mirror of
https://github.com/pyecharts/pyecharts.git
synced 2025-12-08 20:59:23 +00:00
commit
066c845263
@ -1,7 +1,10 @@
|
||||
- [Quick Start](en-us/prepare)
|
||||
- [Charts](en-us/charts)
|
||||
- [pyecharts+Flask](en-us/flask)
|
||||
- [pyecharts+Django](en-us/django)
|
||||
- [Map extensions](en-us/customize_map)
|
||||
- [pyecharts+Flask](en-us/flask)
|
||||
- [pyecharts+Django](en-us/django)
|
||||
- [Web integration](en-us/web_integration)
|
||||
- [Screenshots](zh-en/gallery)
|
||||
- [API](en-us/api)
|
||||
- [FAQ](zh-cn/faq)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,7 @@
|
||||
# pyecharts Documentation
|
||||
> Charts: pyecharts configurations
|
||||
|
||||
pyecharts is a library to generate charts using Echarts. It simply provides the interface between Echarts and Python.
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://travis-ci.org/chenjiandongx/pyecharts) [](https://codecov.io/gh/chenjiandongx/pyecharts) [](https://badge.fury.io/py/pyecharts) [](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
|
||||
|
||||
* First-steps
|
||||
* Global-options
|
||||
* Chart initialization
|
||||
* General options
|
||||
* xyAxis:x, y axis in cartesian coordinate system(Line, Bar, Scatter, EffectScatter, Kline)
|
||||
* dataZoom:dataZoom components for zoom-in and zoom-out. With them, it is possible to magnify a small area, to see the overall picture or to stay away from scattered points(Line, Bar, Scatter, EffectScatter, Kline)
|
||||
* legend:legend component has different symbol, colour and name, and provide the interactive clicking functions to show or hide its associated data series.
|
||||
@ -13,7 +9,7 @@ pyecharts is a library to generate charts using Echarts. It simply provides the
|
||||
* lineStyle:line style for Line, Polar, Radar, Graph, Parallel.
|
||||
* grid3D:gird3D components in cartesian coordinate system(Bar3D, Line3D, Scatter3D)
|
||||
* visualMap:It is a type of component for visual encoding, which maps the data to visual channels
|
||||
* Chart-types
|
||||
* Charts
|
||||
* Bar
|
||||
* Bar3D
|
||||
* EffectScatter
|
||||
@ -35,205 +31,15 @@ pyecharts is a library to generate charts using Echarts. It simply provides the
|
||||
* Scatter3D
|
||||
* WordCloud
|
||||
* Customize
|
||||
* Example
|
||||
* Grid
|
||||
* Overlap
|
||||
* Page
|
||||
* Timeline
|
||||
* Style
|
||||
* About
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# First-steps
|
||||
### Make sure you have installed the latest version pyecharts
|
||||
Now, you are ready to make your first chart!
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
|
||||
bar = Bar("我的第一个图表", "这里是副标题")
|
||||
bar.add("服装", ["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"], [5, 20, 36, 10, 75, 90])
|
||||
bar.show_config()
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** You can click the download button on the right side to download the picture to your local disk.
|
||||
|
||||
* ```add()```
|
||||
main method,add the data and set up various options of the chart
|
||||
* ```show_config()```
|
||||
print and output all options of the chart
|
||||
* ```render()```
|
||||
creat a file named render.html in the root directory defaultly,which supports path parameter and set the location the file save in,for instance render(r"e:\my_first_chart.html"),open file with your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
### The usge pyecharts-snapshot extension
|
||||
If you would to get png or pdf files instead of `render.html`, you can use [pyecharts-snapshot](https://github.com/chfw/pyecharts-snapshot)。However, node.js is required and can be downloaded from [https://nodejs.org/en/download/](https://nodejs.org/en/download/)
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install phantomjs
|
||||
`npm install -g phantomjs-prebuilt`
|
||||
2. install pyecharts-snapshot
|
||||
`pip install pyecharts-snapshot`
|
||||
3. In your program, import pyecharts-snapshot
|
||||
`from pyecharts_snapshot.main import make_a_snapshot`
|
||||
4. Programmatical usage
|
||||
`make_a_snapshot('render.html', 'snapshot.png')`
|
||||
where the frist parameter is the output file(by default, render.html), and the second one is output file with file extension as png or pdf.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, please refer to [pyecharts-snapshot](https://github.com/chfw/pyecharts-snapshot)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### A note on Jupyter notebook
|
||||
|
||||
For existing users, in order to play with the offline mode coming with 0.1.9.5, it is recommended that 1) the old version must be uninstalled. 2) Your existing notebooks must be refreshed and re-ran. 3) You must have installed **jupyter**. This restriction will be gone when jupyter-pip will release its next version.
|
||||
|
||||
How the offline mode works is: all echarts javascript libraries are copied into nbextensions directory. The following command helps you find out whether pyecharts js components are installed or not
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ jupyter nbextension list
|
||||
Known nbextensions:
|
||||
config dir: /Users/jaska/.jupyter/nbconfig
|
||||
notebook section
|
||||
echarts/main enabled
|
||||
- Validating: OK
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rarely, you would enforce pyecharts to reload all echarts javascript libraries. However if you intend to do so, you can issue these commands:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/chfw/jupyter-echarts.git
|
||||
$ cd jupyter-echarts
|
||||
$ jupyter nbextensions install echarts --user
|
||||
```
|
||||
Upon next rendering, all javascript libraries will be copied again.
|
||||
|
||||
And rarely again unless you are a developer of pyecharts, you choose to remove the extension:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ jupyter nbextensions uninstall echarts --user
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### jupyter-notebook export problem
|
||||
|
||||
Since 0.1.9.7, pyecharts has gone into offline mode, drawing without internet connection. Now, the charts in exported note book cannot be display as they have been put outside
|
||||
jupyter environment.
|
||||
|
||||
So the solution is to add the following statement:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
...
|
||||
from pyecharts import online
|
||||
|
||||
online()
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
Above code will take javascripts from https://chfw.github.io/jupyter-echarts/echarts. If
|
||||
you cannot connect to github, you could clone https://github.com/chfw/jupyter-echarts. Then, you put `echarts` folder onto your own server. Here is a simple command to achieve it:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cd jupyter-echarts/echarts
|
||||
$ python -m http.server # for python 2, use python -m SimpleHTTPServer
|
||||
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 8000 ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, add localhost into previous python code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
...
|
||||
from pyecharts import online
|
||||
|
||||
online(host="http://localhost:8000)
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Python2 Coding Problem
|
||||
default code type is UTF-8, there's no problem in Python3, because Python3 have a good support in chinese. But in Python2, please use the following sentence to ensure avoiding wrong coding problem:
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/python
|
||||
#coding=utf-8
|
||||
from __future__ import unicode_literals
|
||||
```
|
||||
The first two sentences are telling your editor that it should use UTF-8 ([PEP-0263](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0263/)). And the last sentence is telling Python all the characters are UTF-8 ([unicode literals](http://python-future.org/unicode_literals.html))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
almost all the chart type drawed like this:
|
||||
1. ```chart_name = Type()``` Initialise the concrete chart type.
|
||||
2. ```add()``` Add data and options.
|
||||
3. ```render()``` Creat .html file.
|
||||
|
||||
```add()``` Data is two lists commonly(the same length),if your data is dictionary or dictionary with tuple,use ```cast()``` to convert.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
cast(seq)
|
||||
``` Convert the sequence with the dictionary and tuple type into k_lst, v_lst. ```
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. Tuple Lists
|
||||
[(A1, B1), (A2, B2), (A3, B3), (A4, B4)] --> k_lst[ A[i1, i2...] ], v_lst[ B[i1, i2...] ]
|
||||
2. Dictionary Lists
|
||||
[{A1: B1}, {A2: B2}, {A3: B3}, {A4: B4}] --> k_lst[ A[i1, i2...] ], v_lst[ B[i1, i2...] ]
|
||||
3. Dictionaries
|
||||
{A1: B1, A2: B2, A3: B3, A4: B4} -- > k_lst[ A[i1, i2...] ], v_lst[ B[i1, i2...] ]
|
||||
|
||||
In the context of Numpy and/or Pandas, ```pdcast(pddata)``` and ``` npcast(npdata)``` methods, provided in 0.19.2 are no log required. Please see the advanced example in README.
|
||||
|
||||
If your DataFrame returns a transposed list(such as, [ [1], [2], [3] ]), you have to tranpose it by yourself (make it like [ 1, 2, 3 ] ). This transpose operation applies to Radar, Parallel, HeatMap.
|
||||
|
||||
Series type
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
pddata = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=[1, 'b', 'c', 'd'])
|
||||
vlst, ilst = Bar.pdcast(pddata)
|
||||
|
||||
print(vlst)
|
||||
>>> [1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0]
|
||||
print(ilst)
|
||||
>>> ['1', 'b', 'c', 'd']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
DataFrame type
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
pddt = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3, 4], [2, 3, 4, 5], [4.1, 5.2, 6.3, 7.4]], index=["A", "B", "C"])
|
||||
vlst, ilst = Bar.pdcast(pddata)
|
||||
|
||||
print(vlst)
|
||||
>>> [[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0], [2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0], [4.1, 5.2, 6.3, 7.4]]
|
||||
print(ilst)
|
||||
>>> ['A', 'B', 'C']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
npcast(),It accepts numpy.array type.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
npcast(npdata)
|
||||
``` handle the ndarray type in Numpy, return a list that ensures the correct type. Returns the nested list if there are multiple dimensions.```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Numpy.array type
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
import numpy ad np
|
||||
|
||||
npdata = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [2, 4, 5.0, 6.3]])
|
||||
print(npdata)
|
||||
>>> [[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0], [2.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.3]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Of course you can use the cooler way,use Jupyter Notebook to show the chart.But what matplotlib have,so do pyecharts**
|
||||
|
||||
like this
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
and this
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
more Jupyter notebook examples, please refer to [notebook-use-cases](https://github.com/chenjiandongx/pyecharts/blob/master/document/notebook-use-cases.ipynb)。you could download and run it on your notebook.
|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** The function was official added in 0.1.9.2 version,please update the newest version to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want use Jupyter Notebook to show your chart,just call Chart instance,compatible with Python2 and Python3's Jupyter Notebook environment at sametime.All the chart can display normaly,the same interaction experience to browser,there's no need to make a complex powerpoint!!
|
||||
|
||||
# Chart initialization
|
||||
The parameter a chart type initialize accept(the same to all the chart type).
|
||||
|
||||
* title -> str
|
||||
@ -275,11 +81,12 @@ The parameter a chart type initialize accept(the same to all the chart type)
|
||||
Background color of title, which is transparent by default.
|
||||
Color can be represented in RGB, for example 'rgb(128, 128, 128)'.RGBA can be used when you need alpha channel, for example 'rgba(128, 128, 128, 0.5)'.
|
||||
You may also use hexadecimal format, for example '#ccc'.
|
||||
* is_grid -> bool
|
||||
defalut -> False
|
||||
It specifies whether to use the grid component. Detail [Customize](https://github.com/chenjiandongx/pyecharts/blob/master/document/en-us/documentation.md#Customize)
|
||||
* page_title -> str
|
||||
You can specify the title for render.html. Default is 'Echarts'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# General options
|
||||
|
||||
# Global-options
|
||||
**Sitting general configuration in```add()```**
|
||||
|
||||
xyAxis:x, y axis in cartesian coordinate system(Line, Bar, Scatter, EffectScatter, Kline)
|
||||
@ -492,7 +299,9 @@ bar.add("商家A", attr, v1, is_stack=True)
|
||||
bar.add("商家B", attr, v2, is_stack=True)
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** Global configuration item needs set in the last ```add()``` or the setting will lose efficacy.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -503,7 +312,7 @@ bar.add("商家A", attr, v1, mark_point=["average"])
|
||||
bar.add("商家B", attr, v2, mark_line=["min", "max"])
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* mark_point -> list
|
||||
mark point data, it can be 'min', 'max', 'average'
|
||||
@ -527,7 +336,7 @@ bar.add("商家A", attr, v1)
|
||||
bar.add("商家B", attr, v2, is_convert=True)
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
dataZoom effect,'slider' type
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -540,7 +349,7 @@ bar.add("", attr, v1, is_label_show=True, is_datazoom_show=True)
|
||||
bar.show_config()
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
'inside' type
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -551,12 +360,83 @@ bar.add("", attr, v1, is_datazoom_show=True, datazoom_type='inside', datazoom_ra
|
||||
bar.show_config()
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
'both' type
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
attr = ["{}天".format(i) for i in range(30)]
|
||||
v1 = [random.randint(1, 30) for _ in range(30)]
|
||||
bar = Bar("Bar - datazoom - inside 示例")
|
||||
bar.add("", attr, v1, is_datazoom_show=True, datazoom_type='both',
|
||||
datazoom_range=[10, 25])
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** datazoom can be used for Line、Bar、Scatter、EffectScatter、Kline
|
||||
|
||||
if axis labels are too long, rotation is a good solution.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
attr = ["{}天".format(i) for i in range(20)]
|
||||
v1 = [random.randint(1, 20) for _ in range(20)]
|
||||
bar = Bar("坐标轴标签旋转示例")
|
||||
bar.add("", attr, v1, xaxis_interval=0, xaxis_rotate=30, yaxis_rotate=30)
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** Datazoom fits all plane rectangular coordinate system figure,that's(Line, Bar, Scatter, EffectScatter, Kline)
|
||||
**Tip:** Through label_color to set column's colour,like ['#eee', '#000'],any type of chart's legend colour can revise by label_color .
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
waterfall example
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
|
||||
attr = ["{}月".format(i) for i in range(1, 8)]
|
||||
v1 = [0, 100, 200, 300, 400, 220, 250]
|
||||
v2 = [1000, 800, 600, 500, 450, 400, 300]
|
||||
bar = Bar("瀑布图示例")
|
||||
# 利用第一个 add() 图例的颜色为透明,即 'rgba(0,0,0,0)',并且设置 is_stack 标志为 True
|
||||
bar.add("", attr, v1, label_color=['rgba(0,0,0,0)'], is_stack=True)
|
||||
bar.add("月份", attr, v2, is_label_show=True, is_stack=True, label_pos='inside')
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
fat histogram example
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
|
||||
attr = ["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"]
|
||||
v1 = [5, 20, 36, 10, 75, 90]
|
||||
v2 = [10, 25, 8, 60, 20, 80]
|
||||
bar = Bar("直方图示例")
|
||||
bar.add("", attr * 2, v1 + v2, bar_category_gap=0)
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Double histograms
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
|
||||
attr = ["{}月".format(i) for i in range(1, 13)]
|
||||
v1 = [2.0, 4.9, 7.0, 23.2, 25.6, 76.7, 135.6, 162.2, 32.6, 20.0, 6.4, 3.3]
|
||||
v2 = [2.6, 5.9, 9.0, 26.4, 28.7, 70.7, 175.6, 182.2, 48.7, 18.8, 6.0, 2.3]
|
||||
bar = Bar("柱状图示例")
|
||||
bar.add("蒸发量", attr, v1, mark_line=["average"], mark_point=["max", "min"])
|
||||
bar.add("降水量", attr, v2, mark_line=["average"], mark_point=["max", "min"])
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Bar3D
|
||||
Bar3D.add() signatures
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -613,7 +493,7 @@ bar3d.add("", x_axis, y_aixs, [[d[1], d[0], d[2]] for d in data], is_visualmap=T
|
||||
bar3d.show_config()
|
||||
bar3d.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
``` grid3D_shading``` could make bar look more real
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -624,7 +504,8 @@ bar3d.add("", x_axis, y_aixs, [[d[1], d[0], d[2]] for d in data], is_visualmap=T
|
||||
bar3d.show_config()
|
||||
bar3d.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```is_grid3D_rotate``` could let it rotate automatically
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -635,7 +516,7 @@ bar3d.add("", x_axis, y_aixs, [[d[1], d[0], d[2]] for d in data], is_visualmap=T
|
||||
bar3d.show_config()
|
||||
bar3d.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
set ``` grid3D_rotate_speed``` to adjust the rotation speed
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -646,7 +527,7 @@ bar3d.add("", x_axis, y_aixs, [[d[1], d[0], d[2]] for d in data], is_visualmap=T
|
||||
bar3d.show_config()
|
||||
bar3d.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** more details aboutt gird3D,please refer to [Global-options](https://github.com/chenjiandongx/pyecharts/blob/master/document/en-us/documentation.md#Global-options)
|
||||
|
||||
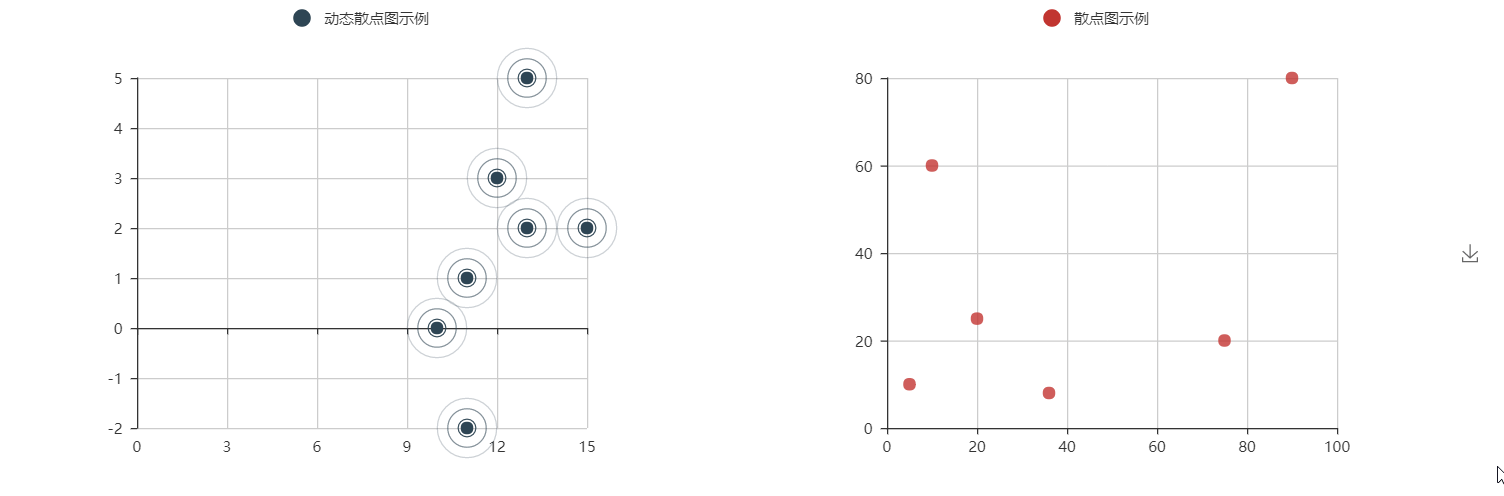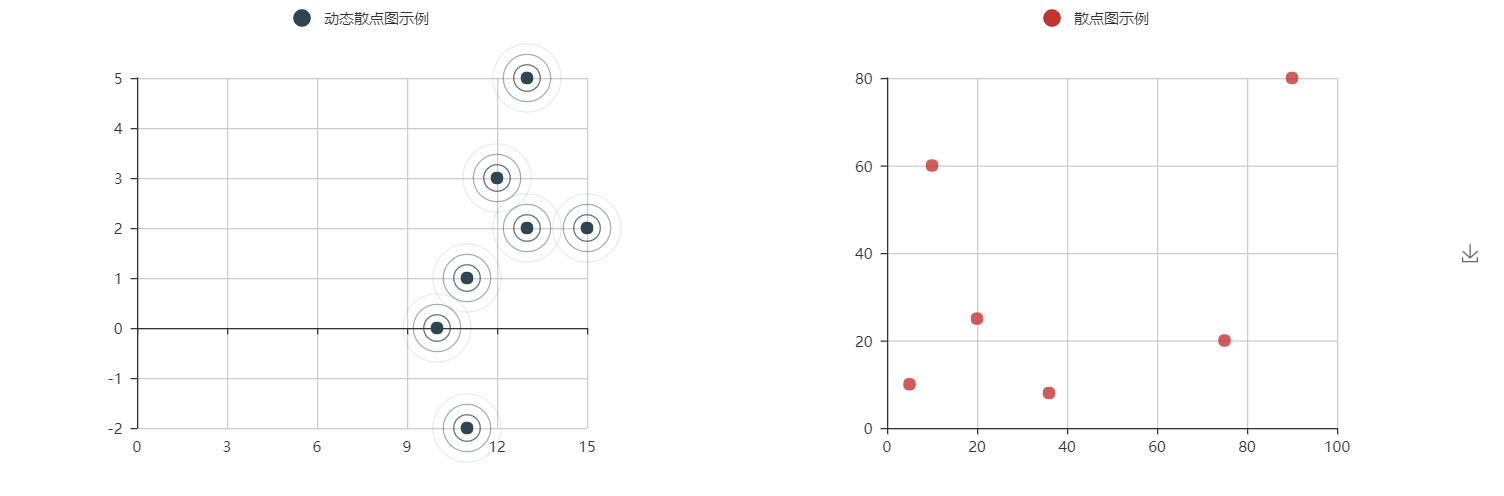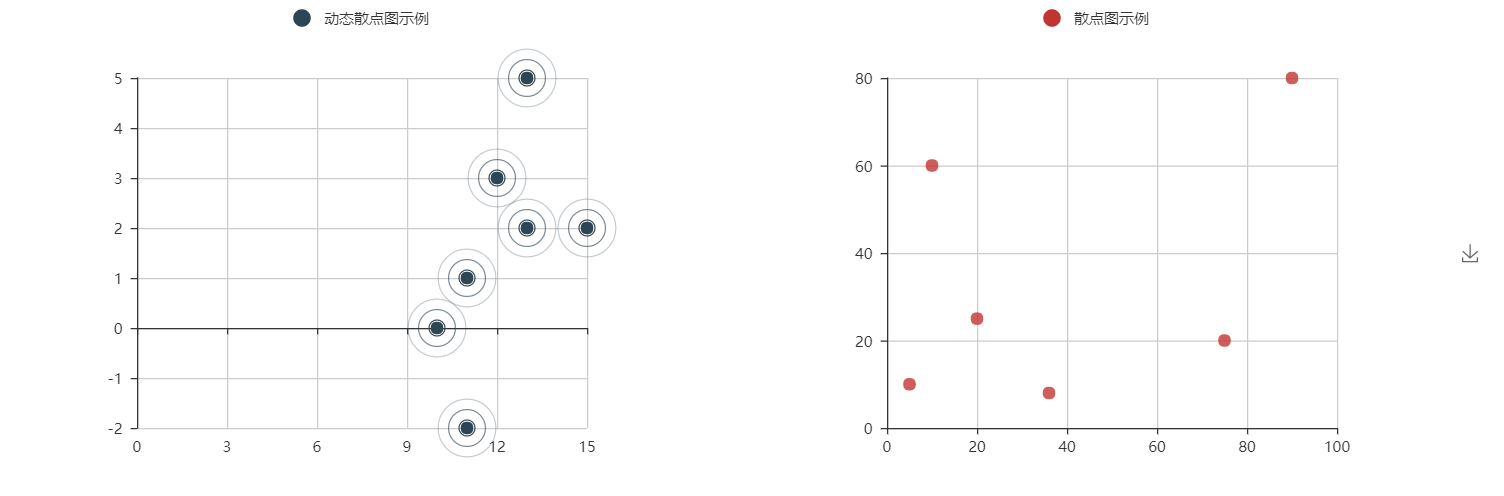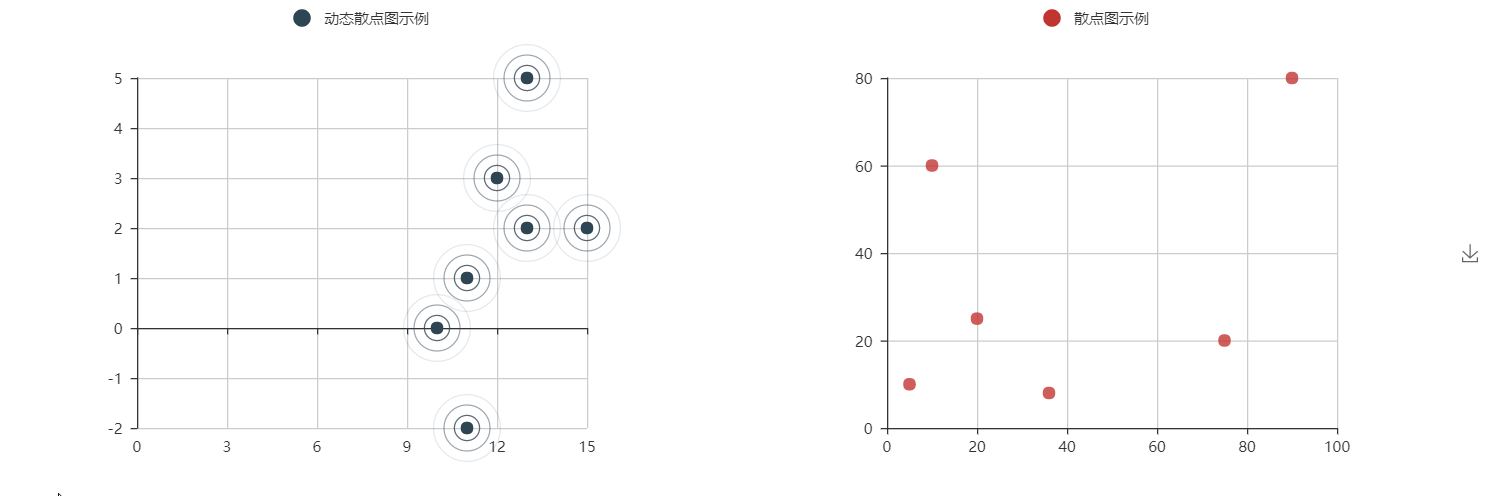
@ -677,7 +558,7 @@ es = EffectScatter("动态散点图示例")
|
||||
es.add("effectScatter", v1, v2)
|
||||
es.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
es = EffectScatter("动态散点图各种图形示例")
|
||||
@ -689,7 +570,8 @@ es.add("", [50], [50], symbol_size=16, effect_scale=5.5, effect_period=3,symbol=
|
||||
es.add("", [60], [60], symbol_size=6, effect_scale=2.5, effect_period=3,symbol="triangle")
|
||||
es.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* symbol -> str
|
||||
symbol shape, it can be 'rect', 'roundRect', 'triangle', 'diamond', 'pin', 'arrow'
|
||||
@ -725,7 +607,7 @@ funnel = Funnel("漏斗图示例")
|
||||
funnel.add("商品", attr, value, is_label_show=True, label_pos="inside", label_text_color="#fff")
|
||||
funnel.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
funnel = Funnel("漏斗图示例", width=600, height=400, title_pos='center')
|
||||
@ -763,7 +645,7 @@ gauge.add("业务指标", "完成率", 66.66)
|
||||
gauge.show_config()
|
||||
gauge.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
gauge = Gauge("仪表盘示例")
|
||||
@ -771,8 +653,8 @@ gauge.add("业务指标", "完成率", 166.66, angle_range=[180, 0], scale_range
|
||||
gauge.show_config()
|
||||
gauge.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Geo
|
||||
> Geographic coorinate system component.Geographic coorinate system component is used to draw maps, which also supports scatter series, and line series.
|
||||
@ -851,7 +733,70 @@ geo.add("", attr, value, visual_range=[0, 200], visual_text_color="#fff", symbol
|
||||
geo.show_config()
|
||||
geo.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** Please use it with Visualmap
|
||||
|
||||
With Scatter
|
||||
```python
|
||||
geo = Geo("全国主要城市空气质量", "data from pm2.5", title_color="#fff",
|
||||
title_pos="center", width=1200,
|
||||
height=600, background_color='#404a59')
|
||||
attr, value = geo.cast(data)
|
||||
geo.add("", attr, value, visual_range=[0, 200], visual_text_color="#fff",
|
||||
symbol_size=15, is_visualmap=True, is_piecewise=True, visual_split_number=6)
|
||||
geo.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
With HeatMap
|
||||
```python
|
||||
geo = Geo("全国主要城市空气质量", "data from pm2.5", title_color="#fff",
|
||||
title_pos="center", width=1200,
|
||||
height=600, background_color='#404a59')
|
||||
attr, value = geo.cast(data)
|
||||
geo.add("", attr, value, type="heatmap", is_visualmap=True, visual_range=[0, 300],
|
||||
visual_text_color='#fff')
|
||||
geo.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
With EffectScatter on China map
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Geo
|
||||
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
("海门", 9), ("鄂尔多斯", 12), ("招远", 12),
|
||||
("舟山", 12), ("齐齐哈尔", 14), ("盐城", 15)
|
||||
]
|
||||
geo = Geo("全国主要城市空气质量", "data from pm2.5", title_color="#fff",
|
||||
title_pos="center", width=1200,
|
||||
height=600, background_color='#404a59')
|
||||
attr, value = geo.cast(data)
|
||||
geo.add("", attr, value, type="effectScatter", is_random=True, effect_scale=5)
|
||||
geo.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
With effectScatter on my home province, Canton
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Geo
|
||||
|
||||
data =[
|
||||
('汕头市', 50), ('汕尾市', 60), ('揭阳市', 35),
|
||||
('阳江市', 44), ('肇庆市', 72)
|
||||
]
|
||||
geo = Geo("广东城市空气质量", "data from pm2.5", title_color="#fff",
|
||||
title_pos="center", width=1200,
|
||||
height=600, background_color='#404a59')
|
||||
attr, value = geo.cast(data)
|
||||
geo.add("", attr, value, maptype='广东', type="effectScatter",
|
||||
is_random=True, effect_scale=5, is_legend_show=False)
|
||||
geo.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
visualMap:visualMap is a type of component for visual encoding, which maps the data to visual channels
|
||||
* is_visualmap -> bool
|
||||
@ -984,7 +929,8 @@ graph.show_config()
|
||||
graph.render()
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
graph = Graph("关系图-环形布局示例")
|
||||
@ -992,7 +938,7 @@ graph.add("", nodes, links, is_label_show=True, repulsion=8000, layout='circular
|
||||
graph.show_config()
|
||||
graph.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Graph
|
||||
@ -1007,7 +953,7 @@ graph.add("", nodes, links, categories, label_pos="right", repulsion=50, is_lege
|
||||
graph.show_config()
|
||||
graph.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** **lineStyle** parameter is configurable
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1048,7 +994,7 @@ heatmap.add("热力图直角坐标系", x_axis, y_aixs, data, is_visualmap=True,
|
||||
heatmap.show_config()
|
||||
heatmap.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import datetime
|
||||
@ -1065,7 +1011,7 @@ heatmap.add("日历热力图", data, date_range=["2017"], is_visualmap=True,
|
||||
visual_pos="center", visual_top="top")
|
||||
heatmap.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** Thermodynamic chart have to cooperate with VisualMap in use.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1108,7 +1054,7 @@ kline.add("日K", ["2017/7/{}".format(i + 1) for i in range(31)], v1)
|
||||
kline.show_config()
|
||||
kline.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Kline + dataZoom
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -1117,7 +1063,7 @@ kline.add("日K", ["2017/7/{}".format(i + 1) for i in range(31)], v1, mark_point
|
||||
kline.show_config()
|
||||
kline.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Line
|
||||
@ -1163,7 +1109,7 @@ line.add("商家B", attr, v2, is_smooth=True, mark_line=["max", "average"])
|
||||
line.show_config()
|
||||
line.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* mark_point -> list
|
||||
mark point data, it can be 'min', 'max', 'average'
|
||||
@ -1189,7 +1135,7 @@ line.add("商家B", attr, v2, mark_point=["average", "max", "min"],
|
||||
line.show_config()
|
||||
line.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
line = Line("折线图-数据堆叠示例")
|
||||
@ -1198,7 +1144,7 @@ line.add("商家B", attr, v2, is_stack=True, is_label_show=True)
|
||||
line.show_config()
|
||||
line.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
line = Line("折线图-阶梯图示例")
|
||||
@ -1206,7 +1152,7 @@ line.add("商家A", attr, v1, is_step=True, is_label_show=True)
|
||||
line.show_config()
|
||||
line.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
line = Line("折线图-面积图示例")
|
||||
@ -1215,7 +1161,7 @@ line.add("商家B", attr, v2, is_fill=True, area_color='#000', area_opacity=0.3,
|
||||
line.show_config()
|
||||
line.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* area_opacity -> float
|
||||
Opacity of the component. Supports value from 0 to 1, and the component will not be drawn when set to 0.
|
||||
@ -1258,7 +1204,8 @@ line3d.add("", _data, is_visualmap=True, visual_range_color=range_color, visual_
|
||||
grid3D_rotate_sensitivity=5)
|
||||
line3d.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
rotating spring
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -1279,7 +1226,7 @@ line3d.add("", _data, is_visualmap=True, visual_range_color=range_color, visual_
|
||||
is_grid3D_rotate=True, grid3D_rotate_speed=180)
|
||||
line3d.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** more details aboutt gird3D,please refer to [Global-options](https://github.com/chenjiandongx/pyecharts/blob/master/document/en-us/documentation.md#Global-options)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1315,7 +1262,7 @@ liquid.add("Liquid", [0.6])
|
||||
liquid.show_config()
|
||||
liquid.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Liquid
|
||||
@ -1325,7 +1272,7 @@ liquid.add("Liquid", [0.6, 0.5, 0.4, 0.3], is_liquid_outline_show=False)
|
||||
liquid.show_config()
|
||||
liquid.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Liquid
|
||||
@ -1335,7 +1282,7 @@ liquid.add("Liquid", [0.6, 0.5, 0.4, 0.3], is_liquid_animation=False, shape='dia
|
||||
liquid.show_config()
|
||||
liquid.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Map
|
||||
> Map is maily used in the visulization of geographic area data,which can be used with visualMap component to visualize the datas such as population distribution density in diffrent areas.
|
||||
@ -1366,7 +1313,7 @@ map.add("", attr, value, maptype='china')
|
||||
map.show_config()
|
||||
map.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Map
|
||||
@ -1378,7 +1325,7 @@ map.add("", attr, value, maptype='china', is_visualmap=True, visual_text_color='
|
||||
map.show_config()
|
||||
map.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** Settings can combine with visualMap component.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1392,7 +1339,7 @@ map.add("", attr, value, maptype='广东', is_visualmap=True, visual_text_color=
|
||||
map.show_config()
|
||||
map.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### About Customized Map
|
||||
Because map contain large area,this program can't cover all the map,but don't worry about it.Echarts officially provide your own custom map [echart-map](http://echarts.baidu.com/download-map.html),this function allow you make map that you need,just download in JS file form.
|
||||
@ -1466,7 +1413,7 @@ parallel.add("parallel", data, is_random=True)
|
||||
parallel.show_config()
|
||||
parallel.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Parallel
|
||||
@ -1504,7 +1451,7 @@ parallel.add("parallel", data)
|
||||
parallel.show_config()
|
||||
parallel.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** **lineStyle** Parameter is Configurable
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1546,7 +1493,7 @@ pie.add("", attr, v1, is_label_show=True)
|
||||
pie.show_config()
|
||||
pie.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Pie
|
||||
@ -1559,7 +1506,7 @@ pie.add("", attr, v1, radius=[40, 75], label_text_color=None, is_label_show=True
|
||||
pie.show_config()
|
||||
pie.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Pie
|
||||
@ -1574,7 +1521,7 @@ pie.add("商品B", attr, v2, center=[75, 50], is_random=True, radius=[30, 75], r
|
||||
pie.show_config()
|
||||
pie.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Polar
|
||||
@ -1638,7 +1585,7 @@ polar.add("", data, boundary_gap=False, type='scatter', is_splitline_show=False,
|
||||
polar.show_config()
|
||||
polar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* is_splitline_show -> bool
|
||||
default -> True
|
||||
@ -1665,7 +1612,7 @@ polar.add("", data_2, type='scatter')
|
||||
polar.show_config()
|
||||
polar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Polar
|
||||
@ -1677,7 +1624,7 @@ polar.add("", data, type='effectScatter', effect_scale=10, effect_period=5)
|
||||
polar.show_config()
|
||||
polar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Polar
|
||||
@ -1690,7 +1637,7 @@ polar.add("C", [1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 5], radius_data=radius, type='barRadius', is_s
|
||||
polar.show_config()
|
||||
polar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Polar
|
||||
@ -1703,8 +1650,7 @@ polar.add("", [1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 5], radius_data=radius, type='barAngle', is_sta
|
||||
polar.show_config()
|
||||
polar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Radar
|
||||
> Radar chart is mainly used to show multi-variable data,such as the analysis of a football player's varied attributes. It relies radar component.
|
||||
@ -1751,7 +1697,7 @@ radar.add("实际开销", v2, label_color=["#4e79a7"], is_area_show=False)
|
||||
radar.show_config()
|
||||
radar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* is_area_show -> bool
|
||||
It specifies whether to show split area.
|
||||
@ -1816,7 +1762,7 @@ radar.add("上海", value_sh, item_color="#b3e4a1", symbol=None)
|
||||
radar.show_config()
|
||||
radar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** symblo=None make marked graphic hiden(small circle)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1850,7 +1796,7 @@ scatter.add("B", v1[::-1], v2)
|
||||
scatter.show_config()
|
||||
scatter.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Scatter also built-in draw method.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -1866,7 +1812,7 @@ convert pixels on the image into array ,when colour is (255,255,255)only ret
|
||||
|
||||
First of all ,you need to prepare a picture,like
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Scatter
|
||||
@ -1877,7 +1823,7 @@ scatter.add("pyecharts", v1, v2, is_random=True)
|
||||
scatter.show_config()
|
||||
scatter.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Scatter3D
|
||||
@ -1904,7 +1850,7 @@ scatter3D = Scatter3D("3D 散点图示例", width=1200, height=600)
|
||||
scatter3D.add("", data, is_visualmap=True, visual_range_color=range_color)
|
||||
scatter3D.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** more details aboutt gird3D,please refer to [Global-options](https://github.com/chenjiandongx/pyecharts/blob/master/document/en-us/documentation.md#Global-options)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1945,7 +1891,7 @@ wordcloud.add("", name, value, word_size_range=[20, 100])
|
||||
wordcloud.show_config()
|
||||
wordcloud.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
wordcloud = WordCloud(width=1300, height=620)
|
||||
@ -1953,7 +1899,7 @@ wordcloud.add("", name, value, word_size_range=[30, 100], shape='diamond')
|
||||
wordcloud.show_config()
|
||||
wordcloud.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** if and only if shape is default'circle' the rotate_step parameter will take effect.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2112,7 +2058,7 @@ bar.grid(line.get_series(), grid_top="60%")
|
||||
bar.show_config()
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**once more Tip:** ```bar.grid(line.get_series(), grid_top="60%")``` do not write ```bar.grid(bar.get_series())``` or get into edless recursion
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2138,7 +2084,7 @@ scatter.grid(es.get_series(), grid_right="60%")
|
||||
scatter.show_config()
|
||||
scatter.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
up,down,left and right type,Bar + Line + Scatter + EffectScatter
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -2168,7 +2114,7 @@ bar.grid(es.get_series(), grid_top="60%", grid_right="60%")
|
||||
bar.show_config()
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
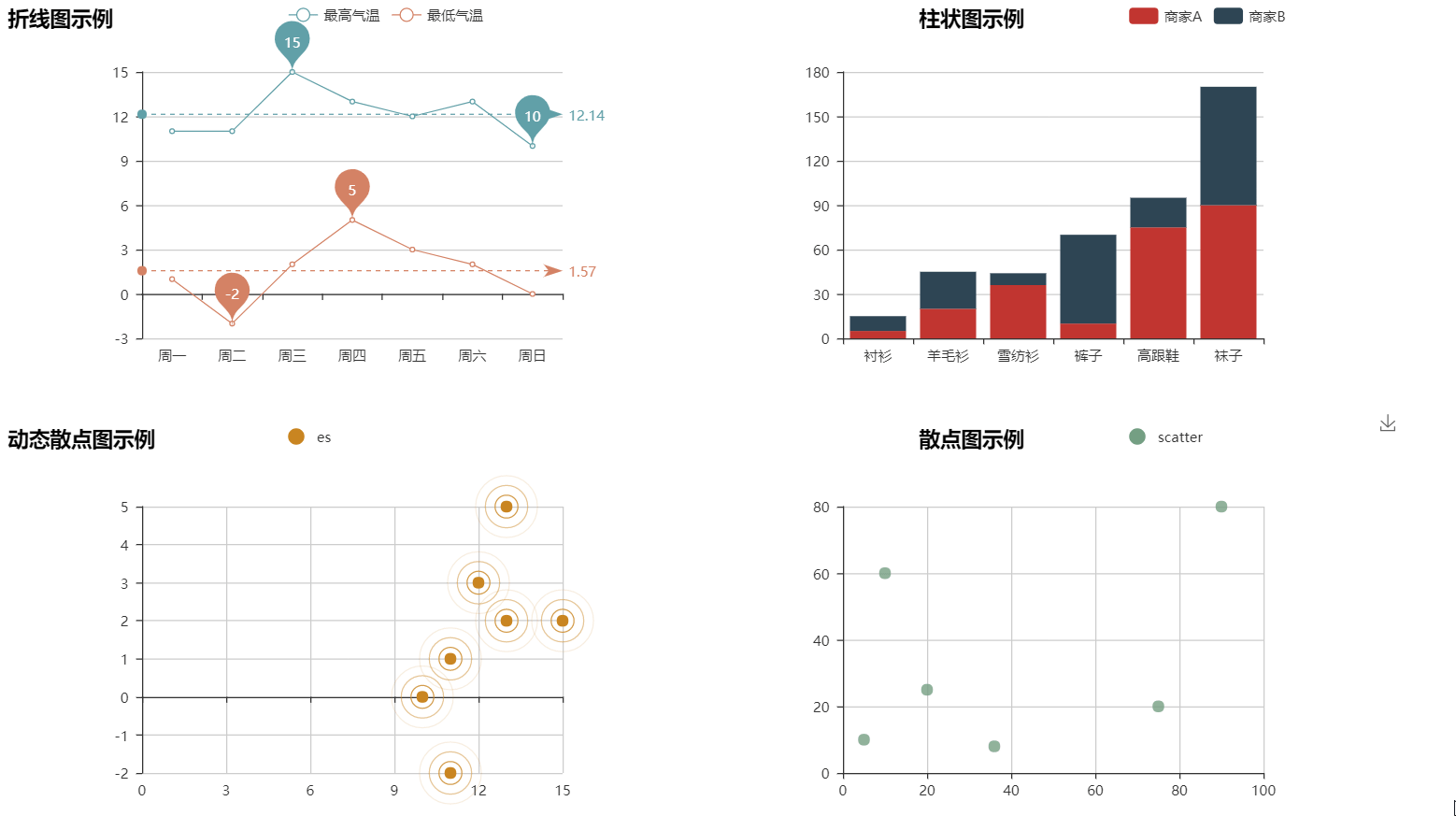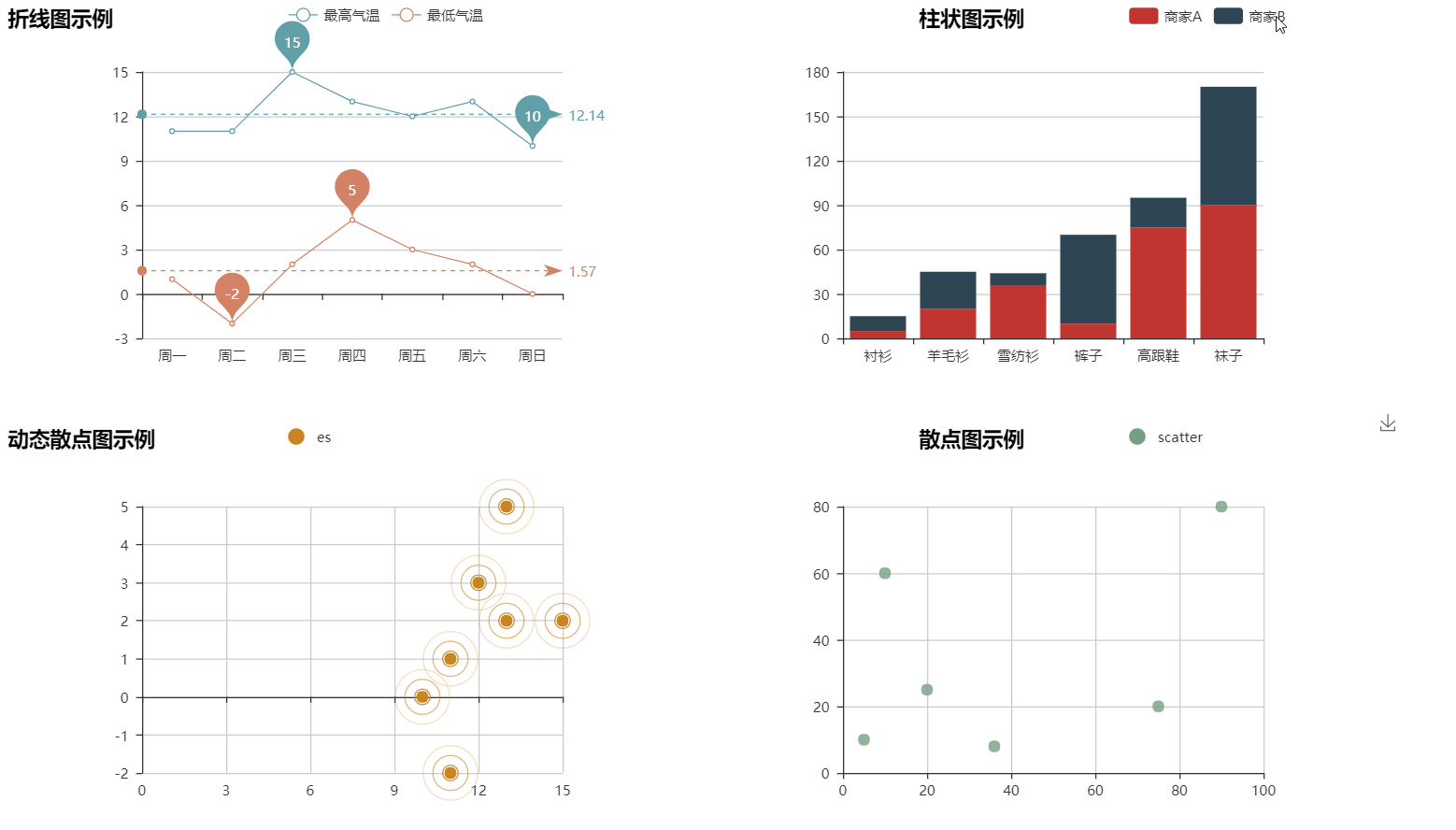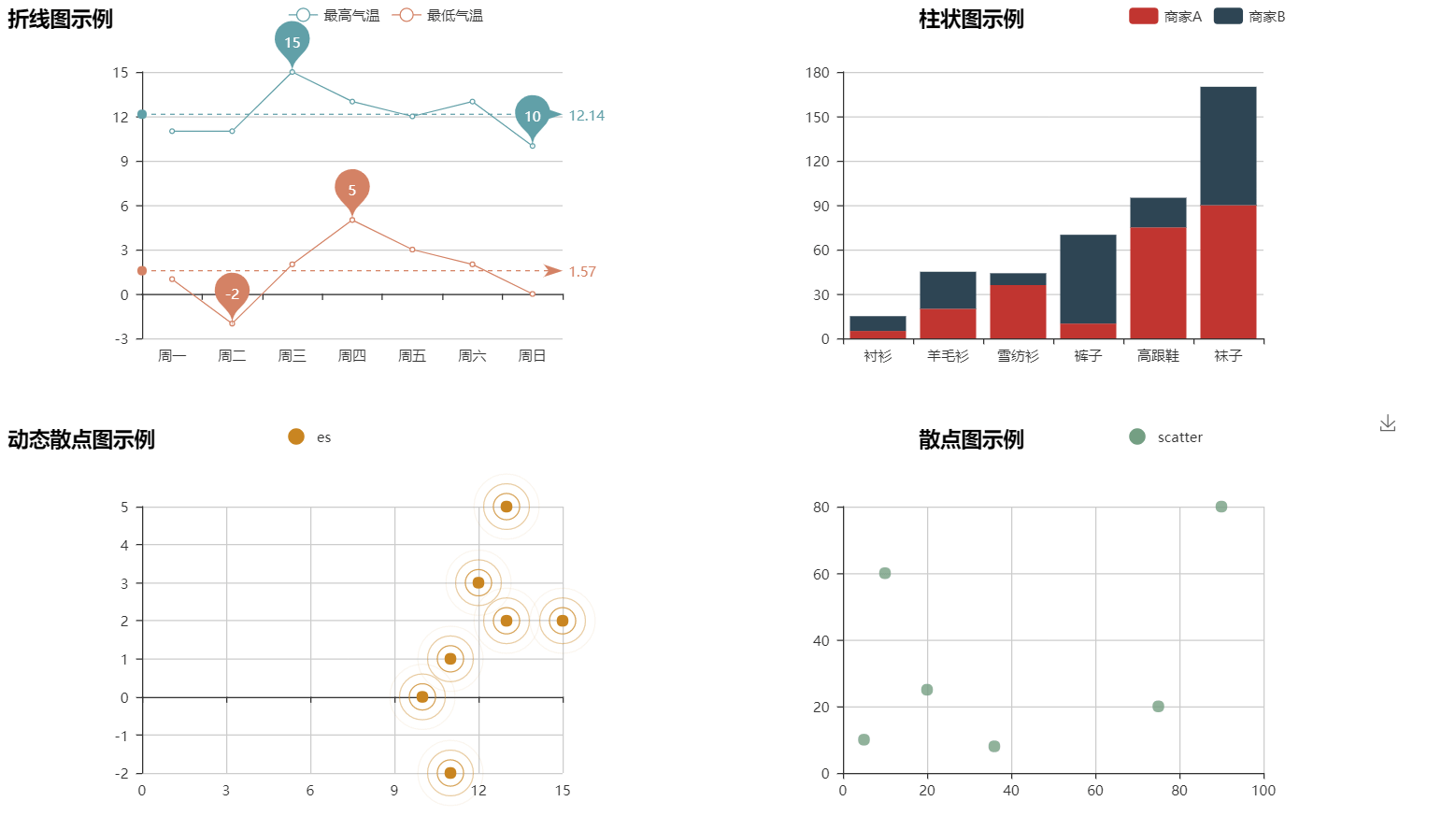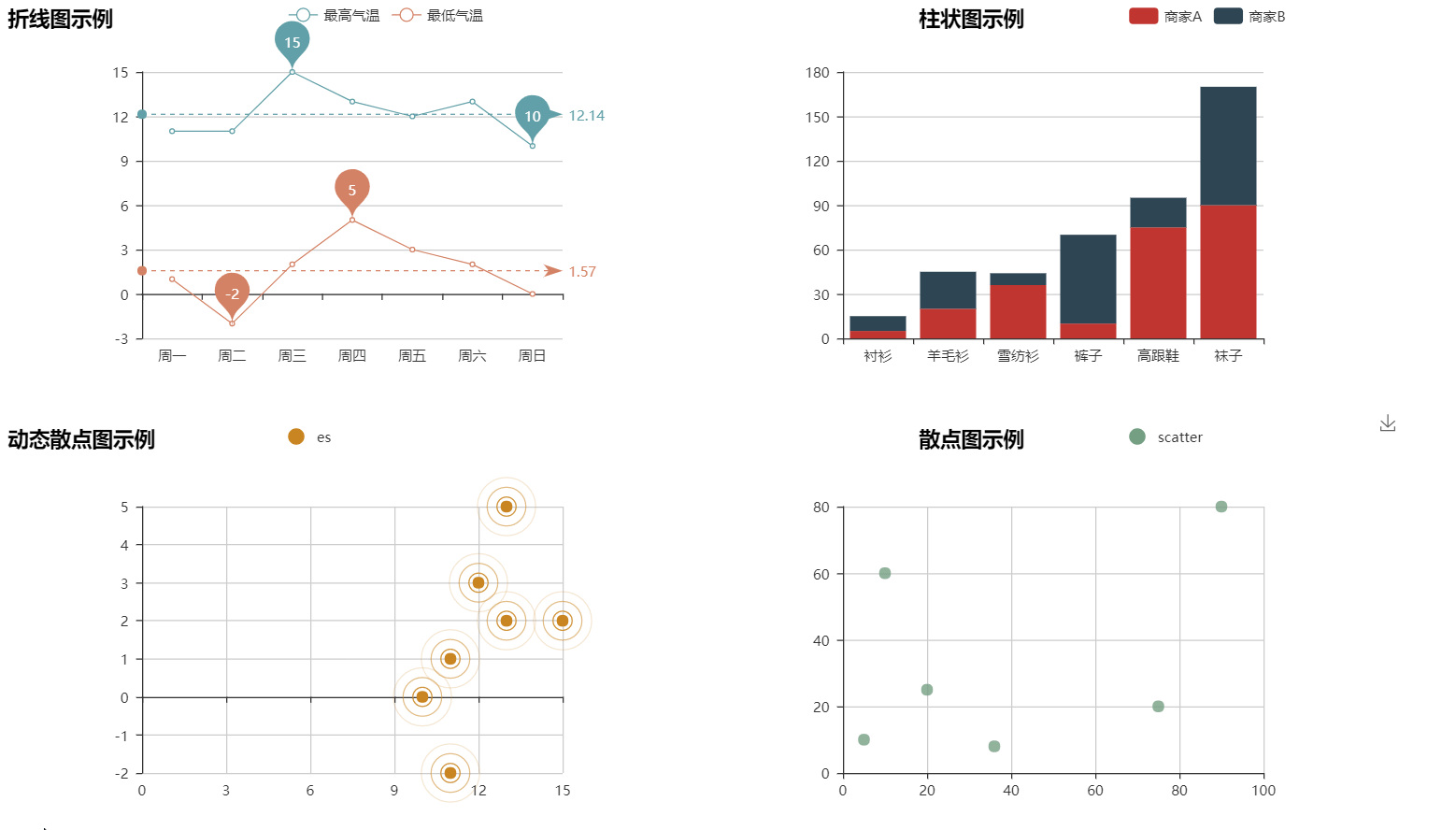
|
||||
|
||||
Line + Pie
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -2188,7 +2134,7 @@ line.grid(pie.get_series(), grid_left="60%")
|
||||
line.show_config()
|
||||
line.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Line + Kline
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -2224,7 +2170,7 @@ line.grid(kline.get_series(), grid_left="55%")
|
||||
line.show_config()
|
||||
line.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
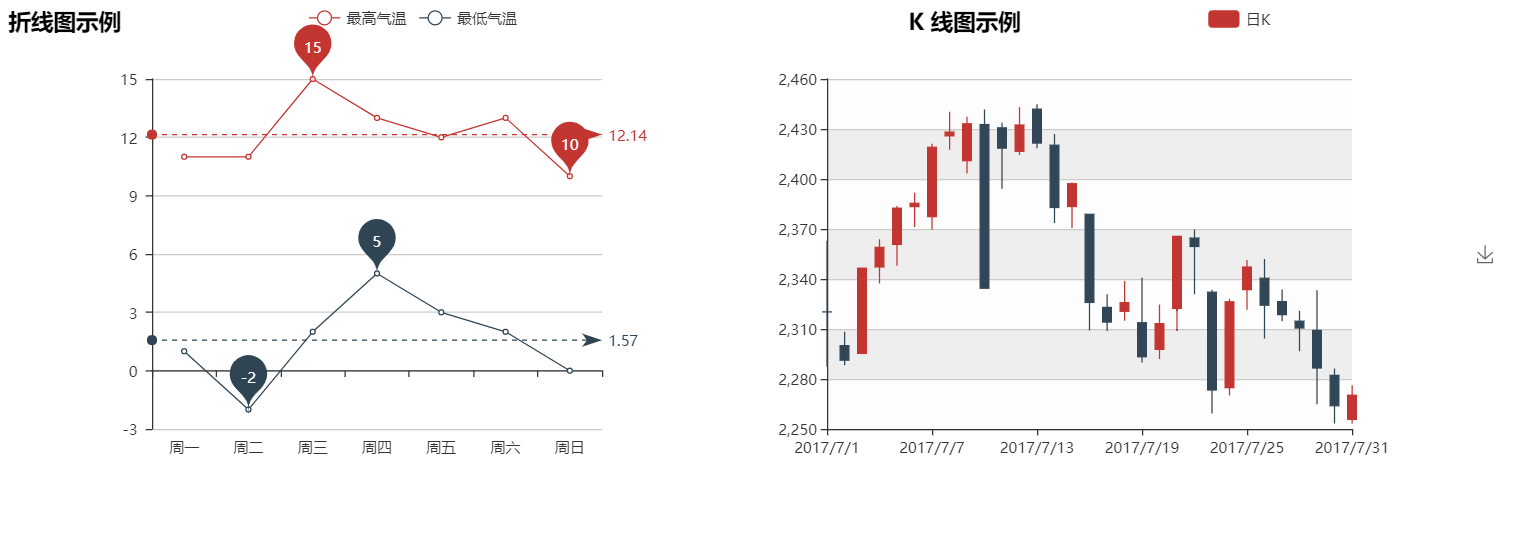
|
||||
|
||||
HeatMap + Bar
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -2249,7 +2195,7 @@ heatmap.grid(bar.get_series(), grid_top="60%")
|
||||
heatmap.show_config()
|
||||
heatmap.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
Bar will influenced by HeatMap,it's funy.
|
||||
|
||||
# Multiple charts in one html page
|
||||
|
||||
44
docs/en-us/faq.md
Normal file
44
docs/en-us/faq.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
|
||||
**jupyter-notebook export problem**
|
||||
|
||||
Since 0.1.9.7, pyecharts has gone into offline mode, drawing without internet connection. Now, the charts in exported note book cannot be display as they have been put outside
|
||||
jupyter environment.
|
||||
|
||||
So the solution is to add the following statement:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
...
|
||||
from pyecharts import online
|
||||
|
||||
online()
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
Above code will take javascripts from github.
|
||||
you cannot connect to github, you could clone https://github.com/pyecharts/assets. Then, you put `js` folder onto your own server. Here is a simple command to achieve it:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/pyecharts/assets
|
||||
$ cd js
|
||||
$ python -m http.server # for python 2, use python -m SimpleHTTPServer
|
||||
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 8000 ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, add localhost into previous python code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
...
|
||||
from pyecharts import online
|
||||
|
||||
online(host="http://localhost:8000)
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Python2 Coding Problem**
|
||||
|
||||
default code type is UTF-8, there's no problem in Python3, because Python3 have a good support in chinese. But in Python2, please use the following sentence to ensure avoiding wrong coding problem:
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/python
|
||||
#coding=utf-8
|
||||
from __future__ import unicode_literals
|
||||
```
|
||||
The first two sentences are telling your editor that it should use UTF-8 ([PEP-0263](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0263/)). And the last sentence is telling Python all the characters are UTF-8 ([unicode literals](http://python-future.org/unicode_literals.html))
|
||||
154
docs/en-us/prepare.md
Normal file
154
docs/en-us/prepare.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
|
||||
# First-steps
|
||||
### Make sure you have installed the latest version pyecharts
|
||||
Now, you are ready to make your first chart!
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
|
||||
bar = Bar("我的第一个图表", "这里是副标题")
|
||||
bar.add("服装", ["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"], [5, 20, 36, 10, 75, 90])
|
||||
bar.show_config()
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** You can click the download button on the right side to download the picture to your local disk.
|
||||
|
||||
* ```add()```
|
||||
main method,add the data and set up various options of the chart
|
||||
* ```show_config()```
|
||||
print and output all options of the chart
|
||||
* ```render()```
|
||||
creat a file named render.html in the root directory defaultly,which supports path parameter and set the location the file save in,for instance render(r"e:\my_first_chart.html"),open file with your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** Click the image download button on the right hand side of the chart. If you need more buttons, please insert `is_more_utils=True` when calling add()
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
|
||||
bar = Bar("我的第一个图表", "这里是副标题")
|
||||
bar.add("服装", ["衬衫", "羊毛衫", "雪纺衫", "裤子", "高跟鞋", "袜子"], [5, 20, 36, 10, 75, 90],
|
||||
is_more_utils=True)
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Rendering as image using pyecharts-snapshot
|
||||
|
||||
If you would to get png, pdf, gif files instead of `render.html`, you can use [pyecharts-snapshot](https://github.com/chfw/pyecharts-snapshot)。However, node.js is required and can be downloaded from [https://nodejs.org/en/download/](https://nodejs.org/en/download/)
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install phantomjs
|
||||
`npm install -g phantomjs-prebuilt`
|
||||
2. install pyecharts-snapshot
|
||||
`pip install pyecharts-snapshot`
|
||||
3. In your program, import pyecharts-snapshot
|
||||
`from pyecharts_snapshot.main import make_a_snapshot`
|
||||
4. Programmatical usage
|
||||
`make_a_snapshot('render.html', 'snapshot.png')`
|
||||
where the frist parameter is the output file(by default, render.html), and the second one is output file with file extension as png or pdf.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, please refer to [pyecharts-snapshot](https://github.com/chfw/pyecharts-snapshot)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Chart rendering process
|
||||
|
||||
almost all the chart type drawed like this:
|
||||
1. ```chart_name = Type()``` Initialise the concrete chart type.
|
||||
2. ```add()``` Add data and options.
|
||||
3. ```render()``` Creat .html file.
|
||||
|
||||
```add()``` Data is two lists commonly(the same length),if your data is dictionary or dictionary with tuple,use ```cast()``` to convert.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
cast(seq)
|
||||
``` Convert the sequence with the dictionary and tuple type into k_lst, v_lst. ```
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. Tuple Lists
|
||||
[(A1, B1), (A2, B2), (A3, B3), (A4, B4)] --> k_lst[ A[i1, i2...] ], v_lst[ B[i1, i2...] ]
|
||||
2. Dictionary Lists
|
||||
[{A1: B1}, {A2: B2}, {A3: B3}, {A4: B4}] --> k_lst[ A[i1, i2...] ], v_lst[ B[i1, i2...] ]
|
||||
3. Dictionaries
|
||||
{A1: B1, A2: B2, A3: B3, A4: B4} -- > k_lst[ A[i1, i2...] ], v_lst[ B[i1, i2...] ]
|
||||
|
||||
### Pandas & Numpy examples
|
||||
|
||||
In the context of Numpy and/or Pandas, ```pdcast(pddata)``` and ``` npcast(npdata)``` methods, provided in 0.19.2 are no log required. Please see the advanced example in README.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If your DataFrame returns a transposed list(such as, [ [1], [2], [3] ]), you have to tranpose it by yourself (make it like [ 1, 2, 3 ] ). This transpose operation applies to Radar, Parallel, HeatMap.
|
||||
|
||||
Series type
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
pddata = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4], index=[1, 'b', 'c', 'd'])
|
||||
vlst, ilst = Bar.pdcast(pddata)
|
||||
|
||||
print(vlst)
|
||||
>>> [1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0]
|
||||
print(ilst)
|
||||
>>> ['1', 'b', 'c', 'd']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
DataFrame type
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
pddt = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3, 4], [2, 3, 4, 5], [4.1, 5.2, 6.3, 7.4]], index=["A", "B", "C"])
|
||||
vlst, ilst = Bar.pdcast(pddata)
|
||||
|
||||
print(vlst)
|
||||
>>> [[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0], [2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0], [4.1, 5.2, 6.3, 7.4]]
|
||||
print(ilst)
|
||||
>>> ['A', 'B', 'C']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
npcast(),It accepts numpy.array type.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
npcast(npdata)
|
||||
``` handle the ndarray type in Numpy, return a list that ensures the correct type. Returns the nested list if there are multiple dimensions.```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Numpy.array type
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar
|
||||
import numpy ad np
|
||||
|
||||
npdata = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [2, 4, 5.0, 6.3]])
|
||||
print(npdata)
|
||||
>>> [[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0], [2.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.3]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Of course you can use the cooler way,use Jupyter Notebook to show the chart.But what matplotlib have,so do pyecharts**
|
||||
|
||||
like this
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
and this
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
more Jupyter notebook examples, please refer to [notebook-use-cases](https://github.com/chenjiandongx/pyecharts/blob/master/document/notebook-use-cases.ipynb)。you could download and run it on your notebook.
|
||||
|
||||
**Tip:** The function was official added in 0.1.9.2 version,please update the newest version to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Offline installation instructions for pyecharts 0.3.2 +
|
||||
|
||||
Please download these three packages from pypi: pyecharts, pyecharts-jupyter-installer, 和 jupyter-echarts-pypkg.
|
||||
|
||||
Then install them sequentially as:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install pyecharts-jupyter-installer.tar.gz
|
||||
pip install jupyter-echarts-pypkg.tar.gz
|
||||
pip install pyecharts.tar.gz
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -5,7 +5,19 @@
|
||||
|
||||
* 更新 jupyter-echarts 至 1.4.0: echarts 3.6.2 -> 4.0.2, echarts-gl 1.0.0-b4 -> 1.0.0-b6, echarts-liquidfill 1.0.5 -> 1.1.1,
|
||||
|
||||
* ### version 0.3.2 (development)
|
||||
* ### version 0.3.3 - 2018.03.01(Current)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Added
|
||||
* 防止将来的依赖包影响 v0.3.2 的功能: lml==0.0.2, jupyter-echarts-pypkg==0.0.11
|
||||
* 新增 `name_map`, [允许用户采用自己地图名称](http://echarts.baidu.com/option.html#series-map.nameMap)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Changed
|
||||
|
||||
* `Chart.render_embed` 返回 `jinja2.Markup` 实例
|
||||
* `Base.show_config` 重命名为 `Base.print_echarts_options`
|
||||
* 移除 `EchartsEnvironment.configure_pyecharts` 方法
|
||||
|
||||
* ### version 0.3.2 - 2018.02.26
|
||||
|
||||
从此版本开始,将不再自带地图 js 文件。有需要的开发人员,请自选安装。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,7 +47,7 @@
|
||||
* [PR#368](https://github.com/pyecharts/pyecharts/pull/368) `pyecharts/templates/js` 被删去了。`jupyter-echarts` 不再内嵌于 pyecharts 。
|
||||
* echarts-china-cities-js 和 echarts-countries-js 不再是必选,而是可选图库。
|
||||
|
||||
* ### version 0.3.1 - 2017.12.13(Current)
|
||||
* ### version 0.3.1 - 2017.12.13
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fixed
|
||||
* [issue#290](https://github.com/pyecharts/pyecharts/issues/290) 紧急修复 v0.3.0 版本不能正常显示图形的严重 bug
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,8 +75,6 @@
|
||||
画布背景颜色,默认为 '#fff'
|
||||
* page_title -> str
|
||||
指定生成的 html 文件中 `<title>` 标签的值。默认为'Echarts'
|
||||
* jshost-> str
|
||||
自定义每个实例的 JavaScript host
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 通用配置项
|
||||
@ -1716,6 +1714,16 @@ add(name, attr, value,
|
||||
如果只想要开启缩放或者平移,可以设置成'scale'或者'move'。设置成 True 为都开启
|
||||
* is_map_symbol_show -> bool
|
||||
是否显示地图标记红点,默认为 True。
|
||||
* name_map -> dict:
|
||||
[用自定义的地图名称](http://echarts.baidu.com/option.html#series-map.nameMap). 有些地图提供行政区号,`name_map` 可以帮助把它们转换成用户满意的地名。比如英国选区地图,伦敦选区的行政区号是 E14000639 ,把它转换成可读地名就需要这么一个字典:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{
|
||||
"E14000639": "Cities of London and Westminster"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
以此类推,把英国选区所有的地名都转换一下,就需要个[更大一些的字典](https://github.com/chfw/echarts-united-kingdom-pypkg/blob/master/echarts_united_kingdom_pypkg/constants.py#L1)。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pyecharts import Map
|
||||
@ -1788,6 +1796,32 @@ map.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
设置 `name_map=...` 采用自己地图名称
|
||||
|
||||
原版:
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img width="382" alt="screen shot 2018-02-27 at 09 24 21" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/4280312/36720467-16fb0a66-1ba0-11e8-8cbd-453d8f2462d3.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
用 `name_map` 改动之后:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
#coding=utf-8
|
||||
from __future__ import unicode_literals
|
||||
|
||||
from pyecharts import Map
|
||||
from echarts_united_kingdom_pypkg import NM_WESTMINSTER_2016_UK
|
||||
|
||||
value = []
|
||||
attr = []
|
||||
map = Map('United Kingdom', width=800, height=600)
|
||||
map.add('', attr, value, maptype='英国选区2016', is_visualmap=True, visual_text_color="#000", name_map=NM_WESTMINSTER_2016_UK)
|
||||
map.render()
|
||||
```
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img width="449" alt="screen shot 2018-02-27 at 09 27 38" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/4280312/36720626-803ff194-1ba0-11e8-998b-548afbedc18e.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
这个方便画图,因为很多数据和地区号直接挂钩,同时也容易做本地化。
|
||||
|
||||
## Parallel(平行坐标系)
|
||||
> 平行坐标系是一种常用的可视化高维数据的图表。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4,8 +4,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何获得更多地图
|
||||
|
||||
自从 0.3.2 开始,所有地图包括[中国各城市地图](https://github.com/pyecharts/echarts-china-cities-js) 和
|
||||
[世界各国的地图](https://github.com/pyecharts/echarts-countries-js)变成了可选地图。需要这些地图的朋友,可以装 pip 命令行:
|
||||
自从 0.3.2 开始,为了缩减项目本身的体积以及维持 pyecharts 项目的轻量化运行,pyecharts 将不再自带地图 js 文件。如用户需要用到地图图表,可自行安装对应的地图文件包。下面介绍如何安装。
|
||||
|
||||
1. [全球国家地图](https://echarts-maps.github.io/echarts-countries-js/): [echarts-countries-pypkg](https://github.com/pyecharts/echarts-countries-pypkg) (1.9MB): 世界地图和213个国家,包括中国地图
|
||||
2. [中国省级地图](https://echarts-maps.github.io/echarts-china-provinces-js/): [echarts-china-provinces-pypkg](https://github.com/pyecharts/echarts-china-provinces-pypkg) (730KB):23个省,5个自治区
|
||||
3. [中国市级地图](https://echarts-maps.github.io/echarts-china-cities-js/): [echarts-china-cities-pypkg](https://github.com/pyecharts/echarts-china-cities-pypkg) (3.8MB):370个中国城市
|
||||
|
||||
需要这些地图的朋友,可以装 pip 命令行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install echarts-countries-pypkg
|
||||
@ -13,6 +18,9 @@ pip install echarts-china-provinces-pypkg
|
||||
pip install echarts-china-cities-pypkg
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
特别注明,中国地图在 echarts-countries-pypkg 里。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何制作自己的地图扩展
|
||||
|
||||
你需要做两个 github 项目:一个是 npm 项目,提供所有的 javascript 脚本;另一个是 python 项目,把前一个项目变成可以用 pip 装的 python 包。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,17 +30,47 @@ from pyecharts import online
|
||||
online()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Q:克隆项目到本地后 template/js 文件夹为空,没有 js 文件?**
|
||||
**jupyter-notebook 输出问题**
|
||||
|
||||
A: pyecharts 项目使用了 submodule 特性,template/js 引用了另一个仓库的代码。
|
||||
jupyter notebook 输出后,你的 notebook 离开了本地 jupyter 环境,图片就不能显示了。
|
||||
为了解决这个问题,再画图之前,你可以多加两个语句:
|
||||
|
||||
这时应当使用下面的命令更新 submodule 模块内容。
|
||||
```python
|
||||
...
|
||||
from pyecharts import online
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git submodule update
|
||||
online()
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
或者删除原有代码后,使用 `git clone --recursive https://github.com/pyecharts/pyecharts.git` 重新克隆代码。
|
||||
这样,所有的脚本会从 github 下载。如果你连不上 Github, 你可以先把 https://github.com/pyecharts/assets 克隆一下。然后在你自己的服务器上,把整个 js 文件夹挂上去。
|
||||
|
||||
下面我简单示范一下
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/pyecharts/assets
|
||||
$ cd js
|
||||
$ python -m http.server # for python 2, use python -m SimpleHTTPServer
|
||||
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 8000 ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后,再把本地服务器加进前面的语句:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
...
|
||||
from pyecharts import online
|
||||
|
||||
online(host="http://localhost:8000)
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
**Python2 编码问题**
|
||||
默认的编码类型为 UTF-8,在 Python3 中是没什么问题的,Python3 对中文的支持好很多。但是在 Python2 中,请应用下面的语句,保证没有编码问题:
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/python
|
||||
#coding=utf-8
|
||||
from __future__ import unicode_literals
|
||||
```
|
||||
前两句告知你的编辑器你用 UTF-8 ([PEP-0263](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0263/)). 最后一句告知 Python 所有字符是 UTF-8 ([unicode literals](http://python-future.org/unicode_literals.html))
|
||||
|
||||
**Q:pyecharts 是否支持 jupyterlab?**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,81 +50,6 @@ bar.render()
|
||||
更多内容请移步至 [pyecharts-snapshot](https://github.com/pyecharts/pyecharts-snapshot)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Jupyter notebook 小贴士
|
||||
对本库的现有用户来说,v0.1.9.5 版本的离线模式要求:
|
||||
1)老版本已完全卸载
|
||||
2)您现有的 notebook 文档需要刷新并重新运行。
|
||||
|
||||
离线模式工作原理:pyecharts 自动把 echarts 脚本文件装在了 jupyter nbextensions 文件夹下面。以下代码可以告诉你 pyecharts 网页脚本是否装到了 Jupyter 里面:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ jupyter nbextension list
|
||||
Known nbextensions:
|
||||
config dir: /Users/jaska/.jupyter/nbconfig
|
||||
notebook section
|
||||
echarts/main enabled
|
||||
- Validating: OK
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在特殊的情况下,如果你想要 pyecharts 更新所有的脚本文件的话,你可以运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/pyecharts/jupyter-echarts.git
|
||||
$ cd jupyter-echarts
|
||||
$ jupyter nbextension install echarts --user
|
||||
```
|
||||
在下一个画图动作的时候,您的脚本文件会被更新。
|
||||
|
||||
下面这个删除命令估计只有参与 pyecharts 开发者才会用到
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
$ jupyter nbextension uninstall echarts --user
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### jupyter-notebook 输出问题
|
||||
自 v0.1.9.7 起,pyecharts 已经进入全部离线模式,也就是没有网络,也能画图。jupyter notebook 输出后,你的 notebook 离开了本地 jupyter 环境,图片就不能显示了。
|
||||
为了解决这个问题,再画图之前,你可以多加两个语句:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
...
|
||||
from pyecharts import online
|
||||
|
||||
online()
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这样,所有的脚本会从 https://pyecharts.github.io/jupyter-echarts/echarts 下载。如果你连不上 Github, 你可以先把 https://github.com/pyecharts/jupyter-echarts 克隆一下。然后在你自己的服务器上,把整个 echarts 挂上去。
|
||||
|
||||
下面我简单示范一下
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cd jupyter-echarts/echarts
|
||||
$ python -m http.server # for python 2, use python -m SimpleHTTPServer
|
||||
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 8000 ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后,再把本地服务器加进前面的语句:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
...
|
||||
from pyecharts import online
|
||||
|
||||
online(host="http://localhost:8000)
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Python2 编码问题
|
||||
默认的编码类型为 UTF-8,在 Python3 中是没什么问题的,Python3 对中文的支持好很多。但是在 Python2 中,请应用下面的语句,保证没有编码问题:
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/python
|
||||
#coding=utf-8
|
||||
from __future__ import unicode_literals
|
||||
```
|
||||
前两句告知你的编辑器你用 UTF-8 ([PEP-0263](https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0263/)). 最后一句告知 Python 所有字符是 UTF-8 ([unicode literals](http://python-future.org/unicode_literals.html))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 图形绘制过程
|
||||
基本上所有的图表类型都是这样绘制的:
|
||||
1. ```chart_name = Type()``` 初始化具体类型图表。
|
||||
@ -176,12 +101,12 @@ cast(seq)
|
||||
|
||||
### 如果在没有互联网的情况下安装 pyecharts 0.3.2 +
|
||||
|
||||
首先,您需要通过有互联网的计算机得到这三个包:pyecharts-cli, pyecharts, 和 jupyter-echarts-master.tar.gz. 前两个可以在 pypi 上下载。后者是在 github 下载: https://github.com/pyecharts/jupyter-echarts/archive/master.zip.
|
||||
首先,您需要通过有互联网的计算机得到这三个包:pyecharts, pyecharts-jupyter-installer, 和 jupyter-echarts-pypkg.
|
||||
|
||||
然后,按照这个顺序组装:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install pyecharts-cli
|
||||
pyecharts-cli install jupyter-echarts-master.tar.gz
|
||||
pip install pyecharts
|
||||
pip install pyecharts-jupyter-installer.tar.gz
|
||||
pip install jupyter-echarts-pypkg.tar.gz
|
||||
pip install pyecharts.tar.gz
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,11 +6,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
从本版本开始,为了缩减项目本身的体积以及维持 pyecharts 项目的轻量化运行,pyecharts 将不再自带地图 js 文件。如用户需要用到地图图表,可自行安装对应的地图文件包。下面介绍如何安装。
|
||||
|
||||
地图文件被分成了三个 Python 包,分别为
|
||||
地图文件被分成了国家、省、市三个 Python 包,分别为
|
||||
|
||||
1. [全球国家地图](https://echarts-maps.github.io/echarts-countries-js/): [echarts-countries-pypkg](https://github.com/pyecharts/echarts-countries-pypkg) (1.9MB)
|
||||
2. [中国省级地图](https://echarts-maps.github.io/echarts-china-provinces-js/): [echarts-china-provinces-pypkg](https://github.com/pyecharts/echarts-china-provinces-pypkg) (730KB)
|
||||
3. [中国市级地图](https://echarts-maps.github.io/echarts-china-cities-js/): [echarts-china-cities-pypkg](https://github.com/pyecharts/echarts-china-cities-pypkg) (3.8MB)
|
||||
1. [全球国家地图](https://echarts-maps.github.io/echarts-countries-js/): [echarts-countries-pypkg](https://github.com/pyecharts/echarts-countries-pypkg) (1.9MB): 世界地图和213个国家,包括中国地图
|
||||
2. [中国省级地图](https://echarts-maps.github.io/echarts-china-provinces-js/): [echarts-china-provinces-pypkg](https://github.com/pyecharts/echarts-china-provinces-pypkg) (730KB):23个省,5个自治区
|
||||
3. [中国市级地图](https://echarts-maps.github.io/echarts-china-cities-js/): [echarts-china-cities-pypkg](https://github.com/pyecharts/echarts-china-cities-pypkg) (3.8MB):370个中国城市
|
||||
|
||||
安装方式也很简单,可以仅选择所需要的包,也可以全部安装
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,2 +1,2 @@
|
||||
__version__ = '0.3.2'
|
||||
__version__ = '0.3.3'
|
||||
__author__ = 'chenjiandongx'
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,9 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
import uuid
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
|
||||
from jinja2 import Markup
|
||||
|
||||
import pyecharts.constants as constants
|
||||
import pyecharts.engine as engine
|
||||
@ -55,11 +58,21 @@ class Base(object):
|
||||
def page_title(self):
|
||||
return self._page_title
|
||||
|
||||
def show_config(self):
|
||||
def print_echarts_options(self):
|
||||
""" 打印输出图形所有配置项
|
||||
"""
|
||||
print(utils.json_dumps(self._option, indent=4))
|
||||
|
||||
def show_config(self):
|
||||
""" 打印输出图形所有配置项
|
||||
"""
|
||||
deprecated_tpl = 'The {} is deprecated, please use {} instead!'
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
deprecated_tpl.format('show_config', 'print_echarts_options'),
|
||||
DeprecationWarning
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.print_echarts_options()
|
||||
|
||||
def render_embed(self):
|
||||
""" 渲染图表的所有配置项,为 web pages 服务,不过需先提供
|
||||
所需要的js 依赖文件
|
||||
@ -70,7 +83,7 @@ class Base(object):
|
||||
chart_id=self._chart_id,
|
||||
my_width=self.width,
|
||||
my_height=self.height)
|
||||
return html
|
||||
return Markup(html)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_js_dependencies(self):
|
||||
""" 声明所有的 js 文件路径
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,6 +24,7 @@ class Map(Chart):
|
||||
maptype="china",
|
||||
is_roam=True,
|
||||
is_map_symbol_show=True,
|
||||
name_map=None,
|
||||
**kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -48,6 +49,8 @@ class Map(Chart):
|
||||
如果只想要开启缩放或者平移,可以设置成'scale'或者'move'。设置成 True 为都开启。
|
||||
:param is_map_symbol_show:
|
||||
是否显示地图标记红点,默认为 True。
|
||||
:param name_map:
|
||||
用自定义的地图名称。默认为 None,也就是用地图自带地名。
|
||||
:param kwargs:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
assert len(attr) == len(value)
|
||||
@ -58,7 +61,7 @@ class Map(Chart):
|
||||
_data.append({"name": _name, "value": _value})
|
||||
self._option.get('legend')[0].get('data').append(name)
|
||||
|
||||
self._option.get('series').append({
|
||||
__option__ = {
|
||||
"type": "map",
|
||||
"name": name,
|
||||
"symbol": chart['symbol'],
|
||||
@ -67,6 +70,9 @@ class Map(Chart):
|
||||
"data": _data,
|
||||
"roam": is_roam,
|
||||
"showLegendSymbol": is_map_symbol_show
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
if name_map:
|
||||
__option__['nameMap'] = name_map
|
||||
self._option.get('series').append(__option__)
|
||||
self._add_chinese_map(maptype)
|
||||
self._config_components(**kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,7 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
from jinja2 import Markup
|
||||
|
||||
import pyecharts.utils as utils
|
||||
import pyecharts.engine as engine
|
||||
from pyecharts.conf import CURRENT_CONFIG
|
||||
@ -43,7 +45,7 @@ class Page(list):
|
||||
|
||||
:return:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return '<br/> '.join([chart.render_embed() for chart in self])
|
||||
return Markup('<br/> '.join([chart.render_embed() for chart in self]))
|
||||
|
||||
def get_js_dependencies(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -151,10 +151,6 @@ class EchartsEnvironment(BaseEnvironment):
|
||||
*args,
|
||||
**kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def configure_pyecharts(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
for k, v in kwargs.items():
|
||||
setattr(self.pyecharts_config, k, v)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def render(template_file, notebook=False, **context):
|
||||
config = conf.CURRENT_CONFIG
|
||||
|
||||
@ -95,6 +95,14 @@ class JsExtensionManager(PluginManager):
|
||||
self.js_extensions.append(__js_extension__)
|
||||
return self.js_extensions
|
||||
|
||||
def get_a_extension(self, name):
|
||||
if len(self.js_extensions) == 0:
|
||||
self.get_all_extensions()
|
||||
for __extension__ in self.js_extensions:
|
||||
if __extension__.registry['JS_FOLDER'] == name:
|
||||
return __extension__
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
EXTENSION_MANAGER = JsExtensionManager()
|
||||
# Load js & map file index into a dictionary.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
jinja2>=2.8
|
||||
future
|
||||
pillow
|
||||
lml
|
||||
jupyter-echarts-pypkg
|
||||
lml>=0.0.2
|
||||
jupyter-echarts-pypkg>=0.0.11
|
||||
|
||||
4
setup.py
4
setup.py
@ -12,8 +12,8 @@ __license__ = 'MIT'
|
||||
__requires__ = ['pillow',
|
||||
'jinja2',
|
||||
'future',
|
||||
'jupyter-echarts-pypkg',
|
||||
'lml']
|
||||
'jupyter-echarts-pypkg==0.0.11',
|
||||
'lml==0.0.2']
|
||||
|
||||
__keywords__ = ['Echarts',
|
||||
'charts',
|
||||
|
||||
@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ def test_bar_waterfall():
|
||||
is_stack=True)
|
||||
bar.add("月份", months, months_v2, is_label_show=True, is_stack=True,
|
||||
label_pos='inside')
|
||||
bar.show_config()
|
||||
bar.print_echarts_options()
|
||||
bar.render()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,9 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
from __future__ import unicode_literals
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import codecs
|
||||
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
@ -13,6 +11,7 @@ import numpy as np
|
||||
from nose.tools import eq_
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar, Map
|
||||
from test.constants import CLOTHES
|
||||
from test.utils import get_default_rendering_file_content
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
TITLE = "柱状图数据堆叠示例"
|
||||
@ -104,9 +103,8 @@ def test_echarts_position_in_render_html():
|
||||
map.add("", attr, value, maptype='广东',
|
||||
is_visualmap=True, visual_text_color='#000')
|
||||
map.render()
|
||||
with codecs.open('render.html', 'r', 'utf-8') as f:
|
||||
actual_content = f.read()
|
||||
assert TITLE in actual_content
|
||||
actual_content = get_default_rendering_file_content()
|
||||
assert TITLE in actual_content
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_show_config():
|
||||
@ -116,7 +114,7 @@ def test_show_config():
|
||||
with open(captured_stdout, 'w') as f:
|
||||
sys.stdout = f
|
||||
bar = create_a_bar("new")
|
||||
bar.show_config()
|
||||
bar.print_echarts_options()
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
# whatever happens, continue and restore stdout
|
||||
print(e)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,30 +54,23 @@ PROVINCE_NAME_PINYIN_MAP = {
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_core_js_libraries():
|
||||
JS_EXTENSIONS = conf.EXTENSION_MANAGER.get_all_extensions()
|
||||
for extension in JS_EXTENSIONS:
|
||||
if extension.registry['JS_FOLDER'] == 'echarts':
|
||||
break
|
||||
__jupyter_echarts__ = conf.EXTENSION_MANAGER.get_a_extension('echarts')
|
||||
__file_map__ = __jupyter_echarts__.registry.get('FILE_MAP')
|
||||
for key, value in DEFAULT_JS_LIBRARIES.items():
|
||||
default_file_map = extension.registry.get('FILE_MAP')
|
||||
eq_(value, default_file_map[key])
|
||||
eq_(value, __file_map__[key])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_province_names():
|
||||
JS_EXTENSIONS = conf.EXTENSION_MANAGER.get_all_extensions()
|
||||
for extension in JS_EXTENSIONS:
|
||||
if extension.registry['JS_FOLDER'] == 'echarts-china-provinces-js':
|
||||
break
|
||||
__PROVINCE_NAME_PINYIN_MAP__ = extension.registry.get('PINYIN_MAP', {})
|
||||
__provinces__ = conf.EXTENSION_MANAGER.get_a_extension(
|
||||
'echarts-china-provinces-js')
|
||||
__pinyin_map__ = __provinces__.registry.get('PINYIN_MAP')
|
||||
for key, value in PROVINCE_NAME_PINYIN_MAP.items():
|
||||
eq_(value, __PROVINCE_NAME_PINYIN_MAP__[key])
|
||||
eq_(value, __pinyin_map__[key])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_city_names():
|
||||
JS_EXTENSIONS = conf.EXTENSION_MANAGER.get_all_extensions()
|
||||
for extension in JS_EXTENSIONS:
|
||||
if extension.registry['JS_FOLDER'] == 'echarts-china-cities-js':
|
||||
break
|
||||
__CITY_NAME_PINYIN_MAP__ = extension.registry.get('PINYIN_MAP', {})
|
||||
__cities__ = conf.EXTENSION_MANAGER.get_a_extension(
|
||||
'echarts-china-cities-js')
|
||||
__pinyin_map__ = __cities__.registry.get('PINYIN_MAP', {})
|
||||
for key, value in CITY_NAME_PINYIN_MAP.items():
|
||||
eq_(value, __CITY_NAME_PINYIN_MAP__[key])
|
||||
eq_(value, __pinyin_map__[key])
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4,7 +4,6 @@ from __future__ import unicode_literals
|
||||
|
||||
from pyecharts import GeoLines, Style
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
style = Style(
|
||||
title_top="#fff",
|
||||
title_pos="center",
|
||||
@ -49,5 +48,5 @@ def test_geolines():
|
||||
lines = GeoLines("GeoLines 示例", **style.init_style)
|
||||
lines.add("从广州出发", data_guangzhou, **style_geo)
|
||||
lines.add("从北京出发", data_beijing, **style_geo)
|
||||
lines.show_config()
|
||||
lines.print_echarts_options()
|
||||
lines.render()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,8 +2,10 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
from __future__ import unicode_literals
|
||||
|
||||
import json
|
||||
from pyecharts import Kline
|
||||
|
||||
from test.utils import get_default_rendering_file_content
|
||||
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
[2320.26, 2320.26, 2287.3, 2362.94],
|
||||
@ -63,12 +65,17 @@ def test_kline_datazoom_vertical():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_kline_user_define_markline_style():
|
||||
kline = Kline("K 线图-自定义标记点风格")
|
||||
title = "K 线图-自定义标记点风格"
|
||||
kline = Kline(title)
|
||||
kline.add("日K", DATE, data, mark_point=["min", "max"],
|
||||
mark_point_symbolsize=80,
|
||||
datazoom_orient='vertical',
|
||||
mark_line_valuedim=['lowest', 'highest'])
|
||||
kline.render()
|
||||
actual_content = get_default_rendering_file_content()
|
||||
assert 'lowest' in actual_content
|
||||
assert 'highest' in actual_content
|
||||
assert json.dumps(title) in actual_content
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_kline_alias_Candlestick():
|
||||
@ -79,3 +86,5 @@ def test_kline_alias_Candlestick():
|
||||
datazoom_orient='vertical',
|
||||
mark_line_valuedim=['lowest', 'highest'])
|
||||
candlestick.render()
|
||||
actual_content = get_default_rendering_file_content()
|
||||
assert 'candlestick' in actual_content
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
from __future__ import unicode_literals
|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,6 +5,8 @@ import json
|
||||
import codecs
|
||||
from pyecharts import Map
|
||||
|
||||
from test.utils import get_default_rendering_file_content
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_map_show_label():
|
||||
# show label
|
||||
@ -16,6 +17,19 @@ def test_map_show_label():
|
||||
map.render()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_map_with_custom_name_map():
|
||||
# show label
|
||||
value = [155, 10, 66, 78]
|
||||
attr = ["福建", "山东", "北京", "上海"]
|
||||
map = Map("全国地图示例", width=1200, height=600)
|
||||
map.add("", attr, value, maptype='china', is_label_show=True,
|
||||
name_map={'test': '--magic--'})
|
||||
map.render()
|
||||
content = get_default_rendering_file_content()
|
||||
assert '--magic--' in content
|
||||
assert 'nameMap' in content
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_map_combine_with_visualmap():
|
||||
value = [155, 10, 66, 78, 33, 80, 190, 53, 49.6]
|
||||
attr = ["福建", "山东", "北京", "上海", "甘肃",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,6 +9,7 @@ from nose.tools import raises
|
||||
from pyecharts.utils import get_resource_dir
|
||||
from pyecharts import Bar, Map
|
||||
from pyecharts.engine import BaseEnvironment, EchartsEnvironment
|
||||
from pyecharts.conf import PyEchartsConfig
|
||||
|
||||
ECHARTS_ENV = EchartsEnvironment()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,18 +27,22 @@ def create_demo_bar(chart_id_demo=None):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_echarts_js_dependencies():
|
||||
ECHARTS_ENV.configure_pyecharts(jshost='http://localhost/echarts')
|
||||
tpl = ECHARTS_ENV.from_string('{{ echarts_js_dependencies(bar) }}')
|
||||
env = EchartsEnvironment(
|
||||
pyecharts_config=PyEchartsConfig(jshost='http://localhost/echarts')
|
||||
)
|
||||
tpl = env.from_string('{{ echarts_js_dependencies(bar) }}')
|
||||
bar = create_demo_bar()
|
||||
html = tpl.render(bar=bar)
|
||||
assert '<script type="text/javascript" src="http://localhost/echarts/echarts.min.js"></script>' == html # flake8: noqa
|
||||
assert '<script type="text/javascript" src="http://localhost/echarts/echarts.min.js"></script>' == html # flake8: noqa
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_echarts_js_dependencies_embed():
|
||||
ECHARTS_ENV.configure_pyecharts(
|
||||
jshost=get_resource_dir('templates', 'js', 'echarts'))
|
||||
tpl = ECHARTS_ENV.from_string(
|
||||
'{{ echarts_js_dependencies_embed("echarts") }}')
|
||||
env = EchartsEnvironment(
|
||||
pyecharts_config=PyEchartsConfig(
|
||||
jshost=get_resource_dir('templates', 'js', 'echarts')
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
tpl = env.from_string('{{ echarts_js_dependencies_embed("echarts") }}')
|
||||
bar = create_demo_bar()
|
||||
html = tpl.render(bar=bar)
|
||||
assert len(html) > 0
|
||||
@ -52,17 +57,17 @@ def test_echarts_js_container():
|
||||
tpl = ECHARTS_ENV.from_string('{{ echarts_container(bar) }}')
|
||||
bar = create_demo_bar('id_demo_chart')
|
||||
html = tpl.render(bar=bar)
|
||||
assert '<div id="id_demo_chart" style="width:800px;height:400px;"></div>' == html # flake8: noqa
|
||||
assert '<div id="id_demo_chart" style="width:800px;height:400px;"></div>' == html # flake8: noqa
|
||||
|
||||
bar.width = 1024
|
||||
bar.height = 768
|
||||
html = tpl.render(bar=bar)
|
||||
assert '<div id="id_demo_chart" style="width:1024px;height:768px;"></div>' == html # flake8: noqa
|
||||
assert '<div id="id_demo_chart" style="width:1024px;height:768px;"></div>' == html # flake8: noqa
|
||||
|
||||
bar.width = '1024px'
|
||||
bar.height = '768px'
|
||||
html = tpl.render(bar=bar)
|
||||
assert '<div id="id_demo_chart" style="width:1024px;height:768px;"></div>' == html # flake8: noqa
|
||||
assert '<div id="id_demo_chart" style="width:1024px;height:768px;"></div>' == html # flake8: noqa
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_echarts_js_content():
|
||||
@ -88,9 +93,12 @@ def test_echarts_js_in_first():
|
||||
value = [20, 190, 253, 77, 65]
|
||||
attr = ['汕头市', '汕尾市', '揭阳市', '阳江市', '肇庆市']
|
||||
map = Map("广东地图示例", width=1200, height=600)
|
||||
map.add("", attr, value, maptype='广东', is_visualmap=True, visual_text_color='#000')
|
||||
ECHARTS_ENV.configure_pyecharts(jshost='http://localhost/echarts')
|
||||
tpl = ECHARTS_ENV.from_string('{{ echarts_js_dependencies(m) }}')
|
||||
map.add("", attr, value, maptype='广东', is_visualmap=True,
|
||||
visual_text_color='#000')
|
||||
env = EchartsEnvironment(
|
||||
pyecharts_config=PyEchartsConfig(jshost='http://localhost/echarts')
|
||||
)
|
||||
tpl = env.from_string('{{ echarts_js_dependencies(m) }}')
|
||||
html = tpl.render(m=map)
|
||||
echarts_js_pos = html.find('echarts.min.js')
|
||||
guangdong_js_pos = html.find('guangdong.js')
|
||||
|
||||
9
test/utils.py
Normal file
9
test/utils.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
import codecs
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_default_rendering_file_content(file_name='render.html'):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply returns the content render.html
|
||||
"""
|
||||
with codecs.open(file_name, 'r', 'utf-8') as f:
|
||||
return f.read()
|
||||
Loading…
x
Reference in New Issue
Block a user