mirror of
https://github.com/trekhleb/javascript-algorithms.git
synced 2025-12-08 19:06:00 +00:00
* Update README.pt-BR.md * TRIE README.pt-BR typo * TREE README.pt-BR typo * Stack README.pt-BR typo * Priority Queue README.pt-BR typo * hash-table README.pt-BR typo * doubly-linked-list README.pt-BR typo * disjoint-set README.pt-BR typo * bloom-filter README.pt-BR typo * merge-sort pt-BR translation * merge-sort README added pt-BR option * insertion sort pt-BR translation * insertion sort README added pt-br option * heap-sort pt-BR translation * heap-sort READMED added pt-BR option * bubble sort pt-BR typo * pt-BR translation for sorting algorithms Fixed typos and translated all the missing algorithms * Update README.pt-BR.md * linked list pt-BR translation * ml pt-BR translation * fix typo in README Co-authored-by: Oleksii Trekhleb <trehleb@gmail.com>
45 lines
2.6 KiB
Markdown
45 lines
2.6 KiB
Markdown
# k-Nearest Neighbors Algorithm
|
|
|
|
_Read this in other languages:_
|
|
[_Português_](README.pt-BR.md)
|
|
|
|
The **k-nearest neighbors algorithm (k-NN)** is a supervised Machine Learning algorithm. It's a classification algorithm, determining the class of a sample vector using a sample data.
|
|
|
|
In k-NN classification, the output is a class membership. An object is classified by a plurality vote of its neighbors, with the object being assigned to the class most common among its `k` nearest neighbors (`k` is a positive integer, typically small). If `k = 1`, then the object is simply assigned to the class of that single nearest neighbor.
|
|
|
|
The idea is to calculate the similarity between two data points on the basis of a distance metric. [Euclidean distance](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_distance) is used mostly for this task.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
_Image source: [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_distance)_
|
|
|
|
The algorithm is as follows:
|
|
|
|
1. Check for errors like invalid data/labels.
|
|
2. Calculate the euclidean distance of all the data points in training data with the classification point
|
|
3. Sort the distances of points along with their classes in ascending order
|
|
4. Take the initial `K` classes and find the mode to get the most similar class
|
|
5. Report the most similar class
|
|
|
|
Here is a visualization of k-NN classification for better understanding:
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
_Image source: [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/K-nearest_neighbors_algorithm)_
|
|
|
|
The test sample (green dot) should be classified either to blue squares or to red triangles. If `k = 3` (solid line circle) it is assigned to the red triangles because there are `2` triangles and only `1` square inside the inner circle. If `k = 5` (dashed line circle) it is assigned to the blue squares (`3` squares vs. `2` triangles inside the outer circle).
|
|
|
|
Another k-NN classification example:
|
|
|
|
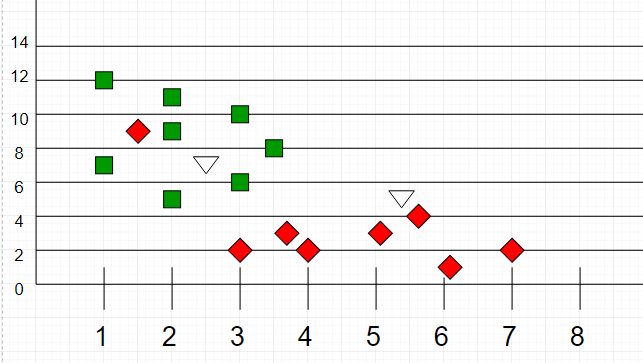
|
|
|
|
_Image source: [GeeksForGeeks](https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/graph2-2.png)_
|
|
|
|
Here, as we can see, the classification of unknown points will be judged by their proximity to other points.
|
|
|
|
It is important to note that `K` is preferred to have odd values in order to break ties. Usually `K` is taken as `3` or `5`.
|
|
|
|
## References
|
|
|
|
- [k-nearest neighbors algorithm on Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/K-nearest_neighbors_algorithm)
|