9.4 KiB
title: Egg and Koa
Asynchronous programming model
Node.js is an asynchronous world, asynchronous programming models in official API support are all in callback form ,it brings many problems. For example:
- callback hell: Notorious "callback hell"。
- release zalgo: Asynchronous functions may call callback function response data synchronously which would bring inconsistency.
The community has provided many solutions for the problems, the winner is Promise, it is built into ECMAScript 2015. On the basis of Promise, and Generator with the ability to switch context, we can write asynchronous code in synchronous way with co and other third party libraries. Meanwhile async function, the official solution has been finalized, and will be published in ECMAScript 2017.
Generator and co
Asynchronous programming model in synchronous way on basis of Generator and Promise.
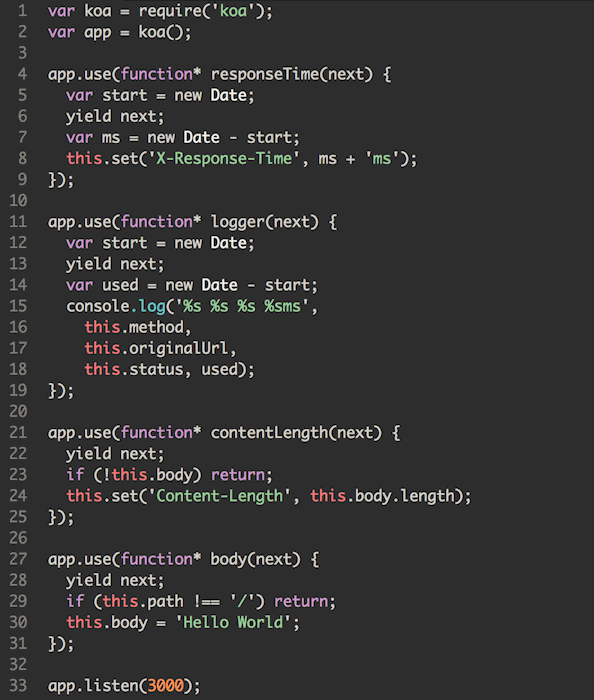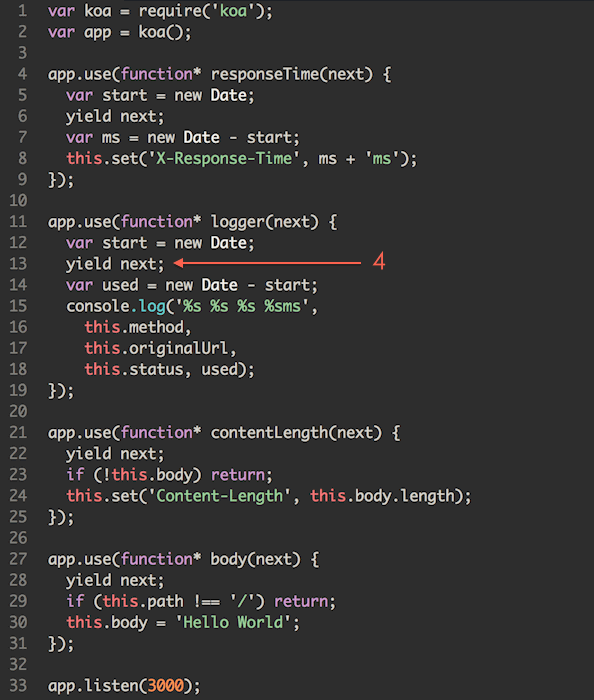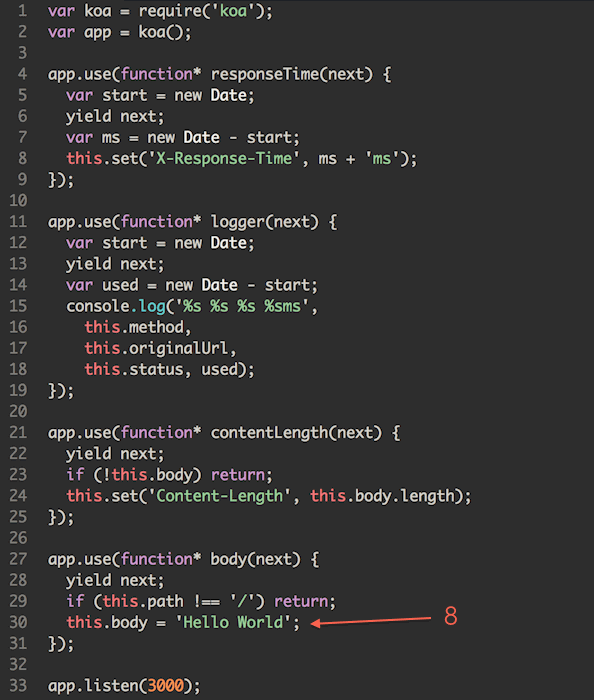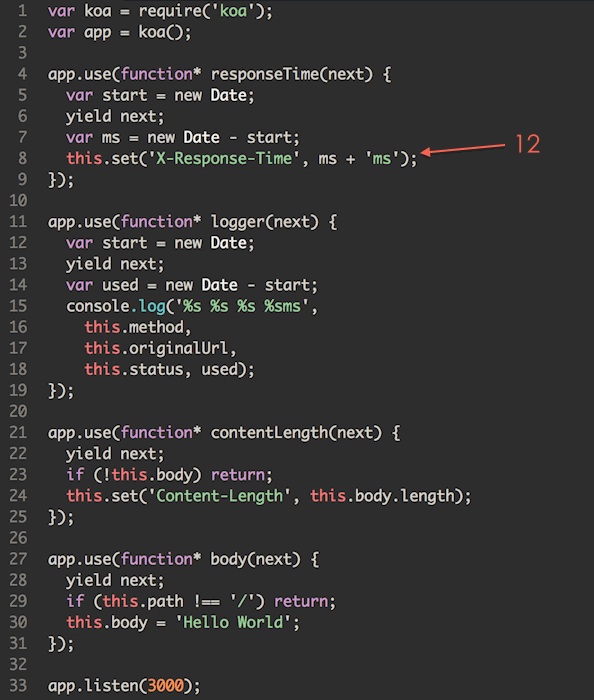
As metioned before, we can write asynchronous code in synchronous way with the help of Generator and Promise. The most popular library implementing this feature is co. the core principle of co can be described by lines of code below:
function run(generator, res) {
const ret = generator.next(res);
if (ret.done) return;
ret.value.then(function (res) {
run(generator, res);
});
}
With the code , you can yield a Promise in Generator Function, and the runtime would execute the following code after being resolved.
let count = 1;
function tick(time) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('tick %s after %s ms', count++, time);
resolve();
}, time);
});
}
function* main() {
console.log('start run...');
yield tick(500);
yield tick(1000);
yield tick(2000);
}
run(main());
With the run function, asynchronous code can be written in synchronous way in main function in the example above. If you want to know more about Generator, you can have a look at this document
Compared with the run function, co has yield [Object / Array / thunk / Generator Function / Generator], and builds a Promise with wrapping a Generator Function. co is also the underlying library of Koa 1 providing the asynchronous feature. Every middleware in Koa 1 must be a generator function.
Async function
Async function has the similar principles to the co, it is a syntactic sugar at the language level. The code written in async function looks like that written in co + generator.
const fn = co(function*() {
const user = yield getUser();
const posts = yield fetchPosts(user.id);
return { user, posts };
});
fn().then(res => console.log(res)).catch(err => console.error(err.stack));
const fn = async function() {
const user = await getUser();
const posts = await fetchPosts(user.id);
return { user, posts };
};
fn().then(res => console.log(res)).catch(err => console.error(err.stack));
Other than the features supported by co, async function can not await a Promise array (You can wrap it with Promise.all), await thunk is not avaliable either.
Though async function has not been published with the spec yet, it is supported in the V8 runtime built in Node.js 7.x, you can use it without flag parameter after 7.6.0 version.
Koa
Koa is a new Web framework designed by the team behind Express, which aims to be a smaller, more expressive, and more robust foundation for Web applications and APIs.
The design style of Koa and Express are very similar, The underlying base library is the same, HTTP library. There are several significant differences between them. Besides the asynchronous solution by default metioned above, there are the following points.
Midlleware
The middleware in Koa is different from Express, Koa use the onion model:
- Middleware onion diagram:
- Middleware execution sequence diagram:
All the requests will be executed twice during one middleware. Compared to Express middleware, it is very easy to implementing post-processing logic. You can obviously feel the advantage of Koa middleware model comparing to the compress middleware implementing in Koa and Express.
- koa-compress for Koa.
- compression for Express.
Context
Unlike that there are only two objects Request and Response in Express, Koa has one more, Context object in one HTTP request(it is this in Koa 1, while it is the first parameter for middleware function in Koa 2). We can attach all the relative things to the object. Such as traceId that runs through the request lifetime (which will be called anywhere afterward) could be attached. It is more semantic other than request and response.
At the same time Request and Response are attached to Context object. Just like Express, the two objects provide lots of easy ways to help developing. For example:
get request.queryget request.hostnameset response.bodyset response.status
Exception handlering
Another enormous advantage for writing asynchronous code in synchronous way is that it is quite at ease to handler exception. You can catch all the exceptions thrown in the codes followed the convention with try catch. We can easily write a customized exception handlering middleware.
function* onerror(next) {
try {
yield next;
} catch (err) {
this.app.emit('error', err);
this.body = 'server error';
this.status = err.status || 500;
}
}
Putting the middleware before others, you can catch all the exceptions thrown by the synchronous or asynchronous code.
Egg inherit from Koa
As the above words, Koa is an excellent framework. However, it is not enough to building an enterprise-class application.
Egg is built around the Koa. On the basis of Koa model, Egg implements enhancements one step further.
Extension
In the framework or application based on Egg, we can extend the prototype of 4 Koa objects by defining app/extend/{application,context,request,response}.js. With this, we can write more utility methods quickly. For example, we have the following code in app/extend/context.js:
// app/extend/context.js
module.exports = {
get isIOS() {
const iosReg = /iphone|ipad|ipod/i;
return iosReg.test(this.get('user-agent'));
},
};
It can be used in controller then:
// app/controller/home.js
exports.handler = function* (ctx) {
ctx.body = this.isIOS
? 'Your operating system is iOS.'
: 'Your operating system is not iOS.';
};
More about extension, please check Exception section.
Plugin
As is known to all, Many middlewares are imported to provide different kind of features in Express and Koa. Eg, koa-session provides the Session support, koa-bodyparser help to parse request body. Egg has provided a powerful plugin mechanism to make it more easy to write stand alone features.
One plugin can include:
- extend:extend the context of base object, provide utility and attributes.
- middleware:add one or more middlewares, provide pre or post processing logic for request.
- config:configure the default value in different environments.
Stand alone module plugin can provide rich features with high maintenancability. You can almost forget the configuration as the plugin supports configuring the default value in different environments.
egg-security is a typical example.
More about plugin, please check plugin section.
Roadmap
Egg 1.x
The Node.js LTS version now does not support async function,so Egg is based on Koa 1.x. On the basis of this, Egg has added full async function support. Egg is completely compatible with middlewares in Koa 2.x, all application layer are implemented based on async function.
- The underlying is based on Koa 1.x, asynchronous solution is based on generator function wrapped by co.
- Official plugin and core of Egg are written in generator function, keep supporting Node.js LTS version, use co when necessary to be compatiable with async function.
- Application developers can choose either async function (Node.js 7.6+) or generator function (Node.js 6.0+), we recommend generator function way for ensuring you application can be runned on Node.js LTS version.
Egg next
Egg will transfer core to Koa 2.x until Node.js LTS supports async function, compatibility with generator function will also be kept.
- The underlying will be based on Koa 2.x, asynchronous solution will be based on async function.
- Official plugin and core of egge will be written in async function.
- Recommend user transfer business layer to async function.
- Node.js 6.x will be no longer supported.