECTED = "legendselected"
|
||||
LEGEND_UNSELECTAED = "legendunselected"
|
||||
LEGEND_SCROLL = "legendscroll"
|
||||
DATA_ZOOM = "datazoom"
|
||||
DATA_RANGE_SELECTED = "datarangeselected"
|
||||
TIMELINE_CHANGED = "timelinechanged"
|
||||
TIMELINE_PLAY_CHANGED = "timelineplaychanged"
|
||||
RESTORE = "restore"
|
||||
DATA_VIEW_CHANGED = "dataviewchanged"
|
||||
MAGIC_TYPE_CHANGED = "magictypechanged"
|
||||
GEO_SELECT_CHANGED = "geoselectchanged"
|
||||
GEO_SELECTED = "geoselected"
|
||||
GEO_UNSELECTED = "geounselected"
|
||||
PIE_SELECT_CHANGED = "pieselectchanged"
|
||||
PIE_SELECTED = "pieselected"
|
||||
PIE_UNSELECTED = "pieunselected"
|
||||
MAP_SELECT_CHANGED = "mapselectchanged"
|
||||
MAP_SELECTED = "mapselected"
|
||||
MAP_UNSELECTED = "mapunselected"
|
||||
AXIS_AREA_SELECTED = "axisareaselected"
|
||||
FOCUS_NODE_ADJACENCY = "focusnodeadjacency"
|
||||
UNFOCUS_NODE_ADJACENCY = "unfocusnodeadjacency"
|
||||
BRUSH = "brush"
|
||||
BRUSH_SELECTED = "brushselected"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The usage is as follows:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
from __future__ import unicode_literals
|
||||
|
||||
import pyecharts.echarts.events as events
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
from pyecharts_javascripthon.dom import alert
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def on_click():
|
||||
alert("点击事件触发")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_mouse_click():
|
||||
bar = Bar("我的第一个图表", "这里是副标题")
|
||||
bar.add(
|
||||
"服装", ["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"], [5, 20, 36, 10, 75, 90]
|
||||
)
|
||||
bar.on(events.MOUSE_CLICK, on_click)
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
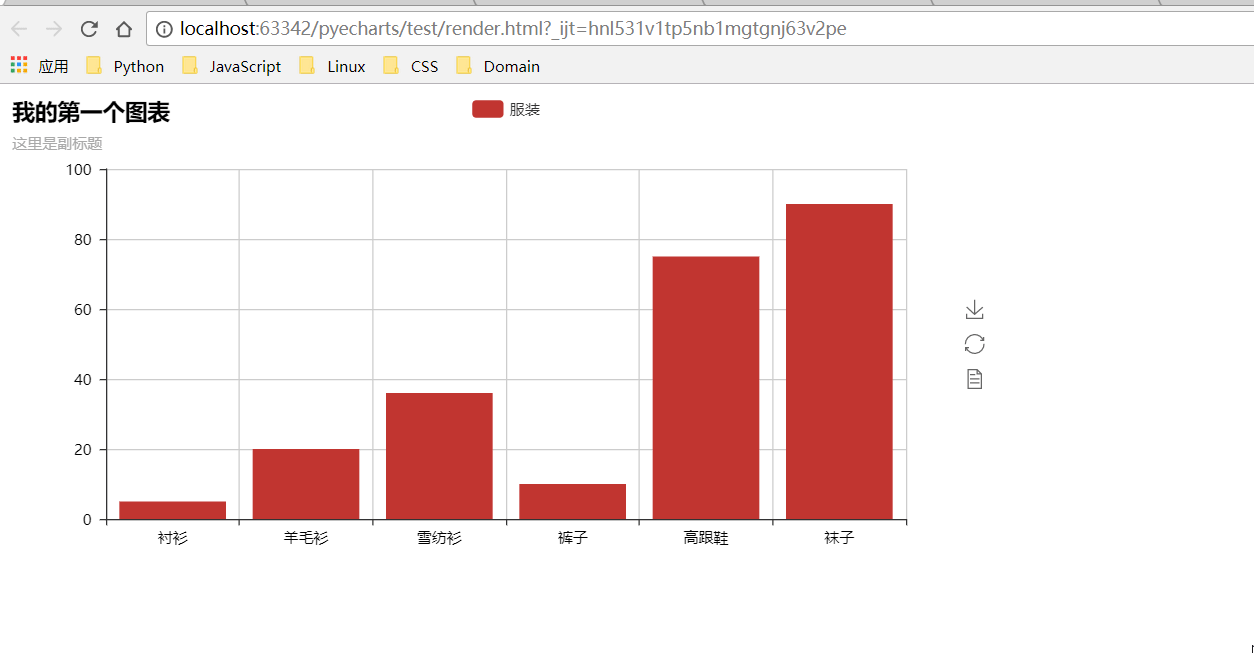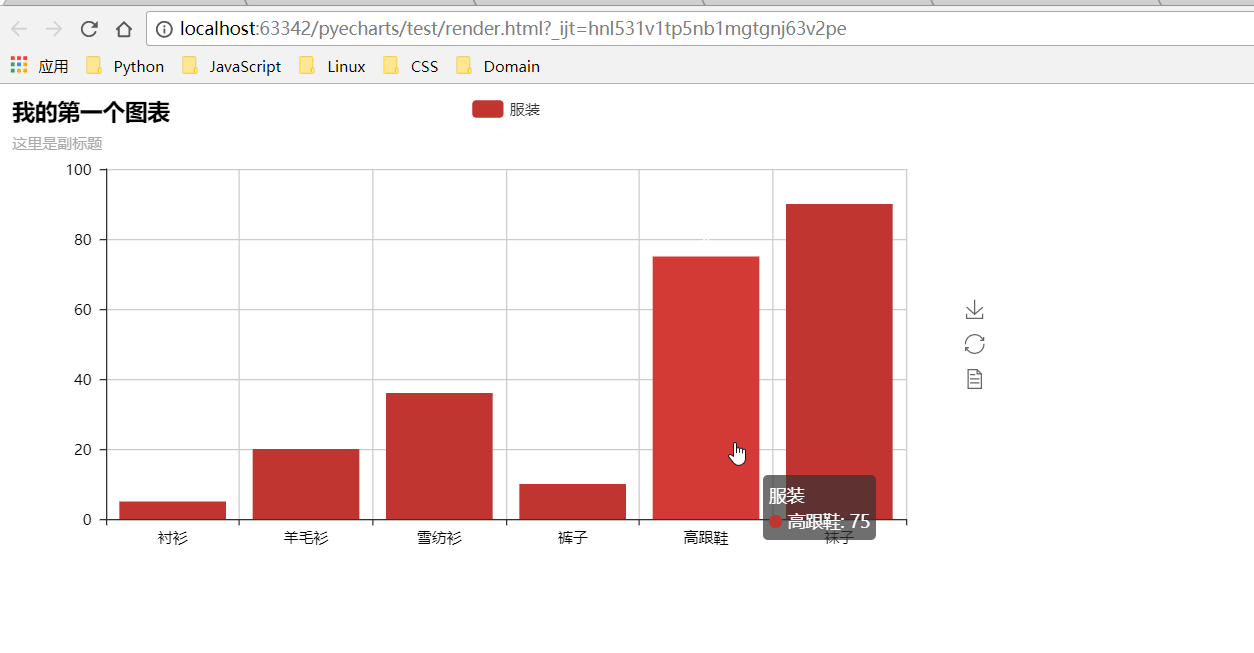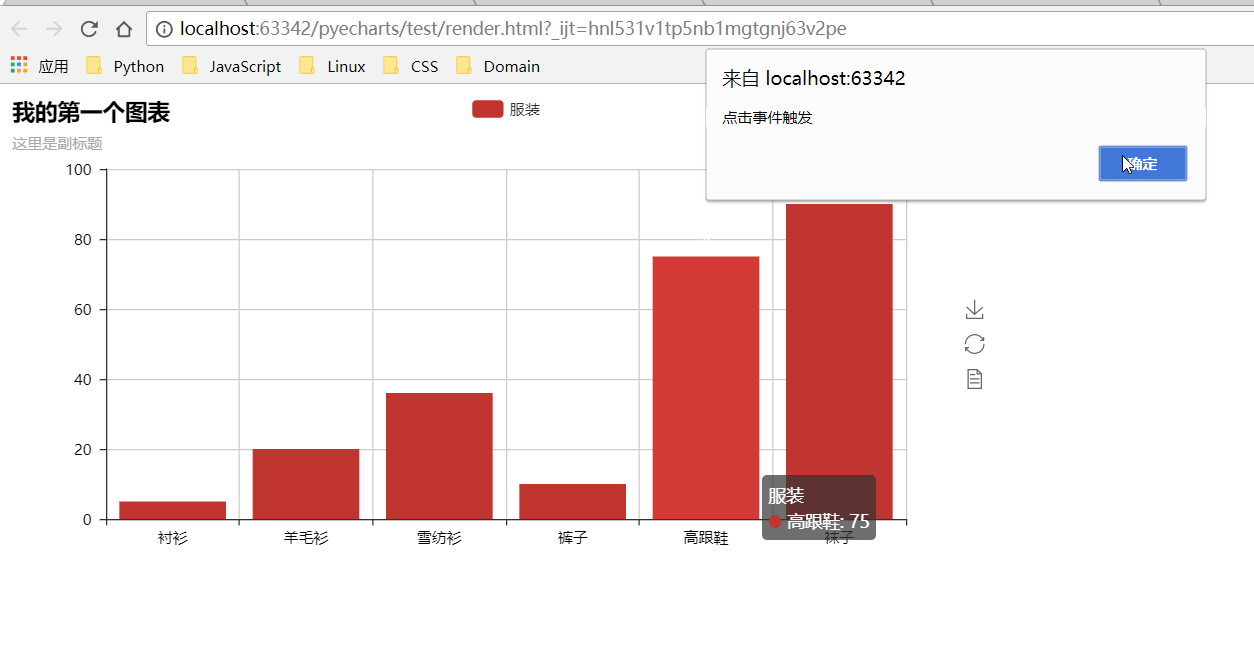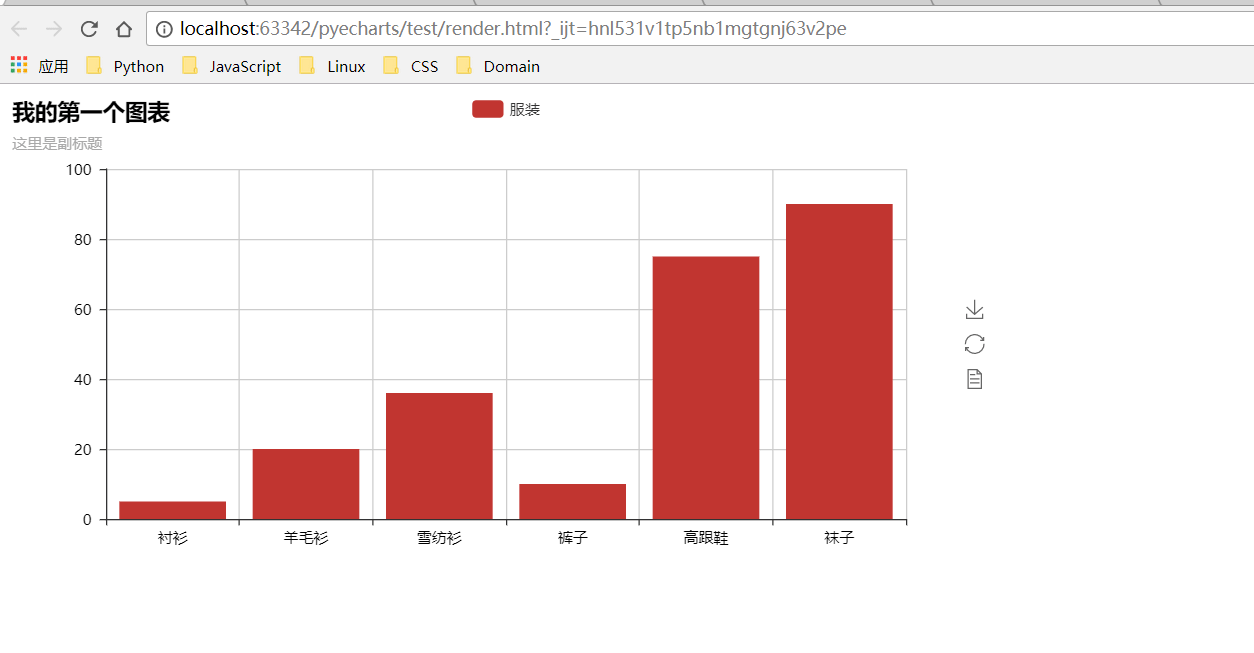
|
||||
|
||||
## Note
|
||||
|
||||
First, pyecharts does not check if the echarts chart configuration option supports callback functions. See the ECharts documentation for this section.
|
||||
|
||||
This refers to whether the options parameter itself supports callback functions, such as :
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def my_title():
|
||||
return 'my_title'
|
||||
bar.add(my_title, [], [])
|
||||
```
|
||||
There are no rendering errors in pyecharts, but it does not meet the requirements for title in ECharts.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Second, in order to improve performance, pyecharts did the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- The actual execution of a function translation is when the `render` function is called, not the `add` function.
|
||||
- Cache the function that has been translated with the **function name** as an index to avoid rendering the function of the same name multiple times.
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, you should avoid using the same function name. The following situations may not achieve the expected results.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
|
||||
def label_formatter(params):
|
||||
return params.name + ' [Good!]'
|
||||
|
||||
attr = ["Jan", "Feb"]
|
||||
v1 = [2.0, 4.9]
|
||||
bar = Bar("Bar chart", "precipitation and evaporation one year")
|
||||
bar.add("precipitation", attr, v1, is_label_show=True, label_formatter=label_formatter)
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
|
||||
def label_formatter(params):
|
||||
return params.name + '[OK!]'
|
||||
|
||||
bar2 = Bar("Bar chart", "precipitation and evaporation one year")
|
||||
bar2.add("precipitation", attr, v1, is_label_show=True, label_formatter=label_formatter)
|
||||
bar2.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -10,46 +10,57 @@ A common proccess can be listed as the following table:
|
||||
| ------------------------ | ---------------------------------------- | ------ |
|
||||
| 1 Create chart instance | `bar = Bar()` | |
|
||||
| 2 Add data | `bar.add(**kwargs)` | |
|
||||
| 3 Create config instance | `config = PyEchartsConfig(**kwargs)` | |
|
||||
| 4 Create template engine | `engine = EchartsEnvironment(pyecharts_config=config)` | |
|
||||
| 5 Get template file | `tpl = engine.get_template('demo_tpl.html')` | |
|
||||
| 6 Render | `html = tpl.render(bar=bar)` | |
|
||||
| 7 Write to target file | `write_utf8_html_file('my_demo_chart.html', html)` | |
|
||||
| 3 Add event handler | `bar.on(event_name, handler)` | added in v0.5.0 |
|
||||
| 4 Create config instance | `config = PyEchartsConfig(**kwargs)` | |
|
||||
| 5 Create template engine | `engine = EchartsEnvironment(pyecharts_config=config)` | |
|
||||
| 6 Get template file | `tpl = engine.get_template('demo_tpl.html')` | |
|
||||
| 7 Render | `html = tpl.render(bar=bar)` | |
|
||||
| 8 Write to target file | `write_utf8_html_file('my_demo_chart.html', html)` | |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## pyecharts Config Items
|
||||
|
||||
pyecharts follows the principle of "Config-Use" . The class `pyecharts.conf.PyEChartsConfig` contains all config items when using *pyecharts* library.Before building chart, you can use module function `configure` to set all config items.
|
||||
pyecharts follows the principle of "Config-Use" . The class `pyecharts.conf.PyEChartsConfig` contains all config items when using *pyecharts* library. If you use the `chart.render()` rendering method, you can modify the default configuration class in pyecharts via the module function `configure`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import pyecharts
|
||||
pyecharts.configure(P1=V1, P2=V2,...)
|
||||
pyecharts.configure(
|
||||
jshost=None,
|
||||
echarts_template_dir=None,
|
||||
force_js_embed=None,
|
||||
output_image=None,
|
||||
global_theme=None
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Config Item List
|
||||
|
||||
**echarts_template_dir**
|
||||
|
||||
The diretory of template files. Default value: '.'(current diretory).
|
||||
|
||||
**jshost**
|
||||
|
||||
The repository of js dependency files.You can set it with a local host url or remote host url(starts with `http://` or `https://` ).
|
||||
js file repository path. You can set a local or remote url. All remote url must start with `http://` or `https://`. This option can also be set with the `pyecharts.online()` function.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use `pyecharts.online()` to set this item.
|
||||
For compatibility, jshost does not have to end with a separator such as '/'.
|
||||
|
||||
WIth the compatibility, this string value do not need `/` as its ending character.
|
||||
**echarts_template_dir**
|
||||
|
||||
The diretory of template files. Default value: '.'(current diretory). Used to customize the template file. The template_name parameter of `render` constitutes the entire path.
|
||||
|
||||
**force_js_embed**
|
||||
|
||||
Whether to force to insert javascript file with internal embed mode. This item will affect the function`echarts_js_dependencies` .
|
||||
Whether to force to insert javascript file with internal embed mode. This item will affect the function `echarts_js_dependencies` .
|
||||
|
||||
**output_image**
|
||||
|
||||
Specify the output image type with `svg` , `jpeg` , `png` options.
|
||||
|
||||
**global_theme**
|
||||
|
||||
Specify global themes, currently available as `dark`, `vintage`, `macarons`, `infographic`, `shine` and `roma`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Charts Classes
|
||||
|
||||
Charts classes is the core component of this library.Each charts class represents the one kind of chart in [Echarts](http://echarts.baidu.com/) .
|
||||
Charts classes is the core component of this library.Each charts class represents the one kind of chart in [ECharts](http://echarts.baidu.com/) .
|
||||
|
||||
This pictures the inherit tree for these charts classes.
|
||||
The following table shows the inheritance of these charts.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -67,27 +78,27 @@ This table list properties for these chart classes.
|
||||
|
||||
**chart_id**
|
||||
|
||||
Data type:str.The identifier string for a chart. E.g.`'d2d9dcc4e28247518186c0882d356ba8'` 。
|
||||
Data type : str. The unique identifier string for a chart. Default value is uuid format string, e.g.`'d2d9dcc4e28247518186c0882d356ba8'` 。
|
||||
|
||||
**width**
|
||||
|
||||
Data type:number/str.A valid string for css length.The width(px) of div container for a chart.
|
||||
Data type : number/str. A valid string for css length.The width(px) of div container for a chart.
|
||||
|
||||
**height**
|
||||
|
||||
Data type:number/str.A valid string for css length.The height(px) of div container for a chart.
|
||||
Data type : number/str. A valid string for css length.The height(px) of div container for a chart.
|
||||
|
||||
> chart_id, width, and height attributes all support writable.
|
||||
|
||||
**options**
|
||||
|
||||
Data type:dict.The config options for a chart。Each chart has its own format and value.Please see more detail at ECharts document。
|
||||
Data type : dict. The config options for a chart. Each chart has its own format and value. Please see more detail at ECharts document。
|
||||
|
||||
**js_dependencies**
|
||||
|
||||
*Changed in v0.4*
|
||||
Data type : list. The js filename collections for a chart's dependencies. Every element do not contain the filename extension(.js), e.g. `{'echarts.min', 'fujian'}` .
|
||||
|
||||
Data type:list.The js filename collections for a chart's dependencies.Every element do not contain the filename extension(.js).E.g `{'echarts.min', 'fujian'}` .
|
||||
|
||||
> In previous v0.4, the js_dependencies returns a unordered set.
|
||||
> Since v0.4, pyecharts rewrites the generation logic of `js_dependencies`. Currently returns an ordered, unique element list object. You can also merge the js dependencies of several charts with the `pyecharts.utils.merge_js_dependencies` function.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Methods
|
||||
@ -104,13 +115,128 @@ Add options and data to a chart.See the source code for more detail.
|
||||
| Timeline | `add(chart, time_point)` |
|
||||
| Page | `add(achart_or_charts)` |
|
||||
|
||||
**on(event_name, handler)**
|
||||
|
||||
Add [event handler function](http://echarts.baidu.com/api.html#events)。
|
||||
|
||||
* event_name:event name
|
||||
* handler:callback function
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Below is all supported events
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
# Mouse Events
|
||||
|
||||
MOUSE_CLICK = 'click'
|
||||
MOUSE_DBCLICK = 'dbclick'
|
||||
MOUSE_DOWN = 'mousedown'
|
||||
MOUSE_OVER = 'mouseover'
|
||||
MOUSE_GLOBALOUT = 'globalout'
|
||||
|
||||
# Other Events
|
||||
|
||||
LEGEND_SELECT_CHANGED = 'legendselectchanged'
|
||||
LEGEND_SELECTED = 'legendselected'
|
||||
LEGEND_UNSELECTAED = 'legendunselected'
|
||||
LEGEND_SCROLL = 'legendscroll'
|
||||
DATA_ZOOM = 'datazoom'
|
||||
DATA_RANGE_SELECTED = 'datarangeselected'
|
||||
TIMELINE_CHANGED = 'timelinechanged'
|
||||
TIMELINE_PLAY_CHANGED = 'timelineplaychanged'
|
||||
RESTORE = 'restore'
|
||||
DATA_VIEW_CHANGED = 'dataviewchanged'
|
||||
MAGIC_TYPE_CHANGED = 'magictypechanged'
|
||||
GEO_SELECT_CHANGED = 'geoselectchanged'
|
||||
GEO_SELECTED = 'geoselected'
|
||||
GEO_UNSELECTED = 'geounselected'
|
||||
PIE_SELECT_CHANGED = 'pieselectchanged'
|
||||
PIE_SELECTED = 'pieselected'
|
||||
PIE_UNSELECTED = 'pieunselected'
|
||||
MAP_SELECT_CHANGED = 'mapselectchanged'
|
||||
MAP_SELECTED = 'mapselected'
|
||||
MAP_UNSELECTED = 'mapunselected'
|
||||
AXIS_AREA_SELECTED = 'axisareaselected'
|
||||
FOCUS_NODE_ADJACENCY = 'focusnodeadjacency'
|
||||
UNFOCUS_NODE_ADJACENCY = 'unfocusnodeadjacency'
|
||||
BRUSH = 'brush'
|
||||
BRUSH_SELECTED = 'brushselected'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Prototype of event handler:
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
def handler(params):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, the structure of params is exactly the same as echarts:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{
|
||||
// type of the component to which the clicked glyph belongs
|
||||
// i.e., 'series', 'markLine', 'markPoint', 'timeLine'
|
||||
componentType: string,
|
||||
// series type (make sense when componentType is 'series')
|
||||
// i.e., 'line', 'bar', 'pie'
|
||||
seriesType: string,
|
||||
// series index in incoming option.series (make sense when componentType is 'series')
|
||||
seriesIndex: number,
|
||||
// series name (make sense when componentType is 'series')
|
||||
seriesName: string,
|
||||
// data name, category name
|
||||
name: string,
|
||||
// data index in incoming data array
|
||||
dataIndex: number,
|
||||
// incoming rwa data item
|
||||
data: Object,
|
||||
// Some series, such as sankey or graph, maintains more than
|
||||
// one types of data (nodeData and edgeData), which can be
|
||||
// distinguished from each other by dataType with its value
|
||||
// 'node' and 'edge'.
|
||||
// On the other hand, most series has only one type of data,
|
||||
// where dataType is not needed.
|
||||
dataType: string,
|
||||
// incoming data value
|
||||
value: number|Array
|
||||
// color of component (make sense when componentType is 'series')
|
||||
color: string
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Example :
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
from __future__ import unicode_literals
|
||||
|
||||
from pyecharts import Map
|
||||
import pyecharts.events as events
|
||||
from pyecharts_javascripthon.dom.functions import alert
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def on_click(params):
|
||||
alert(params.name)
|
||||
|
||||
value = [155, 10, 66, 78]
|
||||
attr = ["福建", "山东", "北京", "上海"]
|
||||
map = Map("全国地图示例", width=1200, height=600)
|
||||
map.add("", attr, value, maptype='china', is_label_show=True)
|
||||
map.on(events.MOUSE_CLICK, on_click)
|
||||
map.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
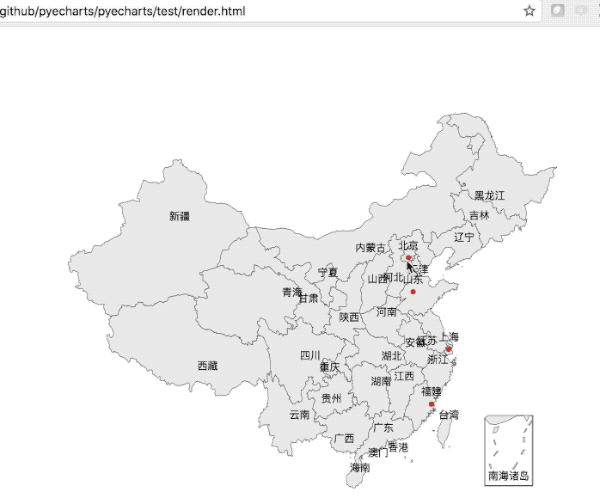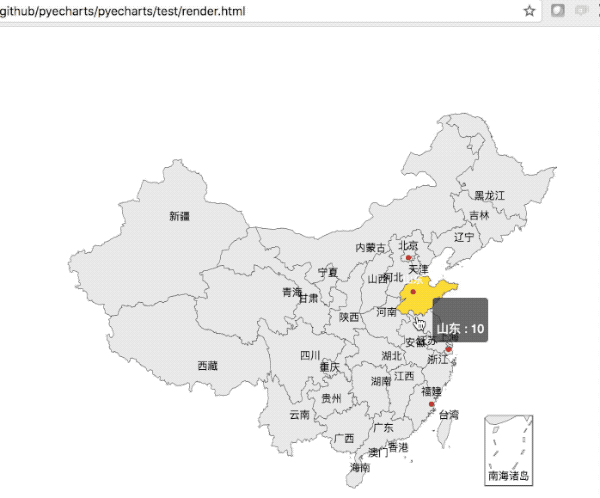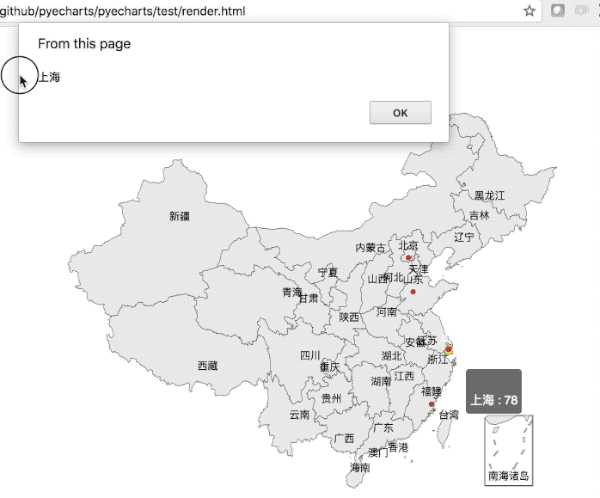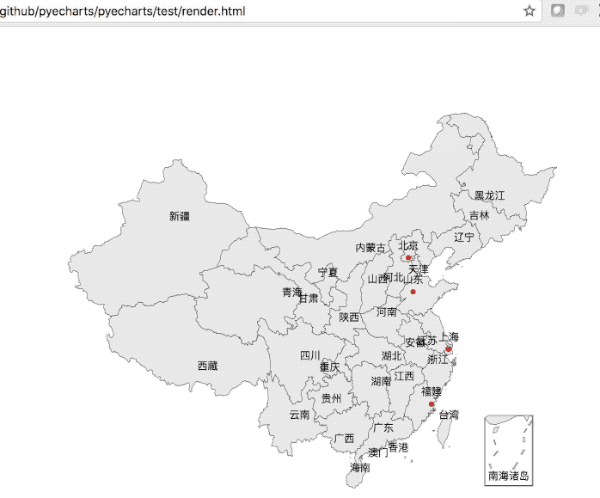
|
||||
|
||||
**get_js_dependencies()**
|
||||
|
||||
Gert the javascript dependencies of a chart.
|
||||
Get the javascript dependencies of a chart. Unlike the attribute *js_dependencies*, the element here contains the full path to the file.
|
||||
|
||||
**render(path='render.html')**
|
||||
**render(path='render.html', template_name='simple_chart.html', object_name='chart', extra_context=None)**
|
||||
|
||||
Render to a HTML page.
|
||||
Render to the specified HTML page, using the default template file for different chart types. The meaning of each parameter is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
- path :final generated file name
|
||||
- template_name : the name of the template file whose directory can be configured via the `pyecharts.configure()` global function
|
||||
- object_name : The name of the variable used by the chart class in the template file
|
||||
- extra_context : Extra data dictionary
|
||||
|
||||
**render_embed()**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -118,80 +244,93 @@ Render javascript code fragment including options.
|
||||
|
||||
**print_echarts_options()**
|
||||
|
||||
Print all options of charts.The new alias form `show_config`.
|
||||
Print all options of charts.
|
||||
|
||||
**show_config()**
|
||||
|
||||
Print all options of charts.From v0.3.3,this method has been deprecated and use `print_echarts_options` instead.
|
||||
Print all options of charts. From v0.3.3,this method has been deprecated and use `print_echarts_options` instead.
|
||||
|
||||
## Multiple Chart
|
||||
## Multiple Chart Page
|
||||
|
||||
`pyecharts.custom.page.Page` is used to show multiple chart in a html page,which includes properties and methods above.
|
||||
> Changed in v0.5.4, override internal implementation, add chart name.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, `Page` inherits built-in `list` and len,iter,index,splice,append,extend are supported.
|
||||
### Basic usage
|
||||
|
||||
Example,print the option for each chart in a page object.
|
||||
Since either the Jinja2 template or the Django template, it is not recommended to use the `{{ charts.1 }}` form to access an element in the list. So reconstruct the Page in v0.5.4 and add a chart named name.
|
||||
|
||||
After creating a `Page` instance page , add a chart object with `add_chart` and use name to give it a reference name.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
from pyecharts import Page, Line, Bar
|
||||
|
||||
page = Page()
|
||||
line = Line('Demo Line')
|
||||
# ... Add data to line
|
||||
page.add(line)
|
||||
kline = KLine('Demo kline')
|
||||
# ... Add data to kline
|
||||
page.append(kline)
|
||||
|
||||
for chart in page:
|
||||
chart.show_config()
|
||||
page.add_chart(line, name='line')
|
||||
bar = Bar('Demo kline')
|
||||
# ... Add data to bar
|
||||
page.add_chart(bar)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Chart access method
|
||||
|
||||
| Project | Python Code | Template Code |
|
||||
| ------ | ------ | ------ |
|
||||
| line instance | `print(page['line'])` | `{{ page.line }}` |
|
||||
| bar instance | `print(page['c1'])` | `{{ page.c1 }}` |
|
||||
|
||||
## Data Hanlder Methods
|
||||
### Methods list
|
||||
|
||||
These methods are tool methods for data handlers.
|
||||
After you create a page instance, you can add an existing chart instance to the instance in a variety of ways.
|
||||
|
||||
**cast**
|
||||
> Page no longer has all the features of list, so methods such as slice, append, and extend are no longer supported.
|
||||
|
||||
`pyecharts.base.Base.cast(seq)`
|
||||
**`__init__(page_title, **name_chart_pair)`**
|
||||
|
||||
Class method for formatting and converting data.It can convert your origin data to the corresponding data for pyecharts library.
|
||||
Constructor, create an instance using `{<name>:<chart>}`. According to [PEP 468] (https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0468/), the order is guaranteed only in Python 3.6+.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
**`add_chart(chart, name=None)`**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
o_data = [('A', '34'), ('B', '45'), ('C', '12')]
|
||||
x, y = Base.cast(o_data)
|
||||
print(x) # ['A', 'B', 'C']
|
||||
print(y) # ['34', '45', '12']
|
||||
```
|
||||
V0.5.4 added and support chaining. Add a chart object. If the `name` parameter is not specified, the default is to use a string like `'c0'`, `'c1'`.
|
||||
|
||||
**json_dumps**
|
||||
**`add(achart_or_charts)`**
|
||||
|
||||
`pyecharts.utils.json_dumps(data, indent=0)`
|
||||
Support chaining. Add one or more chart objects that use the default name.
|
||||
|
||||
Convert *data* to json string, and add encoding for some specified data type:
|
||||
**`cls.from_charts(*charts)`**
|
||||
|
||||
- Convert Datetime and Time objects to ISO8601 format string.
|
||||
- Cast numpy arrays. See the document of [astype](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ndarray.astype.html) and [tolist](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ndarray.tolist.html) .
|
||||
Create a `Page` instance from one or more chart instances.
|
||||
|
||||
### Chart methods
|
||||
|
||||
To be precise, `Page` is not a chart type in ECharts, and the included charts are not required to be relevant. For convenience, `Page` also has associated property methods, including:
|
||||
|
||||
- `page_title`
|
||||
- `js_dependencies`
|
||||
- `render_embed()`
|
||||
- `get_js_dependencies()`
|
||||
- `_repr_html_()`
|
||||
|
||||
These methods are used in the same way as the `Base` class.
|
||||
|
||||
## Template Engine
|
||||
|
||||
### Overview
|
||||
|
||||
*pyecharts* use [Jinja2](http://jinja.pocoo.org/) as its template engine, with some extra template functions.
|
||||
*pyecharts* use [Jinja2](http://jinja.pocoo.org/) as its template engine, with some ECharts chart related template functions.
|
||||
|
||||
> *Tempate function* and *template tag* is the same feature in the area of template engine.In Django it is called *template tag* and it is called *template function* in jinja2.
|
||||
> *Template function* and *template tag* are the same feature in the area of template engine. In Django it is called *template tag* and it is called *template function* in jinja2. The grammatical forms of them are also different.
|
||||
|
||||
### Engine Class
|
||||
|
||||
`pyecharts.engine` module defines some engine class, which inherit from `jinja2.Environment`.Each class has different use case.
|
||||
`pyecharts.engine` module defines some engine class, which inherit from `jinja2.Environment`. Each class has different use case.
|
||||
|
||||
**BaseEnvironment**
|
||||
|
||||
`pyecharts.engine.BaseEnvironment`
|
||||
|
||||
This class is the basic engine in pyecharts,and it inherits `jinja2.Environment` .It has the following extra features:
|
||||
This class is the basic engine in pyecharts, and it inherits from `jinja2.Environment` . It has the following extra features:
|
||||
|
||||
- Add *pyecharts_config* attribute, it is a `PyEchartsConfig` object.
|
||||
- Add `echarts_*` template functions
|
||||
@ -202,7 +341,7 @@ This class can be used for integration with web framework.
|
||||
|
||||
`pyecharts.engine.EChartsEnvironment`
|
||||
|
||||
EChartsEnvironment class inherits `BaseEnvironment` .And it use `pyecharts_config.echarts_template_dir` as the default value of template folder.
|
||||
EChartsEnvironment class inherits from `BaseEnvironment`. And on this basis, the behavior of the template file loader (loader) is rewritten. And it use `pyecharts_config.echarts_template_dir` as the default value of template folder.
|
||||
|
||||
This class should not be used in web integration because of overwriting the default behavior of template file loader.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -210,11 +349,19 @@ This class should not be used in web integration because of overwriting the defa
|
||||
|
||||
`pyecharts.engine.ECHAERTS_TEMPLATE_FUNCTIONS`
|
||||
|
||||
The dictionary containing template functions.It can be used in web integration.
|
||||
The dictionary containing template functions. It can be used in web integration.
|
||||
|
||||
### 模板函数
|
||||
### Engine method
|
||||
|
||||
pyecharts contains some template functions, which receives a or some `Chart` / `Page` objects as its parameter.See the following table.
|
||||
**create_default_environment(filet_ype)**
|
||||
|
||||
* file_type : output file type, 'html', 'svg', 'png', 'jpeg', 'gif', 'pdf' options
|
||||
|
||||
Create a default configuration environment for rendering
|
||||
|
||||
### Template functions
|
||||
|
||||
pyecharts contains some template functions, which receives one or more `Chart` / `Page` objects as its parameter. See the following table.
|
||||
|
||||
| Function Name/Function Sign | F(chart) | F(page) | F(chart1,chart2,...)/F(*page) |
|
||||
| ----------------------------- | -------- | ------- | ----------------------------- |
|
||||
@ -225,12 +372,11 @@ The dictionary containing template functions.It can be used in web integration.
|
||||
| echarts_js_content_wrap | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**echarts_js_dependencies**
|
||||
|
||||
`pyecharts.template.echarts_js_dependencies(*args)`
|
||||
|
||||
Render script html nodes with internal embed mode or enternal link.The mode will follow this table.
|
||||
Render script html nodes with internal embed mode or external link. The mode will follow this table.
|
||||
|
||||
Internal Embed(IE)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -247,13 +393,13 @@ Enternal Link(EL)
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" src="/static/js/echarts.min.js"></script>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Which mode is used is determined by the `PyEchartsConfig.jshost` and `PyEchartsConfig.force_js_embed` .See this table.
|
||||
Which mode is used is determined by the `PyEchartsConfig.jshost` and `PyEchartsConfig.force_js_embed`. See the following table :
|
||||
|
||||
| Value | local/remote | script mode | Use Case | Remark |
|
||||
| ---------------------------------------- | ------------ | ----------- | ------------------------- | --------------------- |
|
||||
| `/template/js/echarts` | local | IE | Generate one file locally | Default value |
|
||||
| `'https://chfw.github.io/jupyter-echarts/echarts'` | remote | IE | Generate on file | switch using `online` |
|
||||
| Other Local Host (E.g. `/static/js`) | local | EL | Integrate with Web | |
|
||||
| `'https://pyecharts.github.io/jupyter-echarts/echarts'` | remote | IE | Generate on file | switch using `online` |
|
||||
| Other Local Host (E.g. `/static/js`) | local | EL, Can be changed to inline by force_embed | Integrate with Web | |
|
||||
| Other Remote Host(E.g. `https://cdn.bootcss.com/echarts/3.7.2`) | remote | EL | Use remote JS | |
|
||||
|
||||
Example
|
||||
@ -272,19 +418,17 @@ bar = Bar('Demo Bar')
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/echarts.js"></script>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**echarts_js_dependencies_embed**
|
||||
|
||||
`pyecharts.template.echarts.js_dependencies_embed(*args)`
|
||||
|
||||
Render script nodes in internal embed mode.Only support local host.
|
||||
Render script nodes in internal embed mode. Only support local jshost.
|
||||
|
||||
**echarts_container**
|
||||
|
||||
`pyecharts.template.echarts_container(chart)`
|
||||
|
||||
Render the html node of container,output `<div></div>` element.
|
||||
Render the html node of container, output `<div></div>` element.
|
||||
|
||||
Example
|
||||
|
||||
@ -297,8 +441,6 @@ bar = Bar('Demo Bar')
|
||||
<div id="d09aa82b55384f84a33055f9878c3679" style="width:800px;height:400px;"></div>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**echarts_js_content**
|
||||
|
||||
`pyecharts.template.echarts_container(*chart)`
|
||||
@ -318,21 +460,25 @@ This is a full example.
|
||||
The pythonfile:demo.py
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from jinja2 import FileSystemLoader
|
||||
from __future__ import unicode_literals
|
||||
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
from pyecharts.conf import PyEchartsConfig
|
||||
from pyecharts.engine import EchartsEnvironment
|
||||
from pyecharts.utils import write_utf8_html_file
|
||||
|
||||
attr = ["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"]
|
||||
v1 = [5, 20, 36, 10, 75, 90]
|
||||
v2 = [10, 25, 8, 60, 20, 80]
|
||||
bar = Bar("柱状图数据堆叠示例", jshost=' https://cdn.bootcss.com/echarts/3.6.2')
|
||||
bar = Bar("柱状图数据堆叠示例")
|
||||
bar.add("商家A", attr, v1, is_stack=True)
|
||||
bar.add("商家B", attr, v2, is_stack=True)
|
||||
env = EchartsEnvironment(loader=FileSystemLoader('.'))
|
||||
tpl = env.get_template('demo.html')
|
||||
config = PyEchartsConfig(echarts_template_dir='my_tpl',
|
||||
jshost='https://cdn.bootcss.com/echarts/3.6.2')
|
||||
env = EchartsEnvironment(pyecharts_config=config)
|
||||
tpl = env.get_template('tpl_demo.html')
|
||||
html = tpl.render(bar=bar)
|
||||
write_utf8_html_file('demo_gen.html', html)
|
||||
write_utf8_html_file('my_tpl_demo2.html', html)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The template file:demo.html
|
||||
|
||||
2350
docs/en-us/charts.md
2350
docs/en-us/charts.md
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
3317
docs/en-us/charts_base.md
Normal file
3317
docs/en-us/charts_base.md
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
738
docs/en-us/charts_configure.md
Normal file
738
docs/en-us/charts_configure.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,738 @@
|
||||
> Charts configuration: pyecharts configuration documents
|
||||
|
||||
* Chart initialization
|
||||
* General options
|
||||
* xyAxis:x, y axis in cartesian coordinate system(Line, Bar, Scatter, EffectScatter, Kline)
|
||||
|
||||
* dataZoom:dataZoom components for zoom-in and zoom-out. With them, it is possible to magnify a small area, to see the overall picture or to stay away from scattered points(Line, Bar, Scatter, EffectScatter, Kline)
|
||||
|
||||
* legend:legend component has different symbol, colour and name, and provide the interactive clicking functions to show or hide its associated data series.
|
||||
|
||||
* label:text string on the chart, for marking the charts with sensible details, such as value, name.
|
||||
|
||||
* lineStyle:line style for Line, Polar, Radar, Graph, Parallel.
|
||||
|
||||
* grid3D:gird3D components in cartesian coordinate system(Bar3D, Line3D, Scatter3D, Surface3D)
|
||||
|
||||
* axis3D: 3D Cartesian coordinate system X, Y, Z axis configuration items for 3D graphics. (Bar3D, Line3D, Scatter3D, Surface3D)
|
||||
|
||||
* visualMap:It is a type of component for visual encoding, which maps the data to visual channels
|
||||
|
||||
* markLine-markPoint: A graphic markup component that marks the specified special data, with both marker lines and marker points. (Bar, Line, Kline)
|
||||
|
||||
* tooltip: prompt box component, used to pop up data content when moving or clicking the mouse
|
||||
|
||||
* toolbox: right utility toolbox
|
||||
|
||||
## Chart initialization
|
||||
>The parameter a chart type initialize accept (the same to all the chart type).
|
||||
|
||||
* title -> str
|
||||
default -> ''
|
||||
The main title text, supporting for \n for newlines.
|
||||
|
||||
* subtitle -> str
|
||||
defalut -> ''
|
||||
Subtitle text, supporting for \n for newlines.
|
||||
|
||||
* width -> int
|
||||
defalut -> 800(px)
|
||||
Canvas width
|
||||
|
||||
* height -> int
|
||||
defalut -> 400(px)
|
||||
Canvas height
|
||||
|
||||
* title_pos -> str/int
|
||||
defalut => 'left'
|
||||
Distance between grid component and the left side of the container.title_pos value can be instant pixel value like 20;
|
||||
It can also be percentage value relative to container width like '20%';it can also be 'left', 'center', or 'right'.
|
||||
If the title_pos value is set to be 'left', 'center', or 'right',then the component will be aligned automatically based on position.
|
||||
|
||||
* title_top -> str/int
|
||||
default -> 'top'
|
||||
Distance between grid component and the top side of the container.top value can be instant pixel value like 20.
|
||||
It can also be percentage value relative to container width like '20%';it can also be 'top', 'middle', or 'bottom'.
|
||||
If the left value is set to be 'top', 'middle', or 'bottom',then the component will be aligned automatically based on position.
|
||||
|
||||
* title_color -> str
|
||||
defalut -> '#000'
|
||||
main title text color.
|
||||
|
||||
* subtitle_color -> str
|
||||
defalut -> '#aaa'
|
||||
subtitle text color.
|
||||
|
||||
* title_text_size -> int
|
||||
defalut -> 18
|
||||
main title font size
|
||||
|
||||
* subtitle_text_size -> int
|
||||
defalut -> 12
|
||||
subtitle text color.
|
||||
|
||||
* background_color -> str
|
||||
defalut -> '#fff'
|
||||
Background color of title, which is transparent by default.
|
||||
Color can be represented in RGB, for example 'rgb(128, 128, 128)'. RGBA can be used when you need alpha channel, for example 'rgba(128, 128, 128, 0.5)'.
|
||||
You may also use hexadecimal format, for example '#ccc'.
|
||||
|
||||
* page_title -> str
|
||||
You can specify the title for render.html. Default is 'Echarts'
|
||||
|
||||
* renderer -> str
|
||||
Specify the use of rendering mode, there are 'svg' and 'canvas' optional, the default is 'canvas'. 3D drawings can only use 'canvas'.
|
||||
|
||||
* extra_html_text_label -> list
|
||||
Additional HTML text tags, `(<p> tag)`. The type is list, list[0] is the text content, and list[1] is the font style (optional). Such as ["this is a p label", "color:red"]. **Only used in a single graphic or page class.**
|
||||
|
||||
* is_animation -> bool
|
||||
Whether to turn on the animation, the default is True. V0.5.9+
|
||||
|
||||
## General options
|
||||
> All general configurations are set in```add()```
|
||||
|
||||
### xyAxis
|
||||
**x, y axis in cartesian coordinate system (Line, Bar, Scatter, EffectScatter, Kline)**
|
||||
|
||||
* is_convert -> bool
|
||||
It specifies whether to convert xAxis and yAxis.
|
||||
|
||||
* is_xaxislabel_align -> bool
|
||||
Whether the x-axis tick marks and labels are aligned, the default is False
|
||||
|
||||
* is_yaxislabel_align -> bool
|
||||
Whether the y-axis tick marks and labels are aligned, the default is False
|
||||
|
||||
* is_xaxis_inverse -> bool
|
||||
Whether to reverse the x axis, the default is False
|
||||
|
||||
* is_yaxis_inverse -> bool
|
||||
Whether to reverse the y axis, the default is False
|
||||
|
||||
* is_xaxis_boundarygap -> bool
|
||||
The white-axis strategy on both sides of the x-axis applies to the category axis. The boundaryGap in the category axis can be configured as True and False. The default is True. That means the scale is only used as a divider. Labels and data points will be in the middle of the band between the two scales, that is, white on both sides.
|
||||
|
||||
* is_yaxis_boundarygap -> bool
|
||||
The white balance strategy on both sides of the y axis applies to the category axis. The boundaryGap in the category axis can be configured as True and False. The default is True. That means the scale is only used as a divider. Labels and data points will be in the middle of the band between the two scales, that is, white on both sides.
|
||||
|
||||
* is_xaxis_show -> bool
|
||||
Whether to display the x axis
|
||||
|
||||
* is_yaxis_show -> bool
|
||||
Whether to display the y axis
|
||||
|
||||
* is_splitline_show -> bool
|
||||
Whether to display the y-axis grid line, the default is True.
|
||||
|
||||
* x_axis -> list
|
||||
xAxis data
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_interval -> int
|
||||
The display interval of the x-axis scale labels is valid in the category axis. By default, labels are displayed with intervals that do not overlap labels.
|
||||
Set to 0 to force all labels to be displayed. Set to 1, which means "Show one label per tab", if the value is 2, it means that one label is displayed between two labels, and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_force_interval -> int/str
|
||||
Forces the x-axis split interval. If set to 50, the scale is [0, 50, 150, ...], and when set to "auto", only two scales are displayed. It is not recommended to set this parameter in general! !
|
||||
Because `splitNumber` is the estimated value, the scale calculated by the actual strategy may not achieve the desired effect. In this case, you can use `interval` and `min`, `max` to force the scale division. Invalid in the category axis.
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_margin -> int
|
||||
The distance between the x-axis scale label and the axis line. Default is 8
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_name -> str
|
||||
Name of xAxis
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_name_size -> int
|
||||
Axis name font size, default is 14
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_name_gap -> int
|
||||
Gap between axis name and axis line, default is 25
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_name_pos -> str
|
||||
Location of xAxis name.It can be 'start','middle','end'
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_min -> int/float
|
||||
The minimun value of xaxis. Default is adaptive. Use the special value "dataMin" to customize the minimum value in the data to the minimum value of the x-axis.
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_max -> int/float
|
||||
The maximun value of xaxis. Default is adaptive. Use the special value "dataMax" to customize the minimum value in the data to the x-axis maximum
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_pos -> str
|
||||
x axis position, with 'top', 'bottom' optional
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_label_textsize -> int
|
||||
x axis label font size, default is 12
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_label_textcolor -> str
|
||||
x axis label font color, default is "#000"
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_type -> str
|
||||
Type of xaxis
|
||||
* 'value': Numerical axis, suitable for continuous data.
|
||||
* 'category': Category axis, suitable for discrete category data. Data should only be set via data for this type.
|
||||
* 'time': Time axis, suitable for continuous time series data. As compared to value axis,it has a better formatting for time and a different tick calculation method. For example,it decides to use month, week, day or hour for tick based on the range of span.
|
||||
* 'log': Log axis, suitable for log data.
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_rotate -> int
|
||||
Rotation degree of xaxis label, which is especially useful when there is no enough space for category axis.Default is 0, ie no rotation. Rotation degree is from -90 to 90.
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_formatter -> str/function
|
||||
The x-axis label formatter, such as 'day', the label of the x-axis is data plus 'day' (3 days, 4 days), the default is ""
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def label_formatter(params):
|
||||
return params.value + ' [Good!]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
Callback function format, please refer to [Advanced Usage](en-us/advanced) for more details.
|
||||
```
|
||||
(params: Object|Array) => string
|
||||
参数 params 是 formatter 需要的单个数据集。格式如下:
|
||||
{
|
||||
componentType: 'series',
|
||||
// Series type
|
||||
seriesType: string,
|
||||
// The index of the series in the passed option.series
|
||||
seriesIndex: number,
|
||||
// Series name
|
||||
seriesName: string,
|
||||
// Data name, category name
|
||||
name: string,
|
||||
// The index of the data in the input data array
|
||||
dataIndex: number,
|
||||
// Input raw data item
|
||||
data: Object,
|
||||
// Input data value
|
||||
value: number|Array,
|
||||
// Data graphic color
|
||||
color: string,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_line_color -> str
|
||||
The color of the x coordinate axis line. The default is None.
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis_line_width -> int
|
||||
The width of the x coordinate axis line, default is 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* y_axis -> list
|
||||
yAxis data
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_interval -> int
|
||||
The display interval of the y-axis scale label is valid in the category axis. By default, labels are displayed with intervals that do not overlap labels.
|
||||
Set to 0 to force all labels to be displayed. Set to 1, which means "Show one label per tab", if the value is 2, it means that one label is displayed between two labels, and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_force_interval -> int/str
|
||||
Forces the y-axis split interval. If set to 50, the scale is [0, 50, 150, ...], and when set to "auto", only two scales are displayed. It is not recommended to set this parameter in general! !
|
||||
Because `splitNumber` is the estimated value, the scale calculated by the actual strategy may not achieve the desired effect. In this case, you can use `interval` and `min`, `max` to force the scale division. Invalid in the category axis.
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_margin -> int
|
||||
The distance between the y-axis scale label and the axis. Default is 8
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_formatter -> str/function
|
||||
The y-axis label formatter, such as 'day', the label of the y-axis is data plus 'day' (3 days, 4 days), the default is ""
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def label_formatter(params):
|
||||
Return params.value + ' [Good!]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
Callback function format, please refer to [Advanced Usage](en-us/advanced) for more details.
|
||||
```
|
||||
(params: Object|Array) => string
|
||||
The parameter params is the single data set required by the formatter. The format is as follows:
|
||||
{
|
||||
componentType: 'series',
|
||||
// series type
|
||||
seriesType: string,
|
||||
// The index of the series in the passed option.series
|
||||
seriesIndex: number,
|
||||
// series name
|
||||
seriesName: string,
|
||||
// data name, category name
|
||||
Name: string,
|
||||
// the index of the data in the passed in data array
|
||||
dataIndex: number,
|
||||
// input raw data item
|
||||
Data: Object,
|
||||
// input data value
|
||||
Value: number|Array,
|
||||
// color of the data graphic
|
||||
Color: string,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_name -> str
|
||||
Name of yAxis
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_name_size -> int
|
||||
y axis name body size, default is 14
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_name_gap -> int
|
||||
The distance between the y axis name and the axis line. Default is 25
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_name_pos -> str
|
||||
Location of yAxis name. It can be 'start','middle','end'
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_min -> int/float
|
||||
The minimun value of yaxis. Use the special value `"dataMin"` to customize the minimum value in the data to the minimum value of the y-axis.
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_max -> int/float
|
||||
The maximun value of yaxis. Use the special value `"dataMax"` to customize the maximum value in the data to the maximum value of the y-axis.
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_pos -> str
|
||||
y coordinate position, with 'left', 'right' optional.
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_label_textsize -> int
|
||||
y axis label font size, default is 12
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_label_textcolor -> str
|
||||
y axis label font color, default is "#000"
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_type -> str
|
||||
Type of yaxis
|
||||
* 'value': Numerical axis, suitable for continuous data.
|
||||
* 'category': Category axis, suitable for discrete category data. Data should only be set via data for this type.
|
||||
* 'time': Time axis, suitable for continuous time series data. As compared to value axis, it has a better formatting for time and a different tick calculation method. For example, it decides to use month, week, day or hour for tick based on the range of span.
|
||||
* 'log': Log axis, suitable for log data.
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_rotate -> int
|
||||
Rotation degree of xaxis label, which is especially useful when there is no enough space for category axis.Rotation degree is from -90 to 90.
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_line_color -> str
|
||||
The color of the y coordinate axis. Default is None.
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis_line_width -> int
|
||||
y coordinate axis width, default is 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### dataZoom
|
||||
**dataZoom components for zoom-in and zoom-out. With them, it is possible to magnify a small area, to see the overall picture or to stay away from scattered points(Line, Bar, Scatter, EffectScatter, Kline)**
|
||||
|
||||
Default dataZoom control bar
|
||||
* is_datazoom_show -> bool
|
||||
Whether to use the area zoom component, default is False
|
||||
|
||||
* datazoom_type -> str
|
||||
Area zoom component type, defaults to 'slider', with 'slider', 'inside', 'both' optional
|
||||
|
||||
* datazoom_range -> list
|
||||
Range of area zoom, default is [50, 100]
|
||||
|
||||
* datazoom_orient -> str
|
||||
The direction of datazoom component in the Cartesian coordinate system. Default is 'horizontal' and the effect is displayed on the x-axis. If set to 'vertical', the effect is displayed on the y-axis.
|
||||
|
||||
* datazoom_xaxis_index -> int/list
|
||||
The x-axis index controlled by the datazoom component.
|
||||
The first x-axis is controlled by default, and no specification is required if there is no special requirement. A single type is int and multiple are controlled as a list type, such as [0, 1] to control the first and second x axes.
|
||||
|
||||
* datazoom_yaxis_index -> int/list
|
||||
The y-axis index controlled by the datazoom component
|
||||
The first y axis is controlled by default, and no specification is required if there is no special requirement. A single type is int and multiple are controlled as a list type, such as [0, 1] to control the first and second x axes.
|
||||
|
||||
Extra dataZoom control strip
|
||||
* is_datazoom_extrashow -> bool
|
||||
Whether to use the extra area zoom component, default is False
|
||||
|
||||
* datazoom_extra_type -> str
|
||||
Extra area zoom component type, default is 'slider', with 'slider', 'inside', 'both' optional
|
||||
|
||||
* datazoom_extra_range -> list
|
||||
Range of extra area zoom, default is [50, 100]
|
||||
|
||||
* datazoom_extra_orient -> str
|
||||
The direction of the extra datazoom component in the Cartesian coordinate system. The default is 'vertical' and the effect is displayed on the y axis. If set to 'horizontal', the effect is displayed on the x-axis.
|
||||
|
||||
* datazoom_extra_xaxis_index -> int/list
|
||||
X-axis index controlled by additional datazoom component
|
||||
The first x-axis is controlled by default, and no specification is required if there is no special requirement. A single type is int and multiple are controlled as a list type, such as [0, 1] to control the first and second x axes.
|
||||
|
||||
* datazoom_extra_yaxis_index -> int/list
|
||||
The y-axis index controlled by the extra datazoom component
|
||||
The first y axis is controlled by default, and no specification is required if there is no special requirement. A single type is int and multiple is controlled as a list type, such as [0, 1] to control the first and second x axes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### legend
|
||||
**legend component has different symbol, color and name, and provide the interactive clicking functions to show or hide its associated data series.**
|
||||
|
||||
* is_legend_show -> bool
|
||||
Whether to display the top legend, default is True
|
||||
|
||||
* legend_orient -> str
|
||||
The layout of the legend list, default is 'horizontal'.
|
||||
'horizontal', 'vertical' optional
|
||||
|
||||
* legend_pos -> str
|
||||
defalut -> 'center'
|
||||
Distance between legend component and the left side of the container.
|
||||
legend_pos value can be instant pixel value like 20;it can also be percentage value relative to container width like '20%'; And it can also be 'left', 'center', or 'right'.
|
||||
|
||||
* legend_top -> str
|
||||
defalut -> 'top'
|
||||
Distance between legend component and the top side of the container.
|
||||
legend_top value can be instant pixel value like 20;it can also be percentage value relative to container width like '20%';
|
||||
and it can also be 'top', 'middle', or 'bottom'.
|
||||
|
||||
* legend_selectedmode -> str/bool
|
||||
State table of selected legend. 'single' or 'multiple'. Or use `False` to disable it.
|
||||
|
||||
* legend_text_size -> int
|
||||
Legend name font size
|
||||
|
||||
* legend_text_color -> str
|
||||
Legend name font color
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### label
|
||||
**Text string on the chart, for marking the charts with sensible details, such as value, name.**
|
||||
|
||||
* is_label_show -> bool
|
||||
defalut -> False
|
||||
It specifies whether to show laebl in normal status.
|
||||
|
||||
* is_label_emphasis -> bool
|
||||
defalut -> True
|
||||
It specifies whether to show label in emphasis status.
|
||||
|
||||
* label_pos -> str
|
||||
defalut -> 'top'
|
||||
Label position. It can be 'top', 'left', 'right', 'bottom', 'inside','outside'
|
||||
|
||||
* label_emphasis_pos -> str
|
||||
Highlight the position of the label, the Bar map defaults to 'top'. Available with 'top', 'left', 'right', 'bottom', 'inside', 'outside'
|
||||
|
||||
* label_text_color -> str
|
||||
defalut -> '#000'
|
||||
Label text color.
|
||||
|
||||
* label_emphasis_textcolor -> str
|
||||
default -> "#fff"
|
||||
Highlight the label font color,
|
||||
|
||||
* label_text_size -> int
|
||||
defalut -> 12
|
||||
Label font size.
|
||||
|
||||
* label_emphasis_textsize -> int
|
||||
default -> 12
|
||||
Highlight label font size.
|
||||
|
||||
* is_random -> bool
|
||||
defalut -> False
|
||||
It specifies whether to random global color list.
|
||||
|
||||
* label_color -> list
|
||||
Customize the label color. It will modify global color list, and all chart legend colors can be config here. Such as Bar's column color, Line's line color, and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
* label_formatter -> str
|
||||
Template variables are {a}, {b}, {c}, {d}, {e}, which represent the series name, data name, data value, and so on. For examples `label_formatter='{a}'`
|
||||
When the `trigger` is `'axis'`, there will be multiple series of data. In this case, the index of the series can be represented by {a0}, {a1}, {a2}.
|
||||
{a}, {b}, {c}, {d} under different chart types have different meanings. The variables {a}, {b}, {c}, {d} represent the meaning of the data under different chart types:
|
||||
|
||||
* Line (area), column (bar), K-line: {a} (series name), {b} (category value), {c} (value), {d} (none)
|
||||
* Scatter plot (bubble) graph: {a} (series name), {b} (data name), {c} (value array), {d} (none)
|
||||
* Maps: {a} (series name), {b} (area name), {c} (merged value), {d} (none)
|
||||
* Pie chart, dashboard, funnel chart: {a} (series name), {b} (data item name), {c} (value), {d} (percent)
|
||||
|
||||
* Label_formatter -> function
|
||||
For details, please refer to xaxis_formatter -> function
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** is_random random disorganize legend colour and list,it's kind of switch style? try it.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### lineStyle
|
||||
**line style for Line, Polar, Radar, Graph, Parallel.**
|
||||
|
||||
* line_width -> int
|
||||
default -> 1
|
||||
Line width.
|
||||
|
||||
* line_opacity -> float
|
||||
default -> 1
|
||||
Opacity of the component. Supports value from 0 to 1, and the component will not be drawn when set to 0.
|
||||
|
||||
* line_curve -> float
|
||||
default -> 0
|
||||
Edge curvature, which supports value from 0 to 1. The larger the value, the greater curvature.
|
||||
|
||||
* line_type -> str
|
||||
default -> 'solid'
|
||||
Line type,it can be 'solid', 'dashed', 'dotted'
|
||||
|
||||
* line_color -> str
|
||||
Line color
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### grid3D
|
||||
**gird3D components in cartesian coordinate system (Bar3D, Line3D, Scatter3D, Surface3D)**
|
||||
|
||||
* grid3d_width -> int
|
||||
default -> 100
|
||||
Width of grid3D component.
|
||||
|
||||
* grid3d_height -> int
|
||||
default -> 100
|
||||
Height of grid3D component.
|
||||
|
||||
* grid3d_depth -> int
|
||||
default -> 100
|
||||
Depth of the three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system component in a three-dimensional scene.
|
||||
|
||||
* is_grid3d_rotate -> bool
|
||||
default -> False
|
||||
Whether to turn on the automatic rotation view of the angle around the object.
|
||||
|
||||
* grid3d_rotate_speed -> int
|
||||
The speed of autobiography of objects. The unit is angle / second, default is 10, which is 36 seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
* grid3d_rotate_sensitivity -> int
|
||||
The sensitivity of the rotation operation, the greater the value, the more sensitive. Default is 1, and it cannot be rotated after setting it to 0.
|
||||
|
||||
### axis3D
|
||||
**3D Cartesian coordinate system X, Y, Z axis configuration items for 3D graphics. (Bar3D, Line3D, Scatter3D, Surface3D)**
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3D X-axis
|
||||
* xaxis3d_name -> str
|
||||
x axis name, default is ""
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis3d_name_size -> int
|
||||
x axis name body size, default is 16
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis3d_name_gap -> int
|
||||
The distance between the x-axis name and the axis. Default is 25
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis3d_min -> int/float
|
||||
x Axis scale minimum, default is adaptive.
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis3d_max -> int/float
|
||||
The maximum value of the x axis scale. Default is adaptive.
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis3d_interval -> int
|
||||
The display interval of the x-axis scale labels is valid in the category axis. By default, labels are displayed with policy intervals that do not overlap labels.
|
||||
Set to 0 to force all labels to be displayed. Set to 1, which means "Show one label per tab", if the value is 2, it means that one label is displayed between two labels, and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
* xaxis3d_margin -> int
|
||||
The distance between the x-axis scale label and the axis. Default is 8
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3D Y-axis
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis3d_name -> str
|
||||
y axis name, default is ""
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis3d_name_size -> int
|
||||
y axis name body size, default is 16
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis3d_name_gap -> int
|
||||
The distance between the y axis name and the axis. Default is 25
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis3d_min -> int/float
|
||||
y Axis scale minimum, default is adaptive.
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis3d_max -> int/float
|
||||
y Axis scale maximum, default is adaptive.
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis3d_interval -> int
|
||||
The display interval of the y-axis scale label is valid in the category axis. By default, labels are displayed with policy intervals that do not overlap labels.
|
||||
Set to 0 to force all labels to be displayed. Set to 1, which means "Show one label per tab", if the value is 2, it means that one label is displayed between two labels, and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
* yaxis3d_margin -> int
|
||||
The distance between the y-axis scale label and the axis. Default is 8
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3D Z axis
|
||||
|
||||
* zaxis3d_name -> str
|
||||
z axis name, default is ""
|
||||
|
||||
* zaxis3d_name_size -> int
|
||||
z axis name body size, default is 16
|
||||
|
||||
* zaxis3d_name_gap -> int
|
||||
|
||||
The distance between the z-axis name and the axis. The default is 25
|
||||
|
||||
* zaxis3d_min -> int/float
|
||||
z Axis scale minimum, default is adaptive.
|
||||
|
||||
* zaxis3d_max -> int/float
|
||||
The maximum value of the z coordinate scale, default is adaptive.
|
||||
|
||||
* zaxis3d_margin -> int
|
||||
The distance between the z-axis scale label and the axis. The default is 8
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### visualMap
|
||||
|
||||
**It is a type of component for visual encoding, which maps the data to visual channels.**
|
||||
|
||||
* is_visualmap -> bool
|
||||
Whether to use the visual mapping component
|
||||
|
||||
* visual_type -> str
|
||||
Formulate the component mapping method, default is 'color'. That is, the value is mapped by color. There are 'color' and 'size' is optional. 'size' maps values by the size of the numeric point, which is the size of the graphic point.
|
||||
|
||||
* visual_range -> list
|
||||
default -> [0, 100]
|
||||
Specify the min and max dataValue for the visualMap component.
|
||||
|
||||
* visual_text_color -> str
|
||||
visualMap text color.
|
||||
|
||||
* visual_range_text -> list
|
||||
default -> ['low', 'hight']
|
||||
The label text on both ends.
|
||||
|
||||
* visual_range_color -> list
|
||||
default -> ['#50a3ba', '#eac763', '#d94e5d']
|
||||
For visual channel color, array is used, like: ['#333', '#78ab23', 'blue'].
|
||||
|
||||
* visual_range_size -> list
|
||||
default -> [20, 50]
|
||||
For visual channel size, array is used.
|
||||
|
||||
* visual_orient -> str
|
||||
default -> 'vertical'
|
||||
How to layout the visualMap component, 'horizontal' or 'vertical'.
|
||||
|
||||
* visual_pos -> str/int
|
||||
default -> 'left'
|
||||
Distance between visualMap component and the left side of the container.
|
||||
visual_pos value can be instant pixel value like 20;it can also be percentage value relative to container width like '20%';and it can also be 'left', 'center', or 'right'.
|
||||
|
||||
* visual_top -> str/int
|
||||
default -> 'top'
|
||||
Distance between visualMap component and the top side of the container.
|
||||
visual_top value can be instant pixel value like 20;it can also be percentage value relative to container width like '20%';and it can also be 'top', 'middle', or 'bottom'.
|
||||
|
||||
* visual_split_number -> int
|
||||
default -> 5
|
||||
The number of segments split in the segmentation type. It takes effect when be set to segmentation. Default is divided into 5 segments.
|
||||
|
||||
* visual_dimension -> int
|
||||
Specify which dimension of the data to use to map to the visual element. Default is mapped to the last dimension. The index starts at 0.
|
||||
In a Cartesian coordinate system, the x-axis is the first dimension (0) and the y-axis is the second dimension (1).
|
||||
|
||||
* is_calculable -> bool
|
||||
default -> True
|
||||
Whether show handles, which can be dragged to adjust "selected range".
|
||||
|
||||
* is_piecewise -> bool
|
||||
default -> False
|
||||
Whether to convert the component to segmentation (the default is continuous)
|
||||
|
||||
* pieces -> list
|
||||
Customize the scope of each segment of the "segmented visual mapping component (visualMapPiecewise)".
|
||||
And the text of each paragraph, as well as the special style of each paragraph. (Only effective when is_piecewise is True) For example:
|
||||
```
|
||||
pieces: [
|
||||
{min: 1500}, // If max is not specified, max is infinity.
|
||||
{min: 900, max: 1500},
|
||||
{min: 310, max: 1000},
|
||||
{min: 200, max: 300},
|
||||
{min: 10, max: 200, label: '10 到 200(自定义label)'},
|
||||
// Indicates that value is equal to 123.
|
||||
{value: 123, label: '123(自定义特殊颜色)', color: 'grey'}
|
||||
{max: 5} // If min is not specified, min is infinity (-Infinity).
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### tooltip
|
||||
**Tip box component for popping data content when moving or clicking the mouse**
|
||||
|
||||
* tooltip_trigger -> str
|
||||
Trigger type. Default is 'item'
|
||||
* 'item': Data item graph triggering, mainly used in charts with no category axes such as scatter plots and pie charts.
|
||||
* 'axis': Axis triggering, mainly used in charts that use the category axis, such as histograms, line charts, etc.
|
||||
* 'none': Nothing triggers.
|
||||
|
||||
* tooltip_trigger_on -> str
|
||||
The condition triggered by the prompt box. Default is "mousemove|click"
|
||||
* 'mousemove': Triggered when the mouse is moving.
|
||||
* 'click': Triggered when the mouse is clicked.
|
||||
* 'mousemove|click': Triggered when the mouse moves and clicks at the same time.
|
||||
* 'none': No trigger in 'mousemove' or 'click'.
|
||||
|
||||
* tooltip_axispointer_type -> str
|
||||
Indicator type. Default is "line"
|
||||
* 'line': line indicator.
|
||||
* 'shadow': shadow indicator.
|
||||
* 'cross': Crosshair indicator. In fact, it is shorthand, which means that the axisPointer of two orthogonal axes is enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
* tooltip_formatter -> str
|
||||
Template variables are {a}, {b}, {c}, {d}, {e}, which represent the series name, data name, data value, and so on.
|
||||
When the trigger is 'axis', there will be multiple series of data. In this case, the index of the series can be represented by {a0}, {a1}, {a2}. {a}, {b}, {c}, {d} under different chart types have different meanings. The variables {a}, {b}, {c}, {d} represent the meaning of the data under different chart types:
|
||||
* Line (area), column (bar), K-line: {a} (series name), {b} (category value), {c} (value), {d} (none)
|
||||
* Scatter plot (bubble) graph: {a} (series name), {b} (data name), {c} (value array), {d} (none)
|
||||
* Maps: {a} (series name), {b} (area name), {c} (merged value), {d} (none)
|
||||
* Pie chart, dashboard, funnel chart: {a} (series name), {b} (data item name), {c} (value), {d} (percent)
|
||||
|
||||
* tooltip_formatter -> function
|
||||
For details, please refer to xaxis_formatter -> function
|
||||
|
||||
* tooltip_text_color -> str
|
||||
Prompt box font color, defaults is '#fff'
|
||||
|
||||
* tooltip_font_size -> int
|
||||
Prompt box font size, default is 14
|
||||
|
||||
* tooltip_background_color -> str
|
||||
The background color of the floating layer of the prompt box. Default is "rgba(50,50,50,0.7)"
|
||||
|
||||
* tooltip_border_color -> str
|
||||
The border color of the floating layer of the prompt box. Default is "#333"
|
||||
|
||||
* tooltip_border_width -> int/float
|
||||
The border of the floating layer of the prompt box is wide. Default is 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### markLine-markPoint
|
||||
**Graphic mark component for marking specified special data. There are marker line and marker point (Bar, Line, Kline)**
|
||||
|
||||
* mark_point -> list
|
||||
Mark points, default is `'min'`. `'max'`, `'average'` is optional. Support custom mark points, the specific usage is as follows :
|
||||
[{"coord": [a1, b1], "name": "first markpoint"}, {"coord": [a2, b2], "name": "second markpoint"}]
|
||||
You need to pass in the point dictionary yourself. There are two key-value pairs. 'coord' corresponds to x y axis coordinates, and 'name' is the point name.
|
||||
|
||||
* mark_point_symbol -> str
|
||||
Point graphic, default is `'pin'`. `'circle'`, `'rect'`, `'roundRect'`, `'triangle'`, `'diamond'`, `'pin'`, `'arrow'` optional
|
||||
|
||||
* mark_point_symbolsize -> int
|
||||
Mark point graphic size, default is 50
|
||||
|
||||
* mark_point_textcolor -> str
|
||||
Mark the dot font color, the default is '#fff'
|
||||
|
||||
* mark_line -> list
|
||||
Marker line, default is `'min'`. `'max'`, `'average'` optional
|
||||
|
||||
* mark_line_symbolsize -> int
|
||||
Mark line graphic size, default is 15
|
||||
|
||||
* mark_line_valuedim -> list
|
||||
The marker line specifies in which dimension the maximum and minimum values are specified. This can be the dimension name. The Line chart can be x, angle, etc. And the Kline chart can be open, close, highest, lowest.
|
||||
Multiple dimensions can be developed at the same time, such as:
|
||||
|
||||
Mark_line=['min', 'max'],
|
||||
mark_line_valuedim=['lowest', 'highest']
|
||||
|
||||
means min uses the lowest dimension, max uses the highest dimension, and so on
|
||||
|
||||
* mark_line_coords -> list
|
||||
The marker line specifies the starting point coordinates and the ending point coordinates, such as [[10, 10], [30, 30]]. And the two points are the horizontal and vertical axis points.
|
||||
|
||||
* mark_point_valuedim -> list
|
||||
The marker line specifies in which dimension the maximum and minimum values are specified. This can be the dimension name, the Line chart can be x, angle, etc., and the Kline chart can be open, close, highest, lowest.
|
||||
Multiple dimensions can be developed at the same time, such as:
|
||||
|
||||
Mark_point=['min', 'max'],
|
||||
mark_point_valuedim=['lowest', 'highest']
|
||||
|
||||
means min uses the lowest dimension, max uses the highest dimension, and so on
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### toolbox
|
||||
**The right utility toolbox**
|
||||
|
||||
* is_toolbox_show - > bool
|
||||
Specifies whether to display the right utility toolbox. The default is True.
|
||||
|
||||
* is_more_utils - > bool
|
||||
Specifies whether to provide more utility buttons. By default, only the "Data View" and "Download" buttons are available.
|
||||
|
||||
**If you have read this document, you can read further [Chart Basic](en-us/charts_base)**
|
||||
1091
docs/en-us/charts_custom.md
Normal file
1091
docs/en-us/charts_custom.md
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
11
docs/en-us/donate.md
Normal file
11
docs/en-us/donate.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
> If you feel that this project could help, reward our contributors and sponsor other Open Source projects.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/19553554/35425853-500d6b5c-0299-11e8-80a1-ebb6629b497e.png" width=231 height=265> <img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/19553554/35425854-504e716a-0299-11e8-81fc-4a511f1c47e8.png" width=231 height=265>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img height="265" width=231 alt="chfw-zhifubao" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/4280312/35767977-23c484ae-08ed-11e8-8985-30ec7fa1f10c.png"> <img height="265" width=231 alt="chfw-wechat" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/4280312/35759160-ce2aa3c0-086f-11e8-8715-b8696da60341.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
This is [donors List](zh-cn/donors), you could e-mail your Github account to (chenjiandongx@qq.com, wangc_2011@hotmail.com). We will add your name on donors list.
|
||||
149
docs/en-us/themes.md
Normal file
149
docs/en-us/themes.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,149 @@
|
||||
> Theme customization: Expand the theme plugin, diversified chart color matching. V0.5.2+ added
|
||||
|
||||
Since 0.5.2+, pyecharts has supported the replacement of themes. The following is an example of replacing with "dark":
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import random
|
||||
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
X_AXIS = ["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"]
|
||||
bar = Bar("我的第一个图表", "这里是副标题")
|
||||
bar.use_theme("dark")
|
||||
bar.add("商家A", X_AXIS, [random.randint(10, 100) for _ in range(6)])
|
||||
bar.add("商家B", X_AXIS, [random.randint(10, 100) for _ in range(6)])
|
||||
bar.add("商家C", X_AXIS, [random.randint(10, 100) for _ in range(6)])
|
||||
bar.add("商家D", X_AXIS, [random.randint(10, 100) for _ in range(6)])
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Default theme effect
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Theme plugins usage
|
||||
|
||||
ECharts comes with the `dark` theme, and pyecharts comes with `dark`.
|
||||
[echarts-themes-pypkg](https://github.com/pyecharts/echarts-themes-pypkg) theme plugin provides the following topics :
|
||||
|
||||
* [vintage](#vintage)
|
||||
* [macarons](#macarons)
|
||||
* [infographic](#infographic)
|
||||
* [shine](#shine)
|
||||
* [roma](#roma)
|
||||
* [westeros](#westeros)
|
||||
* [wonderland](#wonderland)
|
||||
* [chalk](#chalk)
|
||||
* [halloween](#halloween)
|
||||
* [essos](#essos)
|
||||
* [walden](#walden)
|
||||
* [purple-passion](#purple-passion)
|
||||
* [romantic](#romantic)
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing theme plugin
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ pip install echarts-themes-pypkg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Theme usage
|
||||
|
||||
Replace a single graphic theme
|
||||
```python
|
||||
bar.use_theme("vintage")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Replace all chart topics in the operating environment
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import configure
|
||||
|
||||
# Put this line of code in the header
|
||||
configure(global_theme='dark')
|
||||
|
||||
bar = Bar()
|
||||
# other code
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
|
||||
#### vintage
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### macarons
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### infographic
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### shine
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### roma
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### westeros
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### wonderland
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### chalk
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### halloween
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### essos
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### walden
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### purple-passion
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### romantic
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Use your own built theme
|
||||
|
||||
ECharts provides [Theme Build Tools](http://echarts.baidu.com/theme-builder/), from which you can build favorite themes like `myTheme.js`. Then hack the *echarts-themes-pypkg* package. The specific operation is as follows
|
||||
|
||||
1. cd to your Python installation environment `Lib/site-packages/echarts_themes_pypkg/resources`. The specific path varies by operating system
|
||||
2. Move `myTheme.js` to `resources/echarts-themes-js` folder
|
||||
3. Change the `resources/registry.json` file
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
"PINYIN_MAP": {
|
||||
"shine": "shine",
|
||||
...
|
||||
"myTheme": "myTheme" # here
|
||||
},
|
||||
"FILE_MAP": {
|
||||
"shine": "shine",
|
||||
...
|
||||
"myTheme": "myTheme" # and here
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
4. cd to `jupyter/nbextensions/echarts-themes-js` directory in the notebook installation environment, the specific path varies by operating system
|
||||
5. Move `myTheme.js` to `echarts-themes-js` folder
|
||||
6. Use `chart.use_theme("myTheme")`
|
||||
|
||||
**4、5 as options, you can ignore this step if you don't use a notebook.**
|
||||
@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ $ pip install pyecharts-javascripthon
|
||||
|
||||
### 基本使用
|
||||
|
||||
pyecharts 已经封装了底层相关逻辑,对使用者是透明的。因此你可以像之前一样的使用。将回函函数对象通过 `add` 方法赋值到 echarts 配置字典中,这里的回调函数需满足以下条件之一:
|
||||
pyecharts 已经封装了底层相关逻辑,对使用者是透明的。因此你可以像之前一样的使用。将回调函数对象通过 `add` 方法赋值到 echarts 配置字典中,这里的回调函数需满足以下条件之一:
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用 `def` 定义的命名函数
|
||||
|
||||
@ -174,7 +174,7 @@ grid = Grid()
|
||||
grid.add(bar, grid_left="40%")
|
||||
grid.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用 JavaScript 事件处理函数
|
||||
|
||||
@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ js 文件仓库路径。可以设置本地或者远程地址。所有的远程
|
||||
|
||||
## 图表类
|
||||
|
||||
图表类是 pyecharts 库中最为核心的内容,每一个类代表了 [Echarts](http://echarts.baidu.com/) 中一个图表类型。下表显示了这些图表的继承体系。
|
||||
图表类是 pyecharts 库中最为核心的内容,每一个类代表了 [ECharts](http://echarts.baidu.com/) 中一个图表类型。下表显示了这些图表的继承体系。
|
||||
|
||||
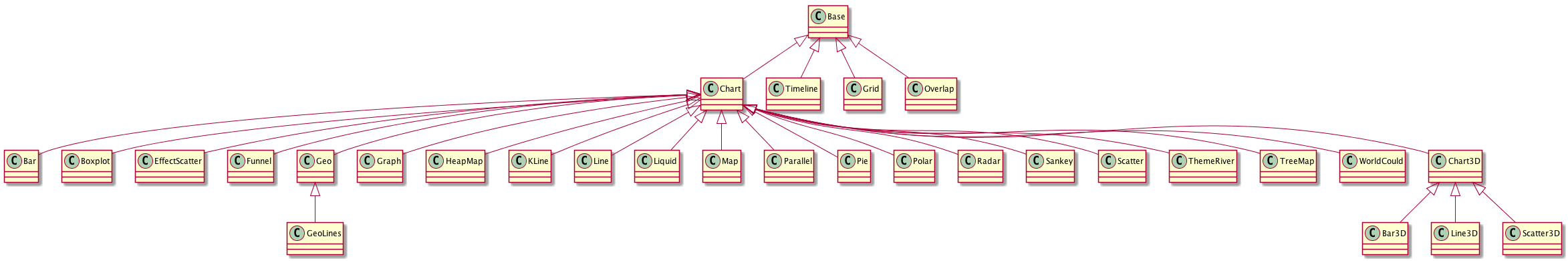
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ js 文件仓库路径。可以设置本地或者远程地址。所有的远程
|
||||
|
||||
**options**
|
||||
|
||||
字典类型(dict),Echarts 图表配置。不同图表类型具有不同数据格式。具体请参考 ECharts 文档。
|
||||
字典类型(dict),ECharts 图表配置。不同图表类型具有不同数据格式。具体请参考 ECharts 文档。
|
||||
|
||||
**js_dependencies**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -243,7 +243,7 @@ bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**进行两次或两次 add 的时候,有一次的某项数据缺失,可用 0 填充**
|
||||
**进行两次或多次 add 的时候,有一次的某项数据缺失,可用 0 填充**
|
||||
```python
|
||||
bar = Bar("折线图示例")
|
||||
bar.add("商家A", CLOTHES, clothes_v1)
|
||||
@ -411,7 +411,7 @@ add(name, x_axis, y_axis, **kwargs)
|
||||
* x_axis -> list
|
||||
x 坐标轴数据
|
||||
* y_axis -> [list], 包含列表的列表
|
||||
y 坐标轴数据,二维数组的每一数组项(上例中的每行)是渲染一个 box,它含有五个量值,依次是:
|
||||
y 坐标轴数据,二维数组的每一数组项(下例中的每行)是渲染一个 box,它含有五个量值,依次是:
|
||||
[min, Q1, median (or Q2), Q3, max]
|
||||
|
||||
可自行计算出所需五个数值,也可通过内置 `prepare_data()` 转换,`prepare_data()` 会将传入的嵌套列表中的数据转换为嵌套的 [min, Q1, median (or Q2), Q3, max],如下所示:
|
||||
@ -2463,7 +2463,7 @@ config(schema=None,
|
||||
* rader_text_color -> str
|
||||
雷达图数据项字体颜色,默认为'#000'
|
||||
* radar_text_size -> int
|
||||
雷达图m数据项字体大小,默认为 12
|
||||
雷达图数据项字体大小,默认为 12
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Radar
|
||||
@ -2636,7 +2636,7 @@ sankey.add(
|
||||
)
|
||||
sankey.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Scatter(散点图)
|
||||
@ -3408,17 +3408,17 @@ add(name, attr, value,
|
||||
* name -> str
|
||||
图例名称
|
||||
* attr -> list
|
||||
属性名称
|
||||
属性名称
|
||||
* value -> list
|
||||
属性所对应的值
|
||||
属性所对应的值
|
||||
* shape -> list
|
||||
词云图轮廓,有'circle', 'cardioid', 'diamond', 'triangle-forward', 'triangle', 'pentagon', 'star'可选
|
||||
词云图轮廓,有'circle', 'cardioid', 'diamond', 'triangle-forward', 'triangle', 'pentagon', 'star'可选
|
||||
* word_gap -> int
|
||||
单词间隔,默认为 20。
|
||||
单词间隔,默认为 20。
|
||||
* word_size_range -> list
|
||||
单词字体大小范围,默认为 [12, 60]。
|
||||
单词字体大小范围,默认为 [12, 60]。
|
||||
* rotate_step -> int
|
||||
旋转单词角度,默认为 45
|
||||
旋转单词角度,默认为 45
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import WordCloud
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,7 @@
|
||||
> 感谢大家对 pyecharts 项目的慷慨捐赠!下面是名单,排名不分先后!
|
||||
|
||||
> Thanks for your generous donation to the pyecharts project! The following is a list without particular order!
|
||||
|
||||
* https://github.com/liuhui9312
|
||||
* https://github.com/sssdjj
|
||||
* https://github.com/rubinliudongpo
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
x
Reference in New Issue
Block a user