mirror of
https://github.com/yewstack/yew.git
synced 2025-12-08 21:26:25 +00:00
Fix links and add CI checks in documentation (#2595)
* Docs overhaul part2 * fix links and require them for CI * remove translations for 0.17 * remove a bunch of unused documentation * run prettier * fixup links and locations of some translations
This commit is contained in:
parent
6992a454e3
commit
dc60d6099e
@ -45,6 +45,8 @@ If you are a native speaker of one of the translated languages,
|
||||
and you are interested in translating your edits yourself,
|
||||
you are welcome to navigate to the folder and do it yourself!
|
||||
|
||||
### Localizing headings
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to write displayed content in `html/jsx` instead of vanilla markdown,
|
||||
You should wrap your text in `<Translate/>` tags.
|
||||
It helps docusaurus to extract those texts and compile them to `.json` files to
|
||||
@ -54,8 +56,8 @@ get further translated in GitLocalize.
|
||||
import Translate from '@docusaurus/Translate'
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>
|
||||
<Translate id="header.translation.id" description="the header description">
|
||||
This header will be translated
|
||||
<Translate id="header.translation.id" description="the heading description">
|
||||
This heading will be translated
|
||||
</Translate>
|
||||
</h2>
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -63,3 +65,17 @@ import Translate from '@docusaurus/Translate'
|
||||
If your pull request adds new `<Translation>` tags,
|
||||
make sure you do `npm run write-translations` to generate the new stubs for later localization.
|
||||
And you are always welcome to add localization yourself in your native languages!
|
||||
|
||||
### Common issues in localization
|
||||
|
||||
Pages (.mdx) are translated one-to-one and the english text is used as fallback if no translation
|
||||
exists. Sometimes, when building you might see a warning, and subsequent error,
|
||||
like this
|
||||
|
||||
> [WARNING] Docs markdown link couldn't be resolved: (../components/refs.mdx) in
|
||||
> <omitted>/yew/website/versioned_docs/version-0.18.0/concepts/html/events.mdx for version 0.18.0
|
||||
|
||||
This means that the _non-translated_ page at `versioned_docs/version-0.18.0/concepts/html/events.mdx`
|
||||
contains a relative link - `../components/refs.mdx` - to a page that _has_ been translated.
|
||||
Change the link to be relative to the doc root folder, in this case `concepts/components/res.mdx`, or,
|
||||
if you find the time, also translate the offending page.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
const {
|
||||
i18n: { locales },
|
||||
i18n: { defaultLocale, locales },
|
||||
} = require('./docusaurus.config.js')
|
||||
const util = require('util')
|
||||
const exec = util.promisify(require('child_process').exec)
|
||||
@ -9,9 +9,70 @@ const os = require('os')
|
||||
const dircompare = require('dir-compare')
|
||||
const writeTranslations = require('./write-translations.js')
|
||||
|
||||
const temp = fs.mkdtempSync(path.join(os.tmpdir(), 'yew-website-'))
|
||||
const VERSION_NAME_CURRENT = 'current'
|
||||
const VERSIONS = (async () => {
|
||||
const listedFiles = await fs.promises.readdir('versioned_docs', {
|
||||
withFileTypes: true,
|
||||
})
|
||||
return [VERSION_NAME_CURRENT].concat(
|
||||
listedFiles.filter((e) => e.isDirectory()).map((e) => e.name)
|
||||
)
|
||||
})()
|
||||
|
||||
async function main() {
|
||||
async function checkSuperfluousTranslations() {
|
||||
const versions = await VERSIONS
|
||||
let success = true
|
||||
for (const locale of locales) {
|
||||
if (locale === defaultLocale) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (const version of versions) {
|
||||
let isCurrentVersion = version == VERSION_NAME_CURRENT
|
||||
const originDir = isCurrentVersion
|
||||
? 'docs'
|
||||
: path.join('versioned_docs', version)
|
||||
const localeDir = path.join(
|
||||
'i18n',
|
||||
locale,
|
||||
'docusaurus-plugin-content-docs',
|
||||
version
|
||||
)
|
||||
if (
|
||||
!(await fs.promises.access(localeDir, fs.constants.F_OK).then(
|
||||
(_) => true,
|
||||
(_) => false
|
||||
))
|
||||
) {
|
||||
console.warn(
|
||||
`Missing translations for locale ${locale}, version ${version}.`
|
||||
)
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const result = await dircompare.compare(originDir, localeDir)
|
||||
if (!result.diffSet) {
|
||||
throw new Error('Expected diff set')
|
||||
}
|
||||
const superfluous = result.diffSet
|
||||
.filter((e) => e.state === 'right')
|
||||
.map((e) => path.join(e.path2, e.name2))
|
||||
if (superfluous.length > 0) {
|
||||
let severity = isCurrentVersion ? console.error : console.warn
|
||||
severity(
|
||||
`Found superfluous translations for locale ${locale}, version ${version}:`,
|
||||
superfluous
|
||||
)
|
||||
if (isCurrentVersion) success = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return success
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
async function checkWriteTranslations() {
|
||||
const temp = await fs.promises.mkdtemp(
|
||||
path.join(os.tmpdir(), 'yew-website-')
|
||||
)
|
||||
await new Promise((resolve) => {
|
||||
fs.cp('i18n', temp, { recursive: true }, () => {
|
||||
resolve()
|
||||
@ -25,12 +86,26 @@ async function main() {
|
||||
})
|
||||
if (result.same) {
|
||||
console.log('Translations unchanged')
|
||||
return true
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
console.error(
|
||||
'Translations changed, please run `npm run write-translations` to generate the stubs'
|
||||
)
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
async function main() {
|
||||
let okay = true
|
||||
okay &= await checkSuperfluousTranslations()
|
||||
okay &= await checkWriteTranslations()
|
||||
|
||||
if (!okay) {
|
||||
process.exitCode = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
main().catch((e) => console.error(e))
|
||||
main().catch((e) => {
|
||||
console.error(e)
|
||||
process.exitCode = 1
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ Yew uses Virtual DOM to render elements to the DOM. The Virtual DOM tree can be
|
||||
much stricter. It also provides super-powers like conditional rendering and rendering of lists using iterators.
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
[Learn more about the `html!` macro, how it's used and its syntax](./html)
|
||||
[Learn more about the `html!` macro, how it's used and its syntax](concepts/html/introduction.mdx)
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Passing data to a component
|
||||
@ -24,9 +24,9 @@ Yew components use _props_ to communicate between parent and children. A parent
|
||||
its children. Props are similar to HTML attributes but any Rust type can be passed as props.
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
[Learn more about the props](./properties)
|
||||
[Learn more about the props](advanced-topics/struct-components/properties.mdx)
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
For other than parent/child communication, use [contexts](./contexts)
|
||||
For other than parent/child communication, use [contexts](../../concepts/contexts.mdx)
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For usage details, check out [the `html!` guide](../html).
|
||||
For usage details, check out [the `html!` guide](concepts/html/introduction.mdx).
|
||||
|
||||
### Rendered
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,4 +85,4 @@ html! {
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We will introduce Yew and HTML further in depth in [more HTML](../html).
|
||||
We will introduce Yew and HTML further in depth in [more HTML](concepts/html/introduction.mdx).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ without having to pass it down with props.
|
||||
|
||||
## The problem with props: "Prop Drilling"
|
||||
|
||||
Passing [props](./function-components/properties) is a great way to pass data directly from parent to a child.
|
||||
Passing [props](./function-components/properties.mdx) is a great way to pass data directly from parent to a child.
|
||||
They become cumbersome to pass down through deeply nested component tree or when multiple components share the same data.
|
||||
A common solution to data sharing is lifting the data to a common ancestor and making the children take it as props.
|
||||
However, this can lead to cases where the prop has to go through multiple components in order to reach the component needs it.
|
||||
@ -134,13 +134,13 @@ fn App() -> Html {
|
||||
#### Function components
|
||||
|
||||
`use_context` hook is used to consume contexts in function components.
|
||||
See [docs for use_context](function-components/hooks/use-context) to learn more.
|
||||
See [docs for use_context](function-components/hooks/use-context.mdx) to learn more.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Struct components
|
||||
|
||||
We have 2 options to consume contexts in struct components:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Higher Order Components](../advanced-topics/struct-components/hoc): A higher order function component will consume the context and pass the data to the struct component which requires it.
|
||||
- [Higher Order Components](../advanced-topics/struct-components/hoc.mdx): A higher order function component will consume the context and pass the data to the struct component which requires it.
|
||||
- Consume context directly in struct component. See [example of struct component as a consumer](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/master/examples/contexts/src/struct_component_subscriber.rs)
|
||||
|
||||
## Use cases
|
||||
@ -164,7 +164,7 @@ You should refactor the `Layout` component to take children as props and display
|
||||
|
||||
Because of Rust's ownership rules, a context cannot have a method that takes `&mut self` that can be called by children.
|
||||
In order to mutate a context's value, we must combine it with a reducer. This is done by using the
|
||||
[`use_reducer`](./function_component/hooks/use_reducer) hook.
|
||||
[`use_reducer`](./function-components/hooks/use-reducer.mdx) hook.
|
||||
|
||||
The [contexts example](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/master/examples/contexts) demonstrates mutable contexts
|
||||
with the help of contexts
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,12 +36,12 @@ Yew comes with the following predefined Hooks:
|
||||
- [`use_effect`](./use-effect.mdx)
|
||||
- [`use_effect_with_deps`](./use-effect.mdx#use_effect_with_deps)
|
||||
- [`use_context`](./use-context.mdx)
|
||||
- [`use_force_update`](./use-force-update)
|
||||
- [`use_force_update`](./use-force-update.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Hooks
|
||||
|
||||
There are cases where you want to define your own Hooks for reasons. Yew allows you to define your own Hooks which lets you extract your potentially stateful logic from the component into reusable functions.
|
||||
See the [Defining custom hooks](./custom-hooks.mdx#defining-custom-hooks) section for more information.
|
||||
See the [Defining custom hooks](concepts/function-components/hooks/custom-hooks.mdx#defining-custom-hooks) section for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
## Further reading
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
title: 'use_context'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
[Contexts](../contexts.mdx) will be introduced later.
|
||||
[Contexts](../../contexts.mdx) will be introduced later.
|
||||
|
||||
`use_context` is used for consuming [contexts](../contexts.mdx) in function components.
|
||||
`use_context` is used for consuming [contexts](../../contexts.mdx) in function components.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ Components are the building blocks of Yew.
|
||||
|
||||
They:
|
||||
|
||||
- Take arguments in form of [Props](./properties)
|
||||
- Take arguments in form of [Props](./properties.mdx)
|
||||
- Can have their own state
|
||||
- Get computed into HTML visible to the user (DOM)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ They:
|
||||
|
||||
You are currently reading about function components - the recommended way to write components when starting with Yew.
|
||||
|
||||
But we have to note that there is a more advanced, but less recommended way to write them - [Struct components](../advanced-topics/struct-components/introduction)
|
||||
But we have to note that there is a more advanced, but less recommended way to write them - [Struct components](advanced-topics/struct-components/introduction.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## Creating function components
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ Yew integrates with the [`web-sys`](https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-bindgen/api/
|
||||
uses the events from that crate. The [table below](#event-types) lists all of the `web-sys`
|
||||
events that are accepted in the `html!` macro.
|
||||
|
||||
You can still add a [`Callback`](../components/callbacks.mdx) for an event that is not listed in the table
|
||||
You can still add a [`Callback`](../function-components/callbacks.mdx) for an event that is not listed in the table
|
||||
below, see [Manual event listener](#manual-event-listener).
|
||||
|
||||
## Event Types
|
||||
@ -355,7 +355,7 @@ does the cast on the target of the event. `TargetCast::target_unchecked_into` is
|
||||
|
||||
### Using `NodeRef`
|
||||
|
||||
[`NodeRef`](../components/refs) can be used instead of querying the event given to a `Callback`.
|
||||
[`NodeRef`](../function-components/node-refs.mdx) can be used instead of querying the event given to a `Callback`.
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
use web_sys::HtmlInputElement;
|
||||
@ -450,7 +450,7 @@ You may want to listen to an event that is not supported by Yew's `html` macro,
|
||||
[supported events listed here](#event-types).
|
||||
|
||||
In order to add an event listener to one of elements manually we need the help of
|
||||
[`NodeRef`](../components/refs) so that in `use_effect_with_deps` we can add a listener using the
|
||||
[`NodeRef`](../function-components/node-refs.mdx) so that in `use_effect_with_deps` we can add a listener using the
|
||||
[`web-sys`](https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-bindgen/api/web_sys/index.html) and
|
||||
[wasm-bindgen](https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-bindgen/api/wasm_bindgen/index.html) API.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -155,7 +155,7 @@ free to [chime in on this issue](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/issues/1334).
|
||||
There are special properties which don't directly influence the DOM but instead act as instructions to Yew's virtual DOM.
|
||||
Currently, there are two such special props: `ref` and `key`.
|
||||
|
||||
`ref` allows you to access and manipulate the underlying DOM node directly. See [Refs](../components/refs) for more details.
|
||||
`ref` allows you to access and manipulate the underlying DOM node directly. See [Refs](../function-components/node-refs.mdx) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
`key` on the other hand gives an element a unique identifier which Yew can use for optimization purposes.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -179,5 +179,5 @@ html! {
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
Read more at [Conditonal Rendering](./html/conditional-rendering)
|
||||
Read more at [Conditonal Rendering](./conditional-rendering.mdx)
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
@ -131,7 +131,7 @@ unsure what type a certain object is you can try to cast it which returns possib
|
||||
[`Option`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/option/enum.Option.html) and
|
||||
[`Result`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/result/enum.Result.html).
|
||||
|
||||
A common example of this in [`web-sys`](wasm-bindgen/web-sys) is when you are trying to get the
|
||||
A common example of this in [`web-sys`](./web-sys.mdx) is when you are trying to get the
|
||||
target of an event, you might know what the target element is but the
|
||||
[`web_sys::Event`](https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-bindgen/api/web_sys/struct.Event.html) API will always return an [`Option<web_sys::EventTarget>`](https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-bindgen/api/web_sys/struct.Event.html#method.target)
|
||||
so you will need to cast it to the element type. so you can call its methods.
|
||||
@ -178,7 +178,8 @@ raise an exception.
|
||||
|
||||
`Closure` is often used when you are working with a `js-sys` or `web-sys` API that accepts a type
|
||||
[`&js_sys::Function`](https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-bindgen/api/js_sys/struct.Function.html).
|
||||
An example of using a `Closure` in Yew can be found in the [Using `Closure` section](html/events#using-closure-verbose) on the [Events](html/events) page.
|
||||
An example of using a `Closure` in Yew can be found in the [Using `Closure` section](../html/events.mdx#using-closure-verbose)
|
||||
on the [Events](../html/events.mdx) page.
|
||||
|
||||
_[`Closure` documentation](https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-bindgen/api/wasm_bindgen/closure/struct.Closure.html)._
|
||||
|
||||
@ -187,7 +188,7 @@ _[`Closure` documentation](https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-bindgen/api/wasm_bind
|
||||
The `js-sys` crate provides bindings / imports of JavaScript's standard, built-in objects, including
|
||||
their methods and properties.
|
||||
|
||||
This does not include any web APIs as this is what [`web-sys`](wasm-bindgen/web-sys) is for!
|
||||
This does not include any web APIs as this is what [`web-sys`](./web-sys.mdx) is for!
|
||||
|
||||
_[`js-sys` documentation](https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-bindgen/api/js_sys/index.html)._
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ general Rust provides an approach to simulate inheritance in JavaScript. This is
|
||||
|
||||
This section is going to look at a specific element and list out it's inheritance using Rust by
|
||||
calling [`Deref::deref`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/ops/trait.Deref.html#tymethod.deref) until
|
||||
the value is [`JsValue`](../wasm-bindgen#jsvalue):
|
||||
the value is [`JsValue`](../wasm-bindgen/introduction.mdx#jsvalue):
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
use std::ops::Deref;
|
||||
@ -79,8 +79,8 @@ _[Inheritance in `web-sys` in The `wasm-bindgen` Guide](https://rustwasm.github.
|
||||
|
||||
## The `Node` in `NodeRef`
|
||||
|
||||
Yew uses a [`NodeRef`](../components/refs) in order to provide a way for keeping a reference to
|
||||
a `Node` made by the [`html!`](../html/introduction.mdx) macro. The `Node` part of `NodeRef` is referring to
|
||||
Yew uses a [`NodeRef`](concepts/function-components/node-refs.mdx) in order to provide a way for keeping a reference to
|
||||
a `Node` made by the [`html!`](concepts/html/introduction.mdx) macro. The `Node` part of `NodeRef` is referring to
|
||||
[`web_sys::Node`](https://rustwasm.github.io/wasm-bindgen/api/web_sys/struct.Node.html). The
|
||||
`NodeRef::get` method will return a `Option<Node>` value, however, most of the time in Yew you want
|
||||
to cast this value to a specific element so you can use it's specific methods. This casting
|
||||
@ -197,8 +197,8 @@ different types so that you can call it's specific methods.
|
||||
|
||||
### Yew example
|
||||
|
||||
In Yew you will mostly be creating [`Callback`](../components/callbacks)s to use in the
|
||||
[`html!`](../html/introduction) macro so the example is going to use this approach instead of completely copying
|
||||
In Yew you will mostly be creating [`Callback`](concepts/function-components/callbacks.mdx)s to use in the
|
||||
[`html!`](concepts/html/introduction.mdx) macro so the example is going to use this approach instead of completely copying
|
||||
the approach above:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml title=Cargo.toml
|
||||
@ -242,4 +242,4 @@ html! {
|
||||
designed with Rust or even a strong type system in mind, this is where community crates come in to
|
||||
provide abstractions over `web-sys` to provide more idiomatic Rust APIs.
|
||||
|
||||
_[External libraries page](../../more/external-libs)_
|
||||
_[External libraries page](community/external-libs)_
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,14 +66,14 @@ replace with `={$1}`
|
||||
|
||||
## Function components
|
||||
|
||||
[Function components](./../../concepts/function-components/introduction) are a brand new way to write components that
|
||||
[Function components](concepts/function-components/introduction.mdx) are a brand new way to write components that
|
||||
requires less boilerplate than their structural counterpart.
|
||||
|
||||
While this change does not force you to change your codebase, as you migrate from `0.18` to `0.19`, this migration time might present a good opportunity to start using them in your codebase.
|
||||
|
||||
## Struct components lifecycle methods and ctx
|
||||
|
||||
[Struct components](./../../concepts/components/introduction) also received changes to their API.
|
||||
[Struct components](advanced-topics/struct-components/introduction.mdx) also received changes to their API.
|
||||
|
||||
### ShouldRender removed in favor of bool
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ It should only be used for testing the release build during development
|
||||
|
||||
### Serving `index.html` as fallback
|
||||
|
||||
If the application uses the [Yew router](../../router), you must configure the server to return the `index.html` when asked for a file that it does not have.
|
||||
If the application uses the [Yew router](concepts/router.mdx), you must configure the server to return the `index.html` when asked for a file that it does not have.
|
||||
|
||||
An application with Yew router is built as a [Single Page Application (SPA)](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Glossary/SPA). When the user navigates to a URL from within a running client, the router interprets the URL and routes to that page.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -460,10 +460,10 @@ element returned by the `Iterator` with a special `{ for ... }` syntax
|
||||
|
||||
Remember the `use_state` used earlier? That is a special function, called a "hook". Hooks are used to "hook" into
|
||||
lifecycle of a function component and perform actions. You can learn more about this hook, and others
|
||||
[here](concepts/function-components/pre-defined-hooks#use_state)
|
||||
[here](concepts/function-components/hooks/introduction.mdx#pre-defined-hooks)
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
Struct components act differently. See [the documentation](concepts/components/introduction) to learn about those.
|
||||
Struct components act differently. See [the documentation](advanced-topics/struct-components/introduction.mdx) to learn about those.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Fetching data (using external REST API)
|
||||
@ -586,9 +586,9 @@ to learn how to add style sheets.
|
||||
### More libraries
|
||||
|
||||
Our app made use of only a few external dependencies. There are lots of crates out there that can be used.
|
||||
See [external libraries](more/external-libs) for more details.
|
||||
See [external libraries](community/external-libs) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
### Learning more about Yew
|
||||
|
||||
Read our [official documentation](getting-started/introduction). It explains a lot of concepts in much more details.
|
||||
Read our [official documentation](../getting-started/introduction.mdx). It explains a lot of concepts in much more details.
|
||||
To learn more about our the Yew API, see our [API docs](https://docs.rs/yew).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ module.exports = {
|
||||
'Yew is a modern Rust framework for creating multi-threaded front-end web apps with WebAssembly.',
|
||||
url: 'https://yew.rs',
|
||||
baseUrl: '/',
|
||||
onBrokenLinks: 'warn',
|
||||
onBrokenLinks: 'throw',
|
||||
onBrokenMarkdownLinks: 'warn',
|
||||
favicon: 'img/logo.png',
|
||||
organizationName: 'yewstack', // Usually your GitHub org/user name.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Table of contents
|
||||
|
||||
- [はじめに](index.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 始める
|
||||
|
||||
- [プロジェクトの準備](getting-started/project-setup.mdx)
|
||||
- [wasm-pack を使う](getting-started/project-setup/using-wasm-pack.mdx)
|
||||
- [wasm-bindgen を使う](getting-started/project-setup/using-wasm-bindgen.mdx)
|
||||
- [cargo-web を使う](getting-started/project-setup/using-cargo-web.mdx)
|
||||
- [入門用テンプレート](getting-started/starter-templates.mdx)
|
||||
- [サンプルアプリを作る](getting-started/build-a-sample-app.mdx)
|
||||
- [web-sys か stdweb 選ぶ](getting-started/choose-web-library.mdx)
|
||||
- [例から学ぶ](getting-started/examples.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 基本となる概念 <a id="concepts"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
- [html!を使う](concepts/html.mdx)
|
||||
- [リスト](concepts/html/lists.mdx)
|
||||
- [要素](concepts/html/elements.mdx)
|
||||
- [リテラルと式](concepts/html/literals-and-expressions.mdx)
|
||||
- [コンポーネント](concepts/html/components.mdx)
|
||||
- [コンポーネント (Components)](concepts/components.mdx)
|
||||
- [属性 (Properties)](concepts/components/properties.mdx)
|
||||
- [コールバック (Callbacks)](concepts/components/callbacks.mdx)
|
||||
- [参照 (Refs)](concepts/components/refs.mdx)
|
||||
- [Agents](concepts/agents.mdx)
|
||||
- [Services](concepts/services.mdx)
|
||||
- [Format](concepts/services/format.mdx)
|
||||
- [ルータ](concepts/router.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 高度な内容
|
||||
|
||||
- [最適化とベストプラクティス](advanced-topics/optimizations.mdx)
|
||||
- [低レベルなライブラリの中身](advanced-topics/how-it-works.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 更なる内容
|
||||
|
||||
- [CSS](more/css.mdx)
|
||||
- [ロードマップ](more/roadmap.mdx)
|
||||
- [テスト](more/testing.mdx)
|
||||
- [デバッグ](more/debugging.mdx)
|
||||
- [外部ライブラリ](more/external-libs.mdx)
|
||||
@ -1,8 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: How it works
|
||||
description: Low level details about the framework
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 低レベルなライブラリの中身
|
||||
|
||||
コンポーネントのライフサイクルの状態機械、VDOM の異なるアルゴリズム
|
||||
@ -1,187 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Optimizations
|
||||
description: Make your app faster
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 最適化とベストプラクティス
|
||||
|
||||
## neq_assign
|
||||
|
||||
親コンポーネントから props を受け取った際、`change`メソッドが呼ばれます。
|
||||
これはコンポーネントの状態を更新することができるのに加え、コンポーネントが props が変わった際に再レンダリングするかどうかを決める
|
||||
`ShouldRender`という真偽値を返すことができます。
|
||||
|
||||
再レンダリングはコストがかかるもので、もし避けられるのであれば避けるべきです。
|
||||
一般的なルールとして props が実際に変化した際にのみ再レンダリングすれば良いでしょう。
|
||||
以下のコードブロックはこのルールを表しており、props が前と変わったときに`true`を返します。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
use yew::ShouldRender;
|
||||
|
||||
#[derive(PartialEq)]
|
||||
struct ExampleProps;
|
||||
|
||||
struct Example {
|
||||
props: ExampleProps,
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
impl Example {
|
||||
fn change(&mut self, props: ExampleProps) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
if self.props != props {
|
||||
self.props = props;
|
||||
true
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
しかし我々は先に進んでいけます!
|
||||
この 6 行のボイラープレードは`PartialEq`を実装したものにトレイトとブランケットを用いることで 1 行のコードへと落とし込むことができます。
|
||||
[こちら](https://docs.rs/yewtil/*/yewtil/trait.NeqAssign.html)にて`yewtil`クレートの`NewAssign`トレイトを見てみてください。
|
||||
|
||||
## 効果的にスマートポインタを使う
|
||||
|
||||
**注意: このセクションで使われている用語がわからなければ Rust book は
|
||||
[スマートポインタについての章](https://doc.rust-lang.org/book/ch15-00-smart-pointers.html)
|
||||
があり、非常に有用です。**
|
||||
|
||||
再レンダリングの際に props を作るデータを大量にコピーしないために、スマートポインタを用いてデータ自体ではなくデータへの参照だけを
|
||||
コピーできます。
|
||||
props や子コンポーネントで関連するデータに実データではなく参照を渡すと、子コンポーネントでデータを変更する必要がなければ
|
||||
データのコピーを避けることができます。
|
||||
その際、`Rc::make_mut`によって変更したいデータの変更可能な参照を得ることができます。
|
||||
|
||||
これにより、props が変更されたときにコンポーネントが再レンダリングされるかどうかを決めるかで`Component::change`に更なる恩恵があります。
|
||||
なぜなら、データの値を比較する代わりに元々のポインタのアドレス (つまりデータが保管されている機械のメモリの場所) を比較できるためです。
|
||||
2 つのポインターが同じデータを指す場合、それらのデータの値は同じでなければならないのです。
|
||||
ただし、その逆は必ずしも成り立たないことに注意してください!
|
||||
もし 2 つのポインタが異なるのであれば、そのデータは同じである可能性があります。
|
||||
この場合はデータを比較するべきでしょう。
|
||||
|
||||
この比較においては`PartialEq`ではなく`Rc::ptr_eq`を使う必要があります。
|
||||
`PartialEq`は等価演算子`==`を使う際に自動的に使われます。
|
||||
Rust のドキュメントには[`Rc::ptr_eq`についてより詳しく書いてあります](https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/std/rc/struct.Rc.html#method.ptr_eq)。
|
||||
|
||||
この最適化は`Copy`を実装していないデータの型に対して極めて有効なものです。
|
||||
もしデータを簡単に変更できるのであれば、スマートポインタに取り換える必要はありません。
|
||||
しかし`Vec`や`HashMap`、`String`などのような重たいデータの構造体に対してはスマートポインタを使うことで
|
||||
パフォーマンスを改善することができるでしょう。
|
||||
|
||||
この最適化は値がまだ一度も子によって更新されていない場合に極めて有効で、親からほとんど更新されない場合においてもかなり有効です。
|
||||
これにより、`Rc<_>s`が純粋なコンポーネントに対してプロパティの値をラップする良い一手となります。
|
||||
|
||||
## View 関数
|
||||
|
||||
コードの可読性の理由から`html!`の部分を関数へと移植するのは意味があります。
|
||||
これは、インデントを減らすのでコードを読みやすくするだけでなく、良いデザインパターンを産むことにも繋がるのです。
|
||||
これらの関数は複数箇所で呼ばれて書くべきコード量を減らせるため、分解可能なアプリケーションを作ることができるのです。
|
||||
|
||||
## 純粋なコンポーネント
|
||||
|
||||
純粋なコンポーネントは状態を変化せず、ただ中身を表示してメッセージを普通の変更可能なコンポーネントへ渡すコンポーネントのことです。
|
||||
View 関数との違いとして、純粋なコンポーネントは式の構文\(`{some_view_function()}`\)ではなく
|
||||
コンポーネントの構文\(`<SomePureComponent />`\)を使うことで`html!`マクロの中で呼ばれる点、
|
||||
そして実装次第で記憶され (つまり、一度関数が呼ばれれば値は"保存"され、
|
||||
同じ引数でもう一度呼ばれても値を再計算する必要がなく最初に関数が呼ばれたときの保存された値を返すことができる)、
|
||||
先述の`neq_assign`ロジックを使う別々の props で再レンダリングを避けられる点があります。
|
||||
|
||||
Yew は純粋な関数やコンポーネントをサポートしていませんが、外部のクレートを用いることで実現できます。
|
||||
|
||||
## 関数型コンポーネント (a.k.a フック)
|
||||
|
||||
関数型コンポーネントはまだ開発中です!
|
||||
開発状況については[プロジェクトボード](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/projects/3)に詳しく書いてあります。
|
||||
|
||||
## キー付き DOM ノード
|
||||
|
||||
## ワークスペースでコンパイル時間を減らす
|
||||
|
||||
間違いなく Yew を使う上での最大の欠点はコンパイルに時間がかかる点です。
|
||||
プロジェクトのコンパイルにかかる時間は`html!`マクロに渡されるコードの量に関係しています。
|
||||
これは小さなプロジェクトにはそこまで問題ないようですが、大きなアプリではコードを複数クレートに分割することでアプリに変更が加られた際に
|
||||
コンパイラの作業量を減らすのが有効です。
|
||||
|
||||
一つ可能なやり方として、ルーティングとページ洗濯を担当するメインのクレートを作り、それぞれのページに対して別のクレートを作ることです。
|
||||
そうして各ページは異なるコンポーネントか、`Html`を生成する大きな関数となります。
|
||||
アプリの異なる部分を含むクレート同士で共有されるコードはプロジェクト全体で依存する分離したクレートに保存されます。
|
||||
理想的には 1 回のコンパイルでコード全てを再ビルドせずメインのクレートかどれかのページのクレートを再ビルドするだけにすることです。
|
||||
最悪なのは、"共通"のクレートを編集して、はじめに戻ってくることです:
|
||||
共有のクレートに依存している全てのコード、恐らく全てのコードをコンパイルすることです。
|
||||
|
||||
もしメインのクレートが重たすぎる、もしくは深くネストしたページ (例えば別ページのトップでレンダリングされるページ)
|
||||
で速く繰り返したい場合、クレートの例を用いてメインページの実装をシンプルにしたりトップで動かしているコンポーネントをレンダリングできます。
|
||||
|
||||
## バイナリサイズを小さくする
|
||||
|
||||
- Rust のコードを最適化する
|
||||
- `wee_alloc` \( tiny allocator を使用 \)
|
||||
- `cargo.toml` \( release profile を定義 \)
|
||||
- `wasm-opt`を用いて wasm のコードを最適化する
|
||||
|
||||
**注意: バイナリサイズを小さくするのについては[Rust Wasm Book](https://rustwasm.github.io/book/reference/code-size.html#optimizing-builds-for-code-size)に詳しく書いてあります。**
|
||||
|
||||
### wee_alloc
|
||||
|
||||
[wee_alloc](https://github.com/rustwasm/wee_alloc)は小さなアロケーターで、Rust のバイナリで使用される通常のものより遥かに小さなものです。
|
||||
デフォルトのアロケーターと置き換えることで、Wasm ファイルをより小さくすることができ、速度とメモリのオーバーヘッドを軽減できます。
|
||||
|
||||
デフォルトのアロケータを含めないことによるサイズの増加と比較して、速度とメモリのオーバーヘッドが悪くなります。
|
||||
ファイルサイズが小さいことで、ページの読み込みが速くなります。
|
||||
そのため、アロケーションのタスクが非常に多い場合でなければデフォルトのものではなく tiny allocator を利用することが一般的に推奨されています。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// `wee_alloc`を使用する。
|
||||
#[global_allocator]
|
||||
static ALLOC: wee_alloc::WeeAlloc = wee_alloc::WeeAlloc::INIT;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Cargo.toml
|
||||
|
||||
`Cargo.toml`で`[profile.release]`のセクションに設定を書き込むことでリリースビルドを小さくすることが可能です。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
[profile.release]
|
||||
# バイナリに含むコードを少なくする
|
||||
panic = 'abort'
|
||||
# コードベース全体での最適化 ( 良い最適化だがビルドが遅くなる)
|
||||
codegen-units = 1
|
||||
# サイズの最適化( よりアグレッシブに )
|
||||
opt-level = 'z'
|
||||
# サイズの最適化
|
||||
# opt-level = 's'
|
||||
# プログラム全体の分析によるリンク時最適化
|
||||
lto = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### wasm-opt
|
||||
|
||||
更に`wasm`のコードのサイズを最適化することができます。
|
||||
|
||||
The Rust Wasm Book には Wasm バイナリのサイズを小さくすることについてのセクションがあります:
|
||||
[Shrinking .wasm size](https://rustwasm.github.io/book/game-of-life/code-size.html)
|
||||
|
||||
- `wasm-pack`でデフォルトの`wasm`のコードをリリースビルド時に最適化する
|
||||
- `wasm-opt`によって直接`wasm`ファイルを最適化する
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
wasm-opt wasm_bg.wasm -Os -o wasm_bg_opt.wasm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### yew/examples/にある例を小さなサイズでビルドする
|
||||
|
||||
注意: `wasm-pack`は Rust と Wasm のコードへの最適化を組み合わせます。`wasm-bindgen`はこの例では Rust のサイズ最適化を用いていません。
|
||||
|
||||
| 使用したツール | サイズ |
|
||||
| :-------------------------- | :----- |
|
||||
| wasm-bindgen | 158KB |
|
||||
| wasm-bindgen + wasm-opt -Os | 116KB |
|
||||
| wasm-pack | 99 KB |
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考文献:
|
||||
|
||||
- [The Rust Book のスマートポインタに関する章](https://doc.rust-lang.org/book/ch15-00-smart-pointers.html)
|
||||
- [the Rust Wasm Book でのバイナリサイズを小さくすることについて](https://rustwasm.github.io/book/reference/code-size.html#optimizing-builds-for-code-size)
|
||||
- [Rust profiles についてのドキュメント](https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/profiles.html)
|
||||
- [binaryen プロジェクト](https://github.com/WebAssembly/binaryen)
|
||||
@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Agents
|
||||
description: Yew's Actor System
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
エージェントは Angular の[サービス](https://angular.io/guide/architecture-services)に似ており\(ただし依存性インジェクションはありません\)、
|
||||
[アクターモデル](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Actor_model)を提供します。
|
||||
エージェントはコンポーネント階層のどこに位置するかに関わらず、コンポーネント間でメッセージをルーティングしたり、共有状態を作成したり、UI をレンダリングするメインスレッドから計算量の多いタスクをオフロードするために使用することができます。
|
||||
また、Yew アプリケーションがタブをまたいで通信できるようにするためのエージェントのサポートも\(将来的には\)計画されています。
|
||||
|
||||
エージェントが並行に動くように Yew は[web-workers](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Web_Workers_API/Using_web_workers)を使用しています。
|
||||
|
||||
## ライフサイクル
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## エージェントの種類
|
||||
|
||||
### Reaches
|
||||
|
||||
- Context - Context エージェントのインスタンスは、常に最大 1 つ存在します。
|
||||
Bridges は、UI スレッド上で既にスポーンされたエージェントをスポーンするか、接続します。
|
||||
これは、コンポーネントまたは他のエージェント間の状態を調整するために使用することができます。
|
||||
このエージェントに Bridges が接続されていない場合、このエージェントは消滅します。
|
||||
|
||||
- Job - 新しいブリッジごとに UI スレッド上で新しいエージェントをスポーンします。
|
||||
これは、ブラウザと通信する共有されているが独立した動作をコンポーネントの外に移動させるのに適しています。
|
||||
(TODO 確認) タスクが完了すると、エージェントは消えます。
|
||||
|
||||
- Public - Context と同じですが、独自の web worker で動作します。
|
||||
|
||||
- Private - Job と同じですが、独自の web worker で動作します。
|
||||
|
||||
- Global \(WIP\)
|
||||
|
||||
## エージェントとコンポーネントのやり取り
|
||||
|
||||
### Bridges
|
||||
|
||||
Bridge は、エージェントとコンポーネント間の双方向通信を可能にします。
|
||||
また、Bridge はエージェント同士の通信を可能にします。
|
||||
|
||||
### Dispatchers
|
||||
|
||||
Dispatcher は、コンポーネントとエージェント間の一方向通信を可能にします。
|
||||
Dispatcher は、コンポーネントがエージェントにメッセージを送信することを可能にします。
|
||||
|
||||
## オーバーヘッド
|
||||
|
||||
独自の独立した web worker(プライベートとパブリック)にあるエージェントは、送受信するメッセージにシリアライズするオーバーヘッドが発生します。
|
||||
他のスレッドとの通信には[bincode](https://github.com/servo/bincode)を使用するので、関数を呼び出すよりもコストはかなり高くなります。
|
||||
計算コストがメッセージの受け渡しコストを上回る場合を除き、ロジックを UI スレッドエージェント\(Job または Context\)に格納する必要があります。
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考資料
|
||||
|
||||
- [pub_sub](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/master/examples/pub_sub)の例でコンポーネントがどのようにエージェントと通信させているかがわかります。
|
||||
@ -1,198 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Introduction
|
||||
description: Components and their lifecycle hooks
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## コンポーネントとは?
|
||||
|
||||
コンポーネントは Yew を構成するブロックです。
|
||||
コンポーネントは状態を管理し、自身を DOM へレンダリングすることができます。
|
||||
コンポーネントはライフサイクルの機能がある`Component`トレイトを実装することによって作られます。
|
||||
|
||||
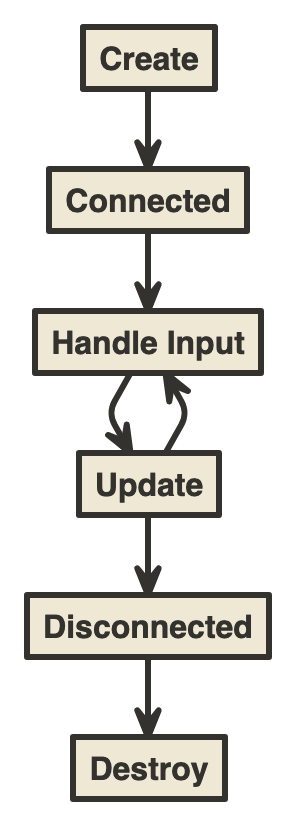
## ライフサイクル
|
||||
|
||||
:::important contribute
|
||||
`Contribute to our docs:` [Add a diagram of the component lifecycle](https://github.com/yewstack/docs/issues/22)
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## ライフサイクルのメソッド
|
||||
|
||||
### Create
|
||||
|
||||
コンポーネントが作られると、`ComponentLink`と同様に親コンポーネントからプロパティを受け取ります。
|
||||
プロパティはコンポーネントの状態を初期化するのに使われ、"link"はコールバックを登録したりコンポーネントにメッセージを送るのに使われます。
|
||||
|
||||
props と link をコンポーネント構造体に格納するのが一般的です。
|
||||
例えば:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub struct MyComponent {
|
||||
props: Props,
|
||||
link: ComponentLink<Self>,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Properties = Props;
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn create(props: Self::Properties, link: ComponentLink<Self>) -> Self {
|
||||
MyComponent { props, link }
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### View
|
||||
|
||||
コンポーネントは`view()`メソッドによってレイアウトを宣言します。
|
||||
Yew は`html!`マクロによって HTML と SVG ノード、リスナー、子コンポーネントを宣言できます。
|
||||
マクロは React の JSX のような動きをしますが、JavaScript の代わりに Rust の式を用います。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
let onclick = self.link.callback(|_| Msg::Click);
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<button onclick=onclick>{ self.props.button_text }</button>
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使い方については[`html!`ガイド](html.mdx)をご確認ください。
|
||||
|
||||
### Rendered
|
||||
|
||||
`rendered()`コンポーネントのライフサイクルのメソッドは`view()`が処理されたて Yew がコンポーネントをレンダリングした後、
|
||||
ブラウザがページを更新する前に呼ばれます。
|
||||
コンポーネントは、コンポーネントが要素をレンダリングした後にのみ実行できるアクションを実行するため、このメソッドを実装したい場合があります。
|
||||
コンポーネントが初めてレンダリングされたかどうかは `first_render` パラメータで確認できます。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
use stdweb::web::html_element::InputElement;
|
||||
use stdweb::web::IHtmlElement;
|
||||
use yew::prelude::*;
|
||||
|
||||
pub struct MyComponent {
|
||||
node_ref: NodeRef,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<input ref=self.node_ref.clone() type="text" />
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn rendered(&mut self, first_render: bool) {
|
||||
if first_render {
|
||||
if let Some(input) = self.node_ref.try_into::<InputElement>() {
|
||||
input.focus();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip note
|
||||
ライフサイクルメソッドは実装の必要がなく、デフォルトでは何もしません。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Update
|
||||
|
||||
コンポーネントは動的で、非同期メッセージを受信するために登録することができます。
|
||||
ライフサイクルメソッド `update()` はメッセージごとに呼び出されます。
|
||||
これにより、コンポーネントはメッセージが何であったかに基づいて自身を更新し、自身を再レンダリングする必要があるかどうかを判断することができます。
|
||||
メッセージは、HTML 要素リスナーによってトリガーされたり、子コンポーネント、エージェント、サービス、または Futures によって送信されたりします。
|
||||
|
||||
`update()`がどのようなのかについての例は以下の通りです:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub enum Msg {
|
||||
SetInputEnabled(bool)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Message = Msg;
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn update(&mut self, msg: Self::Message) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
match msg {
|
||||
Msg::SetInputEnabled(enabled) => {
|
||||
if self.input_enabled != enabled {
|
||||
self.input_enabled = enabled;
|
||||
true // Re-render
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Change
|
||||
|
||||
コンポーネントは親によって再レンダリングされることがあります。
|
||||
このような場合、新しいプロパティを受け取り、再レンダリングを選択する可能性があります。
|
||||
この設計では、プロパティを変更することで、親から子へのコンポーネントの通信が容易になります。
|
||||
|
||||
典型的な実装例は以下の通りです:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn change(&mut self, props: Self::Properties) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
if self.props != props {
|
||||
self.props = props;
|
||||
true
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Destroy
|
||||
|
||||
コンポーネントが DOM からアンマウントされた後、Yew は `destroy()` ライフサイクルメソッドを呼び出し、必要なクリーンアップ操作をサポートします。
|
||||
このメソッドはオプションで、デフォルトでは何もしません。
|
||||
|
||||
## Associated Types
|
||||
|
||||
`Component`トレイトは 2 つの関連型があります: `Message`と`Properties`です。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Message = Msg;
|
||||
type Properties = Props;
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`Message`はコンポーネントによって処理され、何らかの副作用を引き起こすことができるさまざまなメッセージを表します。
|
||||
例えば、API リクエストをトリガーしたり、UI コンポーネントの外観を切り替えたりする `Click` メッセージがあります。
|
||||
コンポーネントのモジュールで `Msg` という名前の列挙型を作成し、それをコンポーネントのメッセージ型として使用するのが一般的です。
|
||||
"message"を"msg"と省略するのも一般的です。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
enum Msg {
|
||||
Click,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`Properties`は、親からコンポーネントに渡される情報を表します。
|
||||
この型は Properties trait を実装していなければならず\(通常はこれを派生させることで\)、特定のプロパティが必須かオプションかを指定することができます。
|
||||
この型は、コンポーネントの作成・更新時に使用されます。
|
||||
コンポーネントのモジュール内に `Props` という構造体を作成し、それをコンポーネントの `Properties` 型として使用するのが一般的です。
|
||||
”Properties”を"props"に短縮するのが一般的です。
|
||||
Props は親コンポーネントから継承されるので、アプリケーションのルートコンポーネントは通常`()`型の`Properties`を持ちます。
|
||||
ルートコンポーネントのプロパティを指定したい場合は、`App::mount_with_props`メソッドを利用します。
|
||||
@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Refs
|
||||
description: Out-of-band DOM access
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
`ref`は、任意の HTML 要素やコンポーネントの内部で、割り当てられている DOM`Element`を取得するために使用することができます。
|
||||
これは、`view` ライフサイクルメソッドの外で DOM に変更を加えるために使用できます。
|
||||
|
||||
これは、キャンバスの要素を取得したり、ページの異なるセクションにスクロールしたりするのに便利です。
|
||||
|
||||
構文は以下の通りです:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// In create
|
||||
self.node_ref = NodeRef::default();
|
||||
|
||||
// In view
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div ref=self.node_ref.clone()></div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// In update
|
||||
let has_attributes = self.node_ref.try_into::<Element>().has_attributes();
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Introduction
|
||||
description: The procedural macro for generating HTML and SVG
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
`html!`マクロによって HTML と SVG のコードを宣言的に書くことができます。
|
||||
JSX \(HTML のようなコードを JavaScript 内部に書くことができる JavaScript の拡張\) に似ています。
|
||||
|
||||
**重要な注意**
|
||||
|
||||
1. `html!`マクロはルートの HTML ノードのみ受け付けます \([フラグメントかイテレータを使う](html/lists.mdx)ことでやり取りできます\)
|
||||
2. 空の`html! {}`の呼び出しは可能ですが何もレンダリングしません
|
||||
3. リテラルはクオーテーションがつけられ、ブレースで囲う必要があります: `html! { "Hello, World" }`
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
`html!`マクロはコンパイラのデフォルトの再帰の上限に簡単に達してしまいます。
|
||||
もしコンパイラエラーに遭遇した場合はその値を押し出すといいかもしれません。
|
||||
クレートのルート\(つまり、`lib.rs`か`main.rs`\)で`#![recursion_limit="1024"]`のような属性を使えば解決します。
|
||||
|
||||
詳しくは[公式ドキュメント](https://doc.rust-lang.org/reference/attributes/limits.html#the-recursion_limit-attribute)と[Stack Overflow の質問](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/27454761/what-is-a-crate-attribute-and-where-do-i-add-it)を見てみてください。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@ -1,105 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Components
|
||||
description: Create complex layouts with component hierarchies
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## 基本
|
||||
|
||||
`Component`を実装しているあらゆる型は`html!`マクロの中で使えます:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html!{
|
||||
<>
|
||||
// No properties
|
||||
<MyComponent />
|
||||
|
||||
// With Properties
|
||||
<MyComponent prop1="lorem" prop2="ipsum" />
|
||||
|
||||
// With the whole set of props provided at once
|
||||
<MyComponent with props />
|
||||
</>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## ネスト
|
||||
|
||||
`children`フィールドが`Properties`の中にある場合はコンポーネントは子に渡されます。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust title="parent.rs"
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<Container>
|
||||
<h4>{ "Hi" }</h4>
|
||||
<div>{ "Hello" }</div>
|
||||
</Container>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```rust title="container.rs"
|
||||
pub struct Container(Props);
|
||||
|
||||
#[derive(Properties, Clone)]
|
||||
pub struct Props {
|
||||
pub children: Children,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for Container {
|
||||
type Properties = Props;
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div id="container">
|
||||
{ self.0.children.clone() }
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
`Properties`を継承した型は`Clone`を実装していなければいけません。
|
||||
これは`#[derive(Properties, Clone)]`を使うか手で`Clone`を実装すれば良いです。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Props とネストした子コンポーネント
|
||||
|
||||
ネストしたコンポーネントのプロパティは格納しているコンポーネントの型が子である場合はアクセス可能、または変更可能です。
|
||||
以下の例では`List`コンポーネントは`ListItem`コンポーネントをラップできています。
|
||||
実際の使用においてこのパターンの例については`yew-router`のソースコードを確認してみてください。
|
||||
より進んだ例としては Yew のメインのリポジトリにある`nested-list`を確認してみてください。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust title="parent.rs"
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<List>
|
||||
<ListItem value="a" />
|
||||
<ListItem value="b" />
|
||||
<ListItem value="c" />
|
||||
</List>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```rust title="list.rs"
|
||||
pub struct List(Props);
|
||||
|
||||
#[derive(Properties, Clone)]
|
||||
pub struct Props {
|
||||
pub children: ChildrenWithProps<ListItem>,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for List {
|
||||
type Properties = Props;
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
html!{{
|
||||
for self.0.children.iter().map(|mut item| {
|
||||
item.props.value = format!("item-{}", item.props.value);
|
||||
item
|
||||
})
|
||||
}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,379 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Elements
|
||||
description: Both HTML and SVG elements are supported
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## タグ構造
|
||||
|
||||
要素のタグは`<... />`のような自己完結タグか、開始タグに対応した終了タグを持っている必要があります。
|
||||
|
||||
<!--DOCUSAURUS_CODE_TABS-->
|
||||
<!--Open - Close-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div id="my_div"></div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--Invalid-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div id="my_div"> // <- MISSING CLOSE TAG
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--Self-closing-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<input id="my_input" />
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--Invalid-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<input id="my_input"> // <- MISSING SELF-CLOSE
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--END_DOCUSAURUS_CODE_TABS-->
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
便利さのために、*普通は*終了タグを必要とする要素は自己完結タグとすることが**できます**。
|
||||
例えば`html! { <div class="placeholder" /> }`と書くのは有効です。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 子
|
||||
|
||||
複雑にネストした HTML や SVG のレイアウトを書くのには以下のようにするのが楽です:
|
||||
\*\*
|
||||
|
||||
<!--DOCUSAURUS_CODE_TABS-->
|
||||
<!--HTML-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<div data-key="abc"></div>
|
||||
<div class="parent">
|
||||
<span class="child" value="anything"></span>
|
||||
<label for="first-name">{ "First Name" }</label>
|
||||
<input type="text" id="first-name" value="placeholder" />
|
||||
<input type="checkbox" checked=true />
|
||||
<textarea value="write a story" />
|
||||
<select name="status">
|
||||
<option selected=true disabled=false value="">{ "Selected" }</option>
|
||||
<option selected=false disabled=true value="">{ "Unselected" }</option>
|
||||
</select>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--SVG-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<svg width="149" height="147" viewBox="0 0 149 147" fill="none" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
|
||||
<path d="M60.5776 13.8268L51.8673 42.6431L77.7475 37.331L60.5776 13.8268Z" fill="#DEB819"/>
|
||||
<path d="M108.361 94.9937L138.708 90.686L115.342 69.8642" stroke="black" stroke-width="4" stroke-linecap="round" stroke-linejoin="round"/>
|
||||
<g filter="url(#filter0_d)">
|
||||
<circle cx="75.3326" cy="73.4918" r="55" fill="#FDD630"/>
|
||||
<circle cx="75.3326" cy="73.4918" r="52.5" stroke="black" stroke-width="5"/>
|
||||
</g>
|
||||
<circle cx="71" cy="99" r="5" fill="white" fill-opacity="0.75" stroke="black" stroke-width="3"/>
|
||||
<defs>
|
||||
<filter id="filter0_d" x="16.3326" y="18.4918" width="118" height="118" filterUnits="userSpaceOnUse" color-interpolation-filters="sRGB">
|
||||
<feGaussianBlur stdDeviation="2"/>
|
||||
<feColorMatrix in="SourceAlpha" type="matrix" values="0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 127 0"/>
|
||||
</filter>
|
||||
</defs>
|
||||
</svg>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--END_DOCUSAURUS_CODE_TABS-->
|
||||
|
||||
## クラス
|
||||
|
||||
要素へのクラスを特定する便利なやり方はたくさんあります:
|
||||
|
||||
<!--DOCUSAURUS_CODE_TABS-->
|
||||
<!--Literal-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div class="container"></div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--Multiple-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div class="container center-align"></div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--Interpolated-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div class=format!("{}-container", size)></div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--Expression-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div class=self.classes()></div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--Tuple-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div class=("class-1", "class-2")></div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--Vector-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div class=vec!["class-1", "class-2"]></div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--END_DOCUSAURUS_CODE_TABS-->
|
||||
|
||||
## リスナー
|
||||
|
||||
リスナー属性はクロージャのラッパーである`Callback`に渡される必要があります。
|
||||
コールバックをどのように作るかはアプリをリスナーイベントにどう反応させたいかによります。
|
||||
|
||||
<!--DOCUSAURUS_CODE_TABS-->
|
||||
<!--Component handler-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
struct MyComponent {
|
||||
link: ComponentLink<Self>,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
enum Msg {
|
||||
Click,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Message = Msg;
|
||||
type Properties = ();
|
||||
|
||||
fn create(_: Self::Properties, link: ComponentLink<Self>) -> Self {
|
||||
MyComponent { link }
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn update(&mut self, msg: Self::Message) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
match msg {
|
||||
Msg::Click => {
|
||||
// Handle Click
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
// Create a callback from a component link to handle it in a component
|
||||
let click_callback = self.link.callback(|_: ClickEvent| Msg::Click);
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<button onclick=click_callback>
|
||||
{ "Click me!" }
|
||||
</button>
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--Agent Handler-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
struct MyComponent {
|
||||
worker: Dispatcher<MyWorker>,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Message = ();
|
||||
type Properties = ();
|
||||
|
||||
fn create(_: Self::Properties, _: ComponentLink<Self>) -> Self {
|
||||
MyComponent {
|
||||
worker: MyWorker::dispatcher()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn update(&mut self, _: Self::Message) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
// Create a callback from a worker to handle it in another context
|
||||
let click_callback = self.worker.callback(|_: ClickEvent| WorkerMsg::Process);
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<button onclick=click_callback>
|
||||
{ "Click me!" }
|
||||
</button>
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--Other Cases-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
struct MyComponent;
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Message = ();
|
||||
type Properties = ();
|
||||
|
||||
fn create(_: Self::Properties, _: ComponentLink<Self>) -> Self {
|
||||
MyComponent
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn update(&mut self, _: Self::Message) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
// Create an ephemeral callback
|
||||
let click_callback = Callback::from(|| {
|
||||
ConsoleService::log("clicked!");
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<button onclick=click_callback>
|
||||
{ "Click me!" }
|
||||
</button>
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--END_DOCUSAURUS_CODE_TABS-->
|
||||
|
||||
## イベントの型
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
以下のテーブルでは`yew`を`web-sys`と使う場合 (デフォルトでは使うようになっている) `web-sys`のイベントの型が使われるべきです。
|
||||
`yew-stdweb`クレートを使う場合は`stdweb`のイベントの型を使用してください。
|
||||
詳細については[`web-sys`と`stdweb`をどちらを使うべきかについてのドキュメント](https://yew.rs/getting-started/choose-web-library)をご確認ください。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
以下のテーブルにある全てのイベントの型は`yew::events`で再エクスポートされています。
|
||||
All the event types mentioned in the following table are re-exported under `yew::events`. Using the types from
|
||||
`yew::events` makes it easier to ensure version compatibility than if you were to manually include `web-sys`
|
||||
or `stdweb` as dependencies in your crate because you won't end up using a version which conflicts with
|
||||
the version Yew specifies.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| イベント名 | `web_sys` イベント型 | `stdweb` イベント型 |
|
||||
| --------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `onabort` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [ResourceAbortEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ResourceAbortEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onauxclick` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [AuxClickEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.AuxClickEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onblur` | [FocusEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.FocusEvent.html) | [BlurEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.BlurEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `oncancel` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `oncanplay` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `oncanplaythrough` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onchange` | [ChangeData](https://docs.rs/yew/latest/yew/events/enum.ChangeData.html) | [ChangeData](https://docs.rs/yew-stdweb/latest/yew_stdweb/events/enum.ChangeData.html) |
|
||||
| `onclick` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [ClickEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ClickEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onclose` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `oncontextmenu` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [ContextMenuEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ContextMenuEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `oncuechange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ondblclick` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [DoubleClickEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DoubleClickEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondrag` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragend` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragEndEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragEndEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragenter` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragEnterEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragEnterEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragexit` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragExitEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragExitEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragleave` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.htmk) | [DragLeaveEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragLeaveEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragover` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragOverEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragOverEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragstart` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragStartEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragStartEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondrop` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragDropEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragDropEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondurationchange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onemptied` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onended` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onerror` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [ResourceErrorEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ResourceErrorEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onfocus` | [FocusEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.FocusEvent.html) | [FocusEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.FocusEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onformdata` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `oninput` | [InputData](https://docs.rs/yew/latest/yew/events/struct.InputData.html) | [InputData](https://docs.rs/yew-stdweb/latest/yew_stdweb/events/struct.InputData.html) |
|
||||
| `oninvalid` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onkeydown` | [KeyboardEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.KeyboardEvent.html) | [KeyDownEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.KeyDownEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onkeypress` | [KeyboardEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.KeyboardEvent.html) | [KeyPressEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.KeyPressEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onkeyup` | [KeyboardEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.KeyboardEvent.html) | [KeyUpEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.KeyUpEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onload` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [ResourceLoadEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ResourceLoadEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onloadeddata` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onloadedmetadata` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onloadstart` | [ProgressEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.ProgressEvent.html) | [LoadStartEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.LoadStartEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmousedown` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseDownEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseDownEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseenter` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseEnterEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseEnterEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseleave` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseLeaveEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseLeaveEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmousemove` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseMoveEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseMoveEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseout` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseOutEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseOutEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseover` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseOverEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseOverEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseup` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseUpEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseUpEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpause` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onplay` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onplaying` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onprogress` | [ProgressEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.ProgressEvent.html) | [ProgressEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ProgressEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onratechange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onreset` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onresize` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [ResizeEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ResizeEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onscroll` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [ScrollEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ScrollEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onsecuritypolicyviolation` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onseeked` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onseeking` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onselect` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onslotchange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [SlotChangeEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.SlotChangeEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onstalled` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onsubmit` | [FocusEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.FocusEvent.html) | [SubmitEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.SubmitEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onsuspend` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ontimeupdate` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ontoggle` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onvolumechange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onwaiting` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onwheel` | [WheelEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.WheelEvent.html) | [MouseWheelEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseWheelEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `oncopy` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `oncut` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onpaste` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onanimationcancel` | [AnimationEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.AnimationEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onanimationend` | [AnimationEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.AnimationEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onanimationiteration` | [AnimationEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.AnimationEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onanimationstart` | [AnimationEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.AnimationEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ongotpointercapture` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [GotPointerCaptureEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.GotPointerCaptureEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onloadend` | [ProgressEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.ProgressEvent.html) | [LoadEndEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.LoadEndEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onlostpointercapture` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [LostPointerCaptureEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.LostPointerCaptureEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointercancel` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerCancelEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerCancelEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerdown` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerDownEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerDownEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerenter` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerEnterEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerEnterEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerleave` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerLeaveEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerLeaveEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerlockchange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [PointerLockChangeEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerLockChangeEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerlockerror` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [PointerLockErrorEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerLockErrorEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointermove` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerMoveEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerMoveEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerout` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerOutEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerOutEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerover` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerOverEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerOverEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerup` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerUpEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerUpEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onselectionchange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [SelectionChangeEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.SelectionChangeEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onselectstart` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onshow` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ontouchcancel` | [TouchEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TouchEvent.html) | [TouchCancel](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.TouchCancel.html) |
|
||||
| `ontouchend` | [TouchEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TouchEvent.html) | [TouchEnd](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.TouchEnd.html) |
|
||||
| `ontouchmove` | [TouchEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TouchEvent.html) | [TouchMove](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.TouchMove.html) |
|
||||
| `ontouchstart` | [TouchEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TouchEvent.html) | [TouchStart](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.TouchStart.html) |
|
||||
| `ontransitioncancel` | [TransitionEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TransitionEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ontransitionend` | [TransitionEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TransitionEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ontransitionrun` | [TransitionEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TransitionEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ontransitionstart` | [TransitionEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TransitionEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Lists
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## フラグメント
|
||||
|
||||
`html!`マクロは常にルートノードが 1 つであることを要求します。
|
||||
この制限のために、空のタグを使って内容をラップすると良いでしょう。
|
||||
|
||||
<!--DOCUSAURUS_CODE_TABS-->
|
||||
<!--Valid-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<>
|
||||
<div></div>
|
||||
<p></p>
|
||||
</>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--Invalid-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
/* error: only one root html element allowed */
|
||||
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div></div>
|
||||
<p></p>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--END_DOCUSAURUS_CODE_TABS-->
|
||||
|
||||
## イテレータ
|
||||
|
||||
Yew はイテレータから HTML をビルドするのに 2 つの方法をサポートしています。
|
||||
|
||||
<!--DOCUSAURUS_CODE_TABS-->
|
||||
<!--Syntax Type 1-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<ul class="item-list">
|
||||
{ self.props.items.iter().map(renderItem).collect::<Html>() }
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--Syntax Type 2-->
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<ul class="item-list">
|
||||
{ for self.props.items.iter().map(renderItem) }
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--END_DOCUSAURUS_CODE_TABS-->
|
||||
@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Literals and Expressions
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## リテラル
|
||||
|
||||
式が`Display`を実装した型を解決する場合、文字列に変換されて DOM に[Text](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Text)ノードとして挿入されます。
|
||||
|
||||
テキストは式として処理されるため、全ての表示される内容は`{}`ブロックによって囲まれる必要があります。
|
||||
これは Yew のアプリと通常の HTML の構文で最も異なる点です。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
let text = "lorem ipsum";
|
||||
html!{
|
||||
<>
|
||||
<div>{text}</div>
|
||||
<div>{"dolor sit"}</div>
|
||||
<span>{42}</span>
|
||||
</>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 式
|
||||
|
||||
HTML に`{}`ブロックを使って式を挿入することができます。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
{
|
||||
if show_link {
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<a href="https://example.com">{"Link"}</a>
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
html! {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
式を関数やクロージャに分離するのはコードの可読性の観点から有効なことがあります。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
let show_link = true;
|
||||
let maybe_display_link = move || -> Html {
|
||||
if show_link {
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<a href="https://example.com">{"Link"}</a>
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
html! {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div>{maybe_display_link()}</div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,95 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Router
|
||||
description: Yew's official router
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
[crates.io にあるルータ](https://crates.io/crates/yew-router)
|
||||
|
||||
シングルページアプリケーション\(SPA\)におけるルータは URL よってページを出し分けます。
|
||||
リンクがクリックされたときに異なるリソースを要求するというデフォルトの動作の代わりに、ルータはアプリケーション内の有効なルートを指すように URL をローカルに設定します。
|
||||
ルータはこの変更を検出してから、何をレンダリングするかを決定します。
|
||||
|
||||
## コアとなる要素
|
||||
|
||||
### `Route`
|
||||
|
||||
URL 内のドメインの後のすべてを表す文字列と、オプションで history API に保存されている状態を含みます。
|
||||
|
||||
### `RouteService`
|
||||
|
||||
ブラウザとやりとりしてルーティングを決めます。
|
||||
|
||||
### `RouteAgent`
|
||||
|
||||
RouteService を所有し、ルートが変更された際の更新を調整するために使用します。
|
||||
|
||||
### `Switch`
|
||||
|
||||
`Switch`トレイトは`Route`をトレイトの実装する側の間で変換するために用いられます。
|
||||
|
||||
### `Router`
|
||||
|
||||
Router コンポーネントは RouteAgent とやり取りし、エージェントがどうスイッチするか Routes を自動的に解決します。
|
||||
これは、結果として得られるスイッチがどのように Html に変換されるかを指定できるようにするため、props を介して公開されます。
|
||||
|
||||
## ルータをどのように使うか
|
||||
|
||||
まず、アプリケーションのすべての状態を表す型を作成します。
|
||||
これは通常は列挙型ですが、構造体もサポートされており、`Switch` を実装した他のアイテムを内部に入れ子にすることができることに注意してください。
|
||||
|
||||
次に、`Switch`を型に継承させなければいけません。
|
||||
列挙型の場合は全ての variant は`#[to = "/some/route"]`とアノテーションされている必要があり、代わり構造体を用いている場合は構造体宣言が外部から見えるようにしてなければいけません。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
#[derive(Switch)]
|
||||
enum AppRoute {
|
||||
#[to="/login"]
|
||||
Login,
|
||||
#[to="/register"]
|
||||
Register,
|
||||
#[to="/delete_account"]
|
||||
Delete,
|
||||
#[to="/posts/{id}"]
|
||||
ViewPost(i32),
|
||||
#[to="/posts/view"]
|
||||
ViewPosts,
|
||||
#[to="/"]
|
||||
Home
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
`Switch`用の派生マクロによって生成された実装は、各 variant を最初から最後までの順にマッチさせようとするので、指定した`to`アノテーションのうち 2 つのルートにマッチする可能性がある場合は、最初のルートがマッチし、2 つ目のルートは試行されないことに注意してください。例えば、以下の`Switch`を定義した場合、マッチするルートは`AppRoute::Home`だけになります。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
#[derive(Switch)]
|
||||
enum AppRoute {
|
||||
#[to="/"]
|
||||
Home,
|
||||
#[to="/login"]
|
||||
Login,
|
||||
#[to="/register"]
|
||||
Register,
|
||||
#[to="/delete_account"]
|
||||
Delete,
|
||||
#[to="/posts/{id}"]
|
||||
ViewPost(i32),
|
||||
#[to="/posts/view"]
|
||||
ViewPosts,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
また、`#[to = ""]`アノテーションの中で`{}`のバリエーションを使ってセクションをキャプチャすることもできます。
|
||||
`{}`は、次の区切り文字\(コンテキストに応じて "/", "?", "&", "#" のいずれか\) までのテキストをキャプチャします。
|
||||
`{*}`は、次の文字が一致するまでテキストをキャプチャすることを意味します。
|
||||
`{<number>}`は、指定した数の区切り文字が見つかるまでテキストをキャプチャすることを意味します
|
||||
\(例: `{2}`は区切り文字が 2 つ見つかるまでキャプチャします\)。
|
||||
|
||||
名前付きフィールドを持つ構造体や列挙型の場合は、キャプチャグループ内で以下のようにフィールドの名前を指定する必要があります。
|
||||
`{user_name}` または `{*:age}` のように、キャプチャグループ内でフィールドの名前を指定しなければなりません。
|
||||
|
||||
Switch トレイトは文字列よりも構造化されたキャプチャグループで動作します。
|
||||
`Switch`を実装した任意の型を指定することができます。
|
||||
そのため、キャプチャグループが `usize` であることを指定することができ、URL のキャプチャ部分がそれに変換できない場合、variant はマッチしません。
|
||||
@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Introduction
|
||||
description: Yew's glue to browser APIs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# サービス
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
このセクションはまだ WIP です。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Format
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
:::important contribute
|
||||
`Contribute to our docs:` [Explain the format module in depth](https://github.com/yewstack/docs/issues/24)
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Build a sample app
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
はじめに、Rust の新規ライブラリを作りましょう(**重要:** `--lib`フラグを渡すことで*バイナリ*ではなく*ライブラリ*を作ってください)
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo new --lib yew-app && cd yew-app
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
依存ライブラリに`yew`と`wasm-bindgen`を追加してください \(最新バージョンについては[こちら](https://docs.rs/yew)を参照してください\)
|
||||
|
||||
```toml title="Cargo.toml"
|
||||
[package]
|
||||
name = "yew-app"
|
||||
version = "0.1.0"
|
||||
authors = ["Yew App Developer <name@example.com>"]
|
||||
edition = "2018"
|
||||
|
||||
[lib]
|
||||
crate-type = ["cdylib", "rlib"]
|
||||
|
||||
[dependencies]
|
||||
yew = "0.17"
|
||||
wasm-bindgen = "0.2"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
以下のテンプレートを `src/lib.rs`ファイルにコピーしてください:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust title="src/lib.rs"
|
||||
use wasm_bindgen::prelude::*;
|
||||
use yew::prelude::*;
|
||||
|
||||
struct Model {
|
||||
link: ComponentLink<Self>,
|
||||
value: i64,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
enum Msg {
|
||||
AddOne,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for Model {
|
||||
type Message = Msg;
|
||||
type Properties = ();
|
||||
fn create(_: Self::Properties, link: ComponentLink<Self>) -> Self {
|
||||
Self {
|
||||
link,
|
||||
value: 0,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn update(&mut self, msg: Self::Message) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
match msg {
|
||||
Msg::AddOne => self.value += 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn change(&mut self, _props: Self::Properties) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
// Should only return "true" if new properties are different to
|
||||
// previously received properties.
|
||||
// This component has no properties so we will always return "false".
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<button onclick=self.link.callback(|_| Msg::AddOne)>{ "+1" }</button>
|
||||
<p>{ self.value }</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#[wasm_bindgen(start)]
|
||||
pub fn run_app() {
|
||||
App::<Model>::new().mount_to_body();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
このテンプレートはルートに`Component`をセットアップし、`Model`と呼ばれるクリックしたら更新するボタンを作ります。
|
||||
`main()`の中にある`App::<Model>::new().mount_to_body()`がアプリをスタートしてページの`<body>`タグをマウントすることに特に注意してください。
|
||||
動的なプロパティでアプリをスタートしたい場合は代わりに`App::<Model>::new().mount_to_body_with_props(..)`を使うことで実現できます。
|
||||
|
||||
最後に、アプリの中の`static`という名前のフォルダに`index.html`ファイルを追加してください。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mkdir static
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```markup title="index.html"
|
||||
<!doctype html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="utf-8">
|
||||
<title>Yew Sample App</title>
|
||||
<script type="module">
|
||||
import init from "./wasm.js"
|
||||
init()
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
<body></body>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## アプリを動かす!
|
||||
|
||||
[`wasm-pack`](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/)を使うのがアプリを動かすのに推奨される方法です。
|
||||
まだ`wasm-pack`をインストールしていない場合、`cargo install wasm-pack`でインストールして開発サーバーを動かしてみましょう:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
wasm-pack build --target web --out-name wasm --out-dir ./static
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`wasm-pack`はコンパイルされた WebAssembly と JavaScript ラッパーをまとめたものを`./static`ディレクトリに作り、
|
||||
アプリの WebAssembly バイナリを読み込んで動かします。
|
||||
|
||||
そして、`./static`以下で好きなサーバーをファイルをサーブしてみましょう。
|
||||
例えば:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo +nightly install miniserve
|
||||
miniserve ./static --index index.html
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,148 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Choosing a web library
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## はじめに
|
||||
|
||||
Yew アプリは[`web-sys`](https://docs.rs/web-sys)か[`stdweb`](https://docs.rs/stdweb)で作ることができます。
|
||||
これらのクレートは Rust と Web API のバインディングを提供しています。
|
||||
Cargo の依存クレートに`yew`を追加する際はどちらかを選ばなければいけません:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
# Choose `web-sys`
|
||||
yew = "0.17"
|
||||
|
||||
# Choose `stdweb`
|
||||
yew = { version = "0.17", package = "yew-stdweb" }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[Rust / Wasm 活動チーム](https://rustwasm.github.io/)のサポートがある`web-sys`が推奨です。
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用例
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// web-sys
|
||||
let window: web_sys::Window = web_sys::window().expect("window not available");
|
||||
window.alert_with_message("hello from wasm!").expect("alert failed");
|
||||
|
||||
// stdweb
|
||||
let window: stdweb::web::Window = stdweb::web::window();
|
||||
window.alert("hello from wasm!");
|
||||
|
||||
// stdweb with js! macro
|
||||
use stdweb::js;
|
||||
use stdweb::unstable::TryFrom;
|
||||
use stdweb::web::Window;
|
||||
|
||||
let window_val: stdweb::Value = js!{ return window; }; // <- JS syntax inside!
|
||||
let window = Window::try_from(window_val).expect("conversion to window failed");
|
||||
window.alert("hello from wasm!");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2 つのクレートの API はわずかに異なりますが、だいたい同じ目的で似た機能が提供されています。
|
||||
|
||||
## 一方を選ぶ
|
||||
|
||||
アプリに`web-sys`と`stdweb`のどちらを選ぶかにおいてはいくつかの見方があります。
|
||||
注意として、一つのアプリに両方を用いることができるのですが、クレートをコンパイルした際にバイナリのサイズを小さくするには
|
||||
一方だけを使用するのが良いです。
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}></th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>web-sys</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>stdweb</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>プロジェクトの進捗状況</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/">Rust / Wasm 活動チーム</a>
|
||||
により活発にメンテナンスされている
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>GitHubで8ヶ月間動きなし</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>Web API のカバー</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
RustのAPIはWeb IDLスペックから自動的に生成される。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Browser APIはコミュニティにより追加。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>RustのAPIのデザイン</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
ほとんどのAPIコールおいて<code>Result</code>
|
||||
が返ってくるよう保守的なアプローチがとられている。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
しばしば<code>Result</code>
|
||||
を返さずpanicするようになっている。例えば <code>
|
||||
stdweb::web::window()
|
||||
</code>
|
||||
ワーカーの中で呼ばれるパニックする。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
サポートされているビルドツール
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<p></p>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm-bindgen</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm-pack</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<p></p>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>cargo-web</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm-bindgen</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm-pack</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポートされているターゲット</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>asmjs-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Examples
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Yew のリポジトリは[例](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/v0.17/examples)がたくさんあります
|
||||
\(メンテナンス状況は様々\)。
|
||||
様々なフレームワークの機能の使い方を知るのにはそれらの例に取り組むのを勧めます。
|
||||
プルリクエストや Issue はウェルカムです。
|
||||
|
||||
- [**Todo アプリ** ](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/v0.17/examples/todomvc)
|
||||
- [**カスタムコンポーネント**](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/v0.17/examples/custom_components)
|
||||
- [**マルチスレッド\(エージェント\)**](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/v0.17/examples/multi_thread)
|
||||
- [**タイマーサービス**](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/v0.17/examples/timer)
|
||||
- [**ネストしたコンポーネント**](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/v0.16.0/examples/nested_list)
|
||||
@ -1,188 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Introduction
|
||||
description: Set yourself up for success
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 始める
|
||||
|
||||
## Rust
|
||||
|
||||
まずはじめに Rust が必要です。Rust とビルドツールの`cargo`をインストールするために、以下の[公式サイト](https://www.rust-lang.org/tools/install)
|
||||
を見てください。
|
||||
|
||||
## **Wasm ビルドツール**
|
||||
|
||||
WebAssembly と JavaScript の互換を持たせるために他にツールが必要です。さらに、選んだツールに応じてブラウザでアプリから`.wasm`ファイルを実行するのに
|
||||
必要な JavaScript ラッパーのコードを生成し、これによってデプロイやパッケージ化での頭痛の種を軽減させるのに役立ちます。
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`wasm-pack`**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/)
|
||||
|
||||
Rust / Wasm 活動チームによって開発されている CLI ツールで、WebAssembly をパッケージ化することができます。
|
||||
Webpack には[`wasm-pack-plugin`](https://github.com/wasm-tool/wasm-pack-plugin)が最もよく使われています。
|
||||
|
||||
[`wasm-pack`で始める](project-setup/using-wasm-pack.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`wasm-bindgen`**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/)
|
||||
|
||||
Rust/Wasm 活動チームによって開発されているライブラリと CLI ツールで、JS / WebAssembly の互換性を持たせるための低レベルなツールです
|
||||
(`wasm-pack`で内部的に使われています)。
|
||||
`wasm-bindgen`は手書きの JavaScript で WebAssembly のバイナリを使う必要があるため、直接使うのは非推奨です。
|
||||
しかし、詳細な情報については[**`wasm-bindgen` ガイド**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/)から得られます。
|
||||
|
||||
[`wasm-bindgen`で始める。](project-setup/using-wasm-bindgen.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`cargo-web`**](https://github.com/koute/cargo-web)
|
||||
|
||||
`wasm-pack`と`wasm-bindgen`を導入する前は好まれた Web ワークフローツールです。
|
||||
`wasm-pack`がサポートされていないサンプルを動かすのにインストールする価値があり、依然として**最もお手軽に**始められる方法です。
|
||||
|
||||
[`cargo web`で始める](project-setup/using-cargo-web.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
### 比較
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}></th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>wasm-pack</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>wasm-bindgen</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>cargo-web</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>プロジェクトの進行状況</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/">Rust / Wasm活動チーム</a>
|
||||
により活発にメンテナンス
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/">Rust / Wasm 活動チーム</a>
|
||||
により活発にメンテナンス
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
6ヶ月間GitHubでの活発な活動無し
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>開発体験</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
ほぼ大丈夫! <code>webpack</code>があればなお良い。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
だいたい大丈夫。開発においては少し流れを書かないといけない。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
しっかり動く!完結していて、外部ライブラリに頼る必要無し。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>ローカルサーバー</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>webpack</code>プラグインによるサポートあり
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポート無し</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポートあり</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
ローカル環境での変更による自動再ビルド
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>webpack</code>プラグインによるサポートあり
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポート無し</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポートあり</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>ヘッドレスブラウザテスト</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/commands/test.html">
|
||||
サポートあり
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/wasm-bindgen-test/index.html">
|
||||
サポートあり
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/koute/cargo-web#features">
|
||||
サポートあり
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポートされているターゲット</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>asmjs-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>web-sys</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性無し</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>stdweb</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>使用例</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/yewstack/yew-wasm-pack-minimal">
|
||||
入門用テンプレート
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Yewで
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/yewstack/yew/blob/master/examples/build.sh">
|
||||
作る例
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Yewで
|
||||
<a href="https://www.github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/master/packages/yew-stdweb/examples">
|
||||
作る例
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Using cargo-web
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Cargo web はクライアント Web アプリを作るための Cargo サブコマンドです。
|
||||
これにより Web アプリのビルドとデプロイを驚くほど簡単にできます。
|
||||
そして同時に Emscripten がターゲットなのを唯一サポートしているツールチェーンです。
|
||||
詳しくは[こちら](https://github.com/koute/cargo-web)。
|
||||
|
||||
**インストール**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo install cargo-web
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## ビルド
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo web build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 動かす
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo web start
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## サポートされているターゲット
|
||||
|
||||
- `wasm32-unknown-unknown`
|
||||
- `wasm32-unknown-emscripten`
|
||||
- `asmjs-unknown-emscripten`
|
||||
|
||||
:::注意
|
||||
`*-emscripten`をターゲットにする場合、Emscripten SDK をインストールする必要があります。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@ -1,51 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Using wasm-bindgen
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## インストール
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo install wasm-bindgen-cli
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## ビルド
|
||||
|
||||
はじめに、Wasm ファイルを生成するアプリをビルドしましょう。
|
||||
[サンプルアプリをビルド](../build-a-sample-app.md)のアプリをビルドしたいとします。
|
||||
生成されたファイルのパスは`target/wasm32-unknown-unknown/debug/yew-app.wasm`にあるはずです。
|
||||
もしクレートに何か別の名前をつけた場合、Wasm ファイルの名前は`yew-app.wasm`ではなく、`Cargo.toml`ファイルに
|
||||
`package.name`として名前をつけたものになるでしょう。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo build --target wasm32-unknown-unknown
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
次に、wasm-bindgen の CLI を動かしましょう。
|
||||
このコマンドは`--out-dir`のディレクトリにいくつかのファイルを生成し、その中には Wasm バイナリを読み込んで動かすための
|
||||
コンパイルされた WebAssembly と JavaScript のラッパーが入っています。
|
||||
現在のブラウザは直接 WebAssembly ファイルを読み込むことができないため、代わりに JavaScript 経由で読み込まれるなければならず、
|
||||
そのためにこれらのラッパーが必要となります。
|
||||
[サンプルアプリを作る(../build-a-sample-app.md)の例では`static`フォルダにファイルが生成されるようにしており
|
||||
(そのために`wasm-bindgen`へ`--out-dir static`と渡す必要があります)、
|
||||
`wasm.js`と`wasm_bg.wasm`という名前になります(`wasm-bindgen`へ`--out-name wasm`と渡すことで実現できます)
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
wasm-bindgen --target web --out-dir static --out-name wasm target/wasm32-unknown-unknown/debug/appname.wasm --no-typescript
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## アプリをサーブする
|
||||
|
||||
好きなサーバーを使ってください。
|
||||
ここではシンプルな Python のサーバーを使います。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m http.server 8000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## サポートされているターゲット
|
||||
|
||||
- `wasm32-unknown-unknown`
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考ドキュメント
|
||||
|
||||
- [The `wasm-bindgen` docs](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/)
|
||||
@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Using wasm-pack
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
このツールは Rust / Wasm 活動チームによって開発され、WebAssembly のアプリを作るのに使われれるツールで最も活発に開発されているものです。
|
||||
コードを`npm`モジュールへパッケージ化するのをサポートし、既存の JavaScript のアプリと簡単に統合できる
|
||||
[Webpack plugin](https://github.com/wasm-tool/wasm-pack-plugin)がついています。
|
||||
詳しい情報は[the `wasm-pack` documentation](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/introduction.html)にあります。
|
||||
|
||||
:::注意
|
||||
`wasm-pack`を使う際は`Cargo.toml`の crate-type は`cdylib`である必要があります。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## インストール
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo install wasm-pack
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## ビルド
|
||||
|
||||
このコマンドは JavaScript ラッパーとアプリの WebAssembly をまとめたものを`./pkg`ディレクトリに生成し、アプリをスタートすることができます。
|
||||
This command will produce a bundle in the `./pkg` directory with your app's compiled WebAssembly
|
||||
along with a JavaScript wrapper which can be used to start your application.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
wasm-pack build --target web
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## バンドル
|
||||
|
||||
ロールアップにについては詳しくは[ガイド](https://rollupjs.org/guide/en/#quick-start)をご覧ください。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
rollup ./main.js --format iife --file ./pkg/bundle.js
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## サーブ
|
||||
|
||||
好きなサーバーを使ってください。
|
||||
ここではシンプルな Python のサーバーを使ってアプリをサーブします。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m http.server 8000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## サポートされているターゲット
|
||||
|
||||
- `wasm32-unknown-unknown`
|
||||
@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Starter templates
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## `wasm-pack`
|
||||
|
||||
- [ミニマルテンプレート](https://github.com/yewstack/yew-wasm-pack-minimal) - アプリをビルドするのに `wasm-pack`と
|
||||
|
||||
`rollup`を使い、サーバーはアプリをサーブします. ベルや笛はここにはありません。
|
||||
|
||||
- [Webpack テンプレート](https://github.com/yewstack/yew-wasm-pack-template) - `wasm-pack`と
|
||||
|
||||
[`wasm-pack-plugin`](https://github.com/wasm-tool/wasm-pack-plugin)を使い、Webpack が開発を滑らかにします。
|
||||
|
||||
これらのテンプレートを使うのと`cargo-web`を使用するのと重要な違いは、このアプローチは`bin`クレートではなく`lib`クレートを用いて
|
||||
`#[wasm_bindgen]`によってエントリーポイントを指定できる点です。
|
||||
|
||||
また、`Cargo.toml`はクレートの種類が"cdylib"であると特定できるようにしましょう。
|
||||
|
||||
```text title="Cargo.toml"
|
||||
[package]
|
||||
name = "yew-app"
|
||||
version = "0.1.0"
|
||||
authors = ["Yew App Developer <name@example.com>"]
|
||||
edition = "2018"
|
||||
|
||||
[lib]
|
||||
crate-type = ["cdylib"]
|
||||
|
||||
[dependencies]
|
||||
# for web_sys
|
||||
yew = "0.17"
|
||||
# or for stdweb
|
||||
# yew = { version = "0.17", package = "yew-stdweb" }
|
||||
wasm-bindgen = "0.2"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## その他のテンプレート
|
||||
|
||||
- [Parcel Template](https://github.com/spielrs/yew-parcel-template) - コミュニティのメンバーによって開発され、
|
||||
Parcel](https://parceljs.org/)を使っています。
|
||||
@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: CSS
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# CSS
|
||||
|
||||
<TODO>
|
||||
|
||||
統合的な CSS サポートについての提案はこちらにあります: [https://github.com/yewstack/yew/issues/533](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/issues/533)
|
||||
|
||||
## スタイルフレームワーク:
|
||||
|
||||
今のところ、コミュニティメンバーは以下のスタイルフレームワークを開発しています。
|
||||
|
||||
- [yew_styles](https://github.com/spielrs/yew_styles) - JavaScript に依存しない Yew のスタイルフレームワーク
|
||||
- [yew-mdc](https://github.com/Follpvosten/yew-mdc) - マテリアルデザインのコンポーネント
|
||||
- [muicss-yew](https://github.com/AlephAlpha/muicss-yew) - MUI の CSS コンポーネント
|
||||
- [Yewtify](https://github.com/yewstack/yewtify) – Yew で Vuetify フレームワークで提供されている機能の実装
|
||||
@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Debugging
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# デバッグ
|
||||
|
||||
## パニック
|
||||
|
||||
Rust シンボルで良いスタックトレースをするには
|
||||
[`console_error_panic`](https://github.com/rustwasm/console_error_panic_hook)クレートを使用してください。
|
||||
注意として、`cargo-web`でビルドされたものとは互換性がありません。
|
||||
|
||||
## コンソールでのログ
|
||||
|
||||
一般的に、Wasm の Web アプリはブラウザの API と連携することができ、`console.log`の API も例外ではありません。
|
||||
いつくかの選択肢があります:
|
||||
|
||||
### [`wasm-logger`](https://crates.io/crates/wasm-logger)
|
||||
|
||||
このクレートは Rust の`log`クレートと親和性があります。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// セットアップ
|
||||
fn main() {
|
||||
wasm_logger::init(wasm_logger::Config::default());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 使用方法
|
||||
log::info!("Update: {:?}", msg);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### [`ConsoleService`](https://docs.rs/yew/latest/yew/services/console/struct.ConsoleService.html)
|
||||
|
||||
このサービスは Yew に含まれており、`"services"`の機能が有効化されている場合は利用可能です。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// 使用方法
|
||||
ConsoleService::info(format!("Update: {:?}", msg).as_ref());
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## ソースマップ
|
||||
|
||||
今のところは Rust/Wasm の Web アプリにはソースマップへの第一級のサポートがありません。
|
||||
もちろん、これは変更される可能性があります。これが当てはまらない場合、または進捗が見られる場合は、変更を提案してください!
|
||||
|
||||
### 最新情報
|
||||
|
||||
\[2019 年 12 月\] [Chrome DevTools update](https://developers.google.com/web/updates/2019/12/webassembly#the_future)
|
||||
|
||||
> やらなければいけないことがまだたくさんあります。例えばツール側では Emscripten\(Binaryen\)と wasm-pack\(wasm-bindgen\)がそれらが実行する変換に関する DWARF 情報の更新をまだサポートしていません。
|
||||
|
||||
\[2020\] [Rust Wasm デバッグガイド](https://rustwasm.github.io/book/reference/debugging.html#using-a-debugger)
|
||||
|
||||
> 残念なことに、WebAssembly のデバッグの物語はまだ未成熟です。ほとんどの Unix のシステムでは[DWARF](http://dwarfstd.org/)は実行中のプログラムをソースレベルで検査するためにデバッガに必要な情報をエンコードするために使用されます。Windows には同様の情報をエンコードする代替形式があります。現在、WebAssembly に相当するものはありません。
|
||||
|
||||
\[2019\] [Rust Wasm ロードマップ](https://rustwasm.github.io/rfcs/007-2019-roadmap.html#debugging)
|
||||
|
||||
> デバッグはトリッキーです。なぜなら、多くの話はこの活動チームの手の届かないところにあり、WebAssembly の標準化団体とブラウザ開発者ツールを実装している人たちの両方に依存しているからです。
|
||||
@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: External libraries
|
||||
description: Libraries that can help with yew development
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 外部ライブラリ
|
||||
|
||||
### Yewtil
|
||||
|
||||
Yewtil は Yew のプログラムを書きやすくするユーティリティ集です。
|
||||
含まれているのは:
|
||||
|
||||
- NeqAssign - 先述の通り、再レンダリングを最小化するよう props を割り当てる方法です
|
||||
- PureComponents - 状態を更新しないコンポーネント。NeqAssign を使用するとマクロの中から通常のコンポーネントのように呼び出される関数がメモ化されます。
|
||||
|
||||
- Lrc - リンクされたリストは、`Rc`のようにカウントされたスマートポインタ関数を参照しますが、新しいデータ更新パターンを可能にします。
|
||||
- Mrc/Irc - Mutable/Immutable 参照カウントのスマートポインタは `Rc` のように機能しますが、`Mrc` に対して `DerefMut` と `BorrowMut` を実装しているため、Yew の中でより使いやすくなっています。これにより、`Mrc` を `NeqAssign` と一緒に使うことができます。`Irc` はデータに対する不変のビューとして機能するので、表示のみのタスクで使用されるデータを保持するのに理想的です。
|
||||
|
||||
- History - `VecDeque` を用いて、表示した過去の値を保持する履歴追跡ラッパーです。
|
||||
- Futures - コンポーネントの更新ループにメッセージを送信するのをサポートします。
|
||||
- Fetch - `web_sys` と前述の futures の機能を用いたフェッチリクエストを処理するための抽象化です。
|
||||
|
||||
## お探しのものは
|
||||
|
||||
エコシステムが必要なライブラリですが、まだありません。
|
||||
|
||||
Bootstrap/MaterialUi/arbitrary といった CSS フレームワークのコンポーネントのラッパー。
|
||||
@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Roadmap
|
||||
description: The planned feature roadmap for the Yew framework
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# ロードマップ
|
||||
|
||||
## 優先順位
|
||||
|
||||
フレームワークの今後の機能やフォーカスの優先順位は、コミュニティによって決定されます。2020 年の春には、プロジェクトの方向性についてのフィードバックを集めるために開発者アンケートが行われました。その概要は [Yew Wiki](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/wiki/Dev-Survey-%5BSpring-2020%5D) で見ることができます。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
主要な取り組みの状況は、Yew の Github の[Project board](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/projects)で確認できます。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 焦点
|
||||
|
||||
1. Top Requested Features
|
||||
2. Production Readiness
|
||||
3. Documentation
|
||||
4. Pain Points
|
||||
|
||||
### Top Requested Features
|
||||
|
||||
1. [関数型コンポーネント](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/projects/3)
|
||||
2. [Component ライブラリ](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/projects/4)
|
||||
3. より良い状態管理
|
||||
4. [サーバーサイドでのレンダリング](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/projects/5)
|
||||
|
||||
### Production Readiness
|
||||
|
||||
- テストカバレッジの向上
|
||||
- バイナリサイズ
|
||||
- [ベンチマークのパフォーマンス](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/issues/5)
|
||||
|
||||
### Documentation
|
||||
|
||||
- チュートリアルを作る
|
||||
- プロジェクトのセットアップをシンプルにする
|
||||
|
||||
### Pain Points
|
||||
|
||||
- [Component のボイラープレート](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/issues/830)
|
||||
- Fetch API
|
||||
- [エージェント](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/projects/6)
|
||||
@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Testing apps
|
||||
description: Testing your app
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Testing
|
||||
|
||||
<TODO>
|
||||
|
||||
## wasm_bindgen_test
|
||||
|
||||
Rust Wasm ワーキンググループは wasm_bindgen_test というフレームワークをメンテナンスしており、組み込みの #[test] プロシージャルマクロの動作と同様の方法でブラウザでテストを実行することができます。詳細は、[Rust Wasm 活動グループのドキュメント](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/wasm-bindgen-test/index.html)に記載されています。
|
||||
@ -3,82 +3,6 @@
|
||||
"message": "Next",
|
||||
"description": "The label for version current"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Getting Started": {
|
||||
"message": "Getting Started",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Getting Started in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Concepts": {
|
||||
"message": "Concepts",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Concepts in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Concepts.link.generated-index.title": {
|
||||
"message": "Yew concepts",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page title for category Concepts in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Concepts.link.generated-index.description": {
|
||||
"message": "Learn about the important Yew concepts!",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page description for category Concepts in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Components": {
|
||||
"message": "Components",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Components in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.HTML": {
|
||||
"message": "HTML",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category HTML in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Function Components": {
|
||||
"message": "Function Components",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Function Components in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.wasm-bindgen": {
|
||||
"message": "wasm-bindgen",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category wasm-bindgen in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.wasm-bindgen.link.generated-index.title": {
|
||||
"message": "wasm-bindgen",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page title for category wasm-bindgen in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.wasm-bindgen.link.generated-index.description": {
|
||||
"message": "Learn about wasm-bindgen",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page description for category wasm-bindgen in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Advanced topics": {
|
||||
"message": "Advanced topics",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Advanced topics in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Advanced topics.link.generated-index.title": {
|
||||
"message": "Advanced topics",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page title for category Advanced topics in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Advanced topics.link.generated-index.description": {
|
||||
"message": "Learn about the advanced topics and inner workings of Yew!",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page description for category Advanced topics in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.More": {
|
||||
"message": "More",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category More in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.More.link.generated-index.title": {
|
||||
"message": "Miscellaneous",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page title for category More in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Migration guides": {
|
||||
"message": "Migration guides",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Migration guides in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.yew": {
|
||||
"message": "yew",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category yew in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.yew-agent": {
|
||||
"message": "yew-agent",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category yew-agent in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.yew-router": {
|
||||
"message": "yew-router",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category yew-router in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.Getting Started": {
|
||||
"message": "Getting Started",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Getting Started in sidebar docs"
|
||||
@ -95,10 +19,6 @@
|
||||
"message": "Learn about the important Yew concepts!",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page description for category Concepts in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.Components": {
|
||||
"message": "Components",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Components in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.HTML": {
|
||||
"message": "HTML",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category HTML in sidebar docs"
|
||||
@ -107,18 +27,6 @@
|
||||
"message": "Function Components",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Function Components in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.wasm-bindgen": {
|
||||
"message": "wasm-bindgen",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category wasm-bindgen in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.wasm-bindgen.link.generated-index.title": {
|
||||
"message": "wasm-bindgen",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page title for category wasm-bindgen in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.wasm-bindgen.link.generated-index.description": {
|
||||
"message": "Learn about wasm-bindgen",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page description for category wasm-bindgen in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.Advanced topics": {
|
||||
"message": "Advanced topics",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Advanced topics in sidebar docs"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使い方については[`html!`ガイド](html.md)をご確認ください。
|
||||
使い方については[`html!`ガイド](concepts/html/introduction.mdx)をご確認ください。
|
||||
|
||||
### Rendered
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Callbacks
|
||||
description: ComponentLink and Callbacks
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
”リンク”コンポーネントはコンポーネントがコールバックを登録できて自身を更新することができるメカニズムです。
|
||||
|
||||
## ComponentLink API
|
||||
|
||||
### callback
|
||||
|
||||
実行時にコンポーネントの更新メカニズムにメッセージを送信するコールバックを登録します。
|
||||
これは、渡されたクロージャから返されるメッセージで `send_self` を呼び出します。
|
||||
`Fn(IN) -> Vec<COMP::Message>`が渡され、`Callback<IN>`が返されます。
|
||||
|
||||
### send_message
|
||||
|
||||
現在のループが終了した直後にコンポーネントにメッセージを送信し、別の更新ループを開始します。
|
||||
|
||||
### send_message_batch
|
||||
|
||||
実行時に一度に多数のメッセージを一括して送信するコールバックを登録します。
|
||||
メッセージによってコンポーネントが再レンダリングされる場合、バッチ内のすべてのメッセージが処理された後、コンポーネントは再レンダリングされます。
|
||||
`Fn(IN) -> COMP::Message`が渡され、`Callback<IN>`が返されます。
|
||||
|
||||
## コールバック
|
||||
|
||||
_\(This might need its own short page.\)_
|
||||
|
||||
コールバックは、Yew 内のサービス、エージェント、親コンポーネントとの通信に使われます。
|
||||
これらは単に `Fn` を `Rc` でラップしただけであり、クローンを作成できるようにするためのものです。
|
||||
|
||||
これらの関数には `emit` 関数があり、`<IN>` 型を引数に取り、それをアドレスが欲しいメッセージに変換します。
|
||||
親からのコールバックが子コンポーネントに props で提供されている場合、子は `update` ライフサイクルフックで `emit` をコールバックに呼び出して親にメッセージを返すことができます。
|
||||
マクロ内で props として提供されたクロージャや関数は自動的にコールバックに変換されます。
|
||||
@ -1,198 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Introduction
|
||||
description: Components and their lifecycle hooks
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## コンポーネントとは?
|
||||
|
||||
コンポーネントは Yew を構成するブロックです。
|
||||
コンポーネントは状態を管理し、自身を DOM へレンダリングすることができます。
|
||||
コンポーネントはライフサイクルの機能がある`Component`トレイトを実装することによって作られます。
|
||||
|
||||
## ライフサイクル
|
||||
|
||||
:::important contribute
|
||||
`Contribute to our docs:` [Add a diagram of the component lifecycle](https://github.com/yewstack/docs/issues/22)
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## ライフサイクルのメソッド
|
||||
|
||||
### Create
|
||||
|
||||
コンポーネントが作られると、`ComponentLink`と同様に親コンポーネントからプロパティを受け取ります。
|
||||
プロパティはコンポーネントの状態を初期化するのに使われ、"link"はコールバックを登録したりコンポーネントにメッセージを送るのに使われます。
|
||||
|
||||
props と link をコンポーネント構造体に格納するのが一般的です。
|
||||
例えば:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub struct MyComponent {
|
||||
props: Props,
|
||||
link: ComponentLink<Self>,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Properties = Props;
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn create(props: Self::Properties, link: ComponentLink<Self>) -> Self {
|
||||
MyComponent { props, link }
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### View
|
||||
|
||||
コンポーネントは`view()`メソッドによってレイアウトを宣言します。
|
||||
Yew は`html!`マクロによって HTML と SVG ノード、リスナー、子コンポーネントを宣言できます。
|
||||
マクロは React の JSX のような動きをしますが、JavaScript の代わりに Rust の式を用います。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
let onclick = self.link.callback(|_| Msg::Click);
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<button {onclick}>{ self.props.button_text }</button>
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使い方については[`html!`ガイド](html.md)をご確認ください。
|
||||
|
||||
### Rendered
|
||||
|
||||
`rendered()`コンポーネントのライフサイクルのメソッドは`view()`が処理されたて Yew がコンポーネントをレンダリングした後、
|
||||
ブラウザがページを更新する前に呼ばれます。
|
||||
コンポーネントは、コンポーネントが要素をレンダリングした後にのみ実行できるアクションを実行するため、このメソッドを実装したい場合があります。
|
||||
コンポーネントが初めてレンダリングされたかどうかは `first_render` パラメータで確認できます。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
use stdweb::web::html_element::InputElement;
|
||||
use stdweb::web::IHtmlElement;
|
||||
use yew::prelude::*;
|
||||
|
||||
pub struct MyComponent {
|
||||
node_ref: NodeRef,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<input ref={self.node_ref.clone()} type="text" />
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn rendered(&mut self, first_render: bool) {
|
||||
if first_render {
|
||||
if let Some(input) = self.node_ref.try_into::<InputElement>() {
|
||||
input.focus();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip note
|
||||
ライフサイクルメソッドは実装の必要がなく、デフォルトでは何もしません。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Update
|
||||
|
||||
コンポーネントは動的で、非同期メッセージを受信するために登録することができます。
|
||||
ライフサイクルメソッド `update()` はメッセージごとに呼び出されます。
|
||||
これにより、コンポーネントはメッセージが何であったかに基づいて自身を更新し、自身を再レンダリングする必要があるかどうかを判断することができます。
|
||||
メッセージは、HTML 要素リスナーによってトリガーされたり、子コンポーネント、エージェント、サービス、または Futures によって送信されたりします。
|
||||
|
||||
`update()`がどのようなのかについての例は以下の通りです:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub enum Msg {
|
||||
SetInputEnabled(bool)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Message = Msg;
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn update(&mut self, msg: Self::Message) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
match msg {
|
||||
Msg::SetInputEnabled(enabled) => {
|
||||
if self.input_enabled != enabled {
|
||||
self.input_enabled = enabled;
|
||||
true // Re-render
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Change
|
||||
|
||||
コンポーネントは親によって再レンダリングされることがあります。
|
||||
このような場合、新しいプロパティを受け取り、再レンダリングを選択する可能性があります。
|
||||
この設計では、プロパティを変更することで、親から子へのコンポーネントの通信が容易になります。
|
||||
|
||||
典型的な実装例は以下の通りです:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn change(&mut self, props: Self::Properties) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
if self.props != props {
|
||||
self.props = props;
|
||||
true
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Destroy
|
||||
|
||||
コンポーネントが DOM からアンマウントされた後、Yew は `destroy()` ライフサイクルメソッドを呼び出し、必要なクリーンアップ操作をサポートします。
|
||||
このメソッドはオプションで、デフォルトでは何もしません。
|
||||
|
||||
## Associated Types
|
||||
|
||||
`Component`トレイトは 2 つの関連型があります: `Message`と`Properties`です。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Message = Msg;
|
||||
type Properties = Props;
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`Message`はコンポーネントによって処理され、何らかの副作用を引き起こすことができるさまざまなメッセージを表します。
|
||||
例えば、API リクエストをトリガーしたり、UI コンポーネントの外観を切り替えたりする `Click` メッセージがあります。
|
||||
コンポーネントのモジュールで `Msg` という名前の列挙型を作成し、それをコンポーネントのメッセージ型として使用するのが一般的です。
|
||||
"message"を"msg"と省略するのも一般的です。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
enum Msg {
|
||||
Click,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`Properties`は、親からコンポーネントに渡される情報を表します。
|
||||
この型は Properties trait を実装していなければならず\(通常はこれを派生させることで\)、特定のプロパティが必須かオプションかを指定することができます。
|
||||
この型は、コンポーネントの作成・更新時に使用されます。
|
||||
コンポーネントのモジュール内に `Props` という構造体を作成し、それをコンポーネントの `Properties` 型として使用するのが一般的です。
|
||||
”Properties”を"props"に短縮するのが一般的です。
|
||||
Props は親コンポーネントから継承されるので、アプリケーションのルートコンポーネントは通常`()`型の`Properties`を持ちます。
|
||||
ルートコンポーネントのプロパティを指定したい場合は、`App::mount_with_props`メソッドを利用します。
|
||||
@ -1,84 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Properties
|
||||
description: Parent to child communication
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
プロパティは、子コンポーネントと親コンポーネントが互いに通信できるようにします。
|
||||
|
||||
## マクロの継承
|
||||
|
||||
`Properties`を自分で実装しようとせず、代わりに`#[derive(Properties)]`を使ってください。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
`Properties`を継承した型は`Clone`を実装していなければいけません。
|
||||
これは`#[derive(Properties, Clone)`か`Clone`を手で実装することで可能です。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### 必要な属性
|
||||
|
||||
デフォルトでは、`Properties` を導出する構造体内のフィールドは必須です。
|
||||
フィールドが欠落していて `html!` マクロでコンポーネントが作成された場合、コンパイラエラーが返されます。
|
||||
オプションのプロパティを持つフィールドについては、`#[prop_or_default]` 属性を使用して、prop が指定されていない場合はその型のデフォルト値を使用します。
|
||||
値を指定するには `#[prop_or(value)]` 属性を用います。
|
||||
ここで value はプロパティのデフォルト値、あるいは代わりに `#[prop_or_else(function)]` を使用して、`function` はデフォルト値を返します。
|
||||
例えば、ブール値のデフォルトを `true` とするには、属性 `#[prop_or(true)]` を使用します。オプションのプロパティでは、デフォルト値 `None` を持つ `Option` 列挙型を使うのが一般的です。
|
||||
|
||||
### PartialEq
|
||||
|
||||
もし可能なら props で `PartialEq` を継承するのが良いかもしれません。
|
||||
`PartialEq`を使うことで、不必要な再レンダリングを避けることができます
|
||||
(これについては、**最適化とベストプラクティス**のセクションで説明しています)。
|
||||
|
||||
## プロパティを使用する際のメモリと速度のオーバーヘッド
|
||||
|
||||
`Compoenent::view`ではコンポーネントの状態への参照を取り、それを使って `Html` を作成します。
|
||||
しかし、プロパティは自身の値です。
|
||||
つまり、それらを作成して子コンポーネントに渡すためには、`view` 関数で提供される参照を所有する必要があるのです。
|
||||
これは所有する値を取得するためにコンポーネントに渡される参照を暗黙のうちにクローンすることで行われます。
|
||||
|
||||
これは、各コンポーネントが親から受け継いだ状態の独自のコピーを持っていることを意味し、コンポーネントを再レンダリングするときはいつでも、再レンダリングしたコンポーネントのすべての子コンポーネントの props がクローンされなければならないことを意味します。
|
||||
|
||||
このことの意味するところは、もしそうでなければ*大量の*データ \(10KB もあるような文字列\) を props として渡してしまうのであれば、子コンポーネントを親が呼び出す `Html` を返す関数にすることを考えた方がいいかもしれないということです。
|
||||
|
||||
props を介して渡されたデータを変更する必要がない場合は、実際のデータそのものではなく、データへの参照カウントされたポインタのみが複製されるように `Rc` でラップすることができます。
|
||||
|
||||
## 例
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
use std::rc::Rc;
|
||||
use yew::Properties;
|
||||
|
||||
#[derive(Clone, PartialEq)]
|
||||
pub enum LinkColor {
|
||||
Blue,
|
||||
Red,
|
||||
Green,
|
||||
Black,
|
||||
Purple,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Default for LinkColor {
|
||||
fn default() -> Self {
|
||||
// The link color will be blue unless otherwise specified.
|
||||
LinkColor::Blue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#[derive(Properties, Clone, PartialEq)]
|
||||
pub struct LinkProps {
|
||||
/// The link must have a target.
|
||||
href: String,
|
||||
/// If the link text is huge, this will make copying the string much cheaper.
|
||||
/// This isn't usually recommended unless performance is known to be a problem.
|
||||
text: Rc<String>,
|
||||
/// Color of the link.
|
||||
#[prop_or_default]
|
||||
color: LinkColor,
|
||||
/// The view function will not specify a size if this is None.
|
||||
#[prop_or_default]
|
||||
size: Option<u32>,
|
||||
/// When the view function doesn't specify active, it defaults to true.
|
||||
#[prop_or(true)]
|
||||
active: bool,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Refs
|
||||
description: Out-of-band DOM access
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
`ref`は、任意の HTML 要素やコンポーネントの内部で、割り当てられている DOM`Element`を取得するために使用することができます。
|
||||
これは、`view` ライフサイクルメソッドの外で DOM に変更を加えるために使用できます。
|
||||
|
||||
これは、キャンバスの要素を取得したり、ページの異なるセクションにスクロールしたりするのに便利です。
|
||||
|
||||
構文は以下の通りです:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// In create
|
||||
self.node_ref = NodeRef::default();
|
||||
|
||||
// In view
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div ref={self.node_ref.clone()}></div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// In update
|
||||
let has_attributes = self.node_ref.try_into::<Element>().has_attributes();
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Introduction
|
||||
description: The procedural macro for generating HTML and SVG
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
`html!`マクロによって HTML と SVG のコードを宣言的に書くことができます。
|
||||
JSX \(HTML のようなコードを JavaScript 内部に書くことができる JavaScript の拡張\) に似ています。
|
||||
|
||||
**重要な注意**
|
||||
|
||||
1. `html!`マクロはルートの HTML ノードのみ受け付けます \([フラグメントかイテレータを使う](html/lists.mdx)ことでやり取りできます\)
|
||||
2. 空の`html! {}`の呼び出しは可能ですが何もレンダリングしません
|
||||
3. リテラルはクオーテーションがつけられ、ブレースで囲う必要があります: `html! { "Hello, World" }`
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
`html!`マクロはコンパイラのデフォルトの再帰の上限に簡単に達してしまいます。
|
||||
もしコンパイラエラーに遭遇した場合はその値を押し出すといいかもしれません。
|
||||
クレートのルート\(つまり、`lib.rs`か`main.rs`\)で`#![recursion_limit="1024"]`のような属性を使えば解決します。
|
||||
|
||||
詳しくは[公式ドキュメント](https://doc.rust-lang.org/reference/attributes/limits.html#the-recursion_limit-attribute)と[Stack Overflow の質問](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/27454761/what-is-a-crate-attribute-and-where-do-i-add-it)を見てみてください。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@ -267,12 +267,6 @@ impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
|
||||
## イベントの型
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
以下のテーブルでは`yew`を`web-sys`と使う場合 (デフォルトでは使うようになっている) `web-sys`のイベントの型が使われるべきです。
|
||||
`yew-stdweb`クレートを使う場合は`stdweb`のイベントの型を使用してください。
|
||||
詳細については[`web-sys`と`stdweb`をどちらを使うべきかについてのドキュメント](https://yew.rs/getting-started/choose-web-library)をご確認ください。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
以下のテーブルにある全てのイベントの型は`yew::events`で再エクスポートされています。
|
||||
All the event types mentioned in the following table are re-exported under `yew::events`. Using the types from
|
||||
@ -281,99 +275,99 @@ or `stdweb` as dependencies in your crate because you won't end up using a versi
|
||||
the version Yew specifies.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
| イベント名 | `web_sys` イベント型 | `stdweb` イベント型 |
|
||||
| --------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `onabort` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [ResourceAbortEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ResourceAbortEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onauxclick` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [AuxClickEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.AuxClickEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onblur` | [FocusEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.FocusEvent.html) | [BlurEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.BlurEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `oncancel` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `oncanplay` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `oncanplaythrough` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onchange` | [ChangeData](https://docs.rs/yew/latest/yew/events/enum.ChangeData.html) | [ChangeData](https://docs.rs/yew-stdweb/latest/yew_stdweb/events/enum.ChangeData.html) |
|
||||
| `onclick` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [ClickEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ClickEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onclose` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `oncontextmenu` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [ContextMenuEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ContextMenuEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `oncuechange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ondblclick` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [DoubleClickEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DoubleClickEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondrag` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragend` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragEndEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragEndEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragenter` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragEnterEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragEnterEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragexit` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragExitEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragExitEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragleave` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.htmk) | [DragLeaveEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragLeaveEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragover` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragOverEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragOverEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragstart` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragStartEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragStartEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondrop` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) | [DragDropEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.DragDropEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondurationchange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onemptied` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onended` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onerror` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [ResourceErrorEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ResourceErrorEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onfocus` | [FocusEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.FocusEvent.html) | [FocusEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.FocusEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onformdata` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `oninput` | [InputData](https://docs.rs/yew/latest/yew/events/struct.InputData.html) | [InputData](https://docs.rs/yew-stdweb/latest/yew_stdweb/events/struct.InputData.html) |
|
||||
| `oninvalid` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onkeydown` | [KeyboardEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.KeyboardEvent.html) | [KeyDownEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.KeyDownEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onkeypress` | [KeyboardEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.KeyboardEvent.html) | [KeyPressEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.KeyPressEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onkeyup` | [KeyboardEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.KeyboardEvent.html) | [KeyUpEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.KeyUpEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onload` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [ResourceLoadEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ResourceLoadEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onloadeddata` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onloadedmetadata` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onloadstart` | [ProgressEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.ProgressEvent.html) | [LoadStartEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.LoadStartEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmousedown` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseDownEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseDownEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseenter` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseEnterEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseEnterEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseleave` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseLeaveEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseLeaveEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmousemove` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseMoveEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseMoveEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseout` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseOutEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseOutEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseover` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseOverEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseOverEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseup` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) | [MouseUpEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseUpEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpause` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onplay` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onplaying` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onprogress` | [ProgressEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.ProgressEvent.html) | [ProgressEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ProgressEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onratechange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onreset` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onresize` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [ResizeEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ResizeEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onscroll` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [ScrollEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.ScrollEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onsecuritypolicyviolation` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onseeked` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onseeking` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onselect` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onslotchange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [SlotChangeEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.SlotChangeEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onstalled` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onsubmit` | [FocusEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.FocusEvent.html) | [SubmitEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.SubmitEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onsuspend` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ontimeupdate` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ontoggle` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onvolumechange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onwaiting` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onwheel` | [WheelEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.WheelEvent.html) | [MouseWheelEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.MouseWheelEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `oncopy` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `oncut` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onpaste` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onanimationcancel` | [AnimationEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.AnimationEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onanimationend` | [AnimationEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.AnimationEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onanimationiteration` | [AnimationEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.AnimationEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onanimationstart` | [AnimationEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.AnimationEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ongotpointercapture` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [GotPointerCaptureEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.GotPointerCaptureEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onloadend` | [ProgressEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.ProgressEvent.html) | [LoadEndEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.LoadEndEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onlostpointercapture` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [LostPointerCaptureEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.LostPointerCaptureEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointercancel` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerCancelEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerCancelEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerdown` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerDownEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerDownEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerenter` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerEnterEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerEnterEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerleave` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerLeaveEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerLeaveEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerlockchange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [PointerLockChangeEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerLockChangeEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerlockerror` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [PointerLockErrorEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerLockErrorEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointermove` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerMoveEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerMoveEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerout` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerOutEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerOutEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerover` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerOverEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerOverEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerup` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) | [PointerUpEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.PointerUpEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onselectionchange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | [SelectionChangeEvent](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.SelectionChangeEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onselectstart` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `onshow` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ontouchcancel` | [TouchEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TouchEvent.html) | [TouchCancel](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.TouchCancel.html) |
|
||||
| `ontouchend` | [TouchEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TouchEvent.html) | [TouchEnd](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.TouchEnd.html) |
|
||||
| `ontouchmove` | [TouchEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TouchEvent.html) | [TouchMove](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.TouchMove.html) |
|
||||
| `ontouchstart` | [TouchEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TouchEvent.html) | [TouchStart](https://docs.rs/stdweb/latest/stdweb/web/event/struct.TouchStart.html) |
|
||||
| `ontransitioncancel` | [TransitionEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TransitionEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ontransitionend` | [TransitionEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TransitionEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ontransitionrun` | [TransitionEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TransitionEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| `ontransitionstart` | [TransitionEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TransitionEvent.html) | サポート無し |
|
||||
| イベント名 | `web_sys` イベント型 |
|
||||
| --------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `onabort` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onauxclick` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onblur` | [FocusEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.FocusEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `oncancel` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `oncanplay` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `oncanplaythrough` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onchange` | [ChangeData](https://docs.rs/yew/latest/yew/events/enum.ChangeData.html) |
|
||||
| `onclick` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onclose` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `oncontextmenu` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `oncuechange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `ondblclick` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondrag` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragend` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragenter` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragexit` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragleave` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.htmk) |
|
||||
| `ondragover` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondragstart` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondrop` | [DragEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.DragEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ondurationchange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onemptied` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onended` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onerror` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onfocus` | [FocusEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.FocusEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onformdata` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `oninput` | [InputData](https://docs.rs/yew/latest/yew/events/struct.InputData.html) |
|
||||
| `oninvalid` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onkeydown` | [KeyboardEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.KeyboardEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onkeypress` | [KeyboardEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.KeyboardEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onkeyup` | [KeyboardEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.KeyboardEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onload` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onloadeddata` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onloadedmetadata` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onloadstart` | [ProgressEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.ProgressEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmousedown` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseenter` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseleave` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmousemove` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseout` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseover` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onmouseup` | [MouseEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.MouseEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpause` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onplay` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onplaying` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onprogress` | [ProgressEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.ProgressEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onratechange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onreset` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onresize` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onscroll` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onsecuritypolicyviolation` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onseeked` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onseeking` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onselect` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onslotchange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onstalled` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onsubmit` | [FocusEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.FocusEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onsuspend` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `ontimeupdate` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `ontoggle` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onvolumechange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onwaiting` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onwheel` | [WheelEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.WheelEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `oncopy` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `oncut` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onpaste` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onanimationcancel` | [AnimationEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.AnimationEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onanimationend` | [AnimationEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.AnimationEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onanimationiteration` | [AnimationEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.AnimationEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onanimationstart` | [AnimationEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.AnimationEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ongotpointercapture` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onloadend` | [ProgressEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.ProgressEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onlostpointercapture` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointercancel` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerdown` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerenter` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerleave` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerlockchange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerlockerror` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointermove` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerout` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerover` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onpointerup` | [PointerEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.PointerEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `onselectionchange` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onselectstart` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `onshow` | [Event](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.Event.html) |
|
||||
| `ontouchcancel` | [TouchEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TouchEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ontouchend` | [TouchEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TouchEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ontouchmove` | [TouchEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TouchEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ontouchstart` | [TouchEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TouchEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ontransitioncancel` | [TransitionEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TransitionEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ontransitionend` | [TransitionEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TransitionEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ontransitionrun` | [TransitionEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TransitionEvent.html) |
|
||||
| `ontransitionstart` | [TransitionEvent](https://docs.rs/web-sys/latest/web_sys/struct.TransitionEvent.html) |
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Introduction
|
||||
description: The procedural macro for generating HTML and SVG
|
||||
slug: /concepts/html
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
`html!`マクロによって HTML と SVG のコードを宣言的に書くことができます。
|
||||
@ -8,7 +9,7 @@ JSX \(HTML のようなコードを JavaScript 内部に書くことができる
|
||||
|
||||
**重要な注意**
|
||||
|
||||
1. `html!`マクロはルートの HTML ノードのみ受け付けます \([フラグメントかイテレータを使う](html/lists.md)ことでやり取りできます\)
|
||||
1. `html!`マクロはルートの HTML ノードのみ受け付けます \([フラグメントかイテレータを使う](./lists.mdx)ことでやり取りできます\)
|
||||
2. 空の`html! {}`の呼び出しは可能ですが何もレンダリングしません
|
||||
3. リテラルはクオーテーションがつけられ、ブレースで囲う必要があります: `html! { "Hello, World" }`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Introduction
|
||||
description: Yew's glue to browser APIs
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# サービス
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
このセクションはまだ WIP です。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Format
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
:::important contribute
|
||||
`Contribute to our docs:` [Explain the format module in depth](https://github.com/yewstack/docs/issues/24)
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@ -1,148 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Choosing a web library
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## はじめに
|
||||
|
||||
Yew アプリは[`web-sys`](https://docs.rs/web-sys)か[`stdweb`](https://docs.rs/stdweb)で作ることができます。
|
||||
これらのクレートは Rust と Web API のバインディングを提供しています。
|
||||
Cargo の依存クレートに`yew`を追加する際はどちらかを選ばなければいけません:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
# Choose `web-sys`
|
||||
yew = "0.17"
|
||||
|
||||
# Choose `stdweb`
|
||||
yew = { version = "0.17", package = "yew-stdweb" }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[Rust / Wasm 活動チーム](https://rustwasm.github.io/)のサポートがある`web-sys`が推奨です。
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用例
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// web-sys
|
||||
let window: web_sys::Window = web_sys::window().expect("window not available");
|
||||
window.alert_with_message("hello from wasm!").expect("alert failed");
|
||||
|
||||
// stdweb
|
||||
let window: stdweb::web::Window = stdweb::web::window();
|
||||
window.alert("hello from wasm!");
|
||||
|
||||
// stdweb with js! macro
|
||||
use stdweb::js;
|
||||
use stdweb::unstable::TryFrom;
|
||||
use stdweb::web::Window;
|
||||
|
||||
let window_val: stdweb::Value = js!{ return window; }; // <- JS syntax inside!
|
||||
let window = Window::try_from(window_val).expect("conversion to window failed");
|
||||
window.alert("hello from wasm!");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2 つのクレートの API はわずかに異なりますが、だいたい同じ目的で似た機能が提供されています。
|
||||
|
||||
## 一方を選ぶ
|
||||
|
||||
アプリに`web-sys`と`stdweb`のどちらを選ぶかにおいてはいくつかの見方があります。
|
||||
注意として、一つのアプリに両方を用いることができるのですが、クレートをコンパイルした際にバイナリのサイズを小さくするには
|
||||
一方だけを使用するのが良いです。
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}></th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>web-sys</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>stdweb</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>プロジェクトの進捗状況</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/">Rust / Wasm 活動チーム</a>
|
||||
により活発にメンテナンスされている
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>GitHubで8ヶ月間動きなし</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>Web API のカバー</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
RustのAPIはWeb IDLスペックから自動的に生成される。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Browser APIはコミュニティにより追加。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>RustのAPIのデザイン</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
ほとんどのAPIコールおいて<code>Result</code>
|
||||
が返ってくるよう保守的なアプローチがとられている。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
しばしば<code>Result</code>
|
||||
を返さずpanicするようになっている。例えば <code>
|
||||
stdweb::web::window()
|
||||
</code>
|
||||
ワーカーの中で呼ばれるパニックする。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
サポートされているビルドツール
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<p></p>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm-bindgen</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm-pack</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<p></p>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>cargo-web</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm-bindgen</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm-pack</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポートされているターゲット</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>asmjs-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
@ -1,188 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Introduction
|
||||
description: Set yourself up for success
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 始める
|
||||
|
||||
## Rust
|
||||
|
||||
まずはじめに Rust が必要です。Rust とビルドツールの`cargo`をインストールするために、以下の[公式サイト](https://www.rust-lang.org/tools/install)
|
||||
を見てください。
|
||||
|
||||
## **Wasm ビルドツール**
|
||||
|
||||
WebAssembly と JavaScript の互換を持たせるために他にツールが必要です。さらに、選んだツールに応じてブラウザでアプリから`.wasm`ファイルを実行するのに
|
||||
必要な JavaScript ラッパーのコードを生成し、これによってデプロイやパッケージ化での頭痛の種を軽減させるのに役立ちます。
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`wasm-pack`**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/)
|
||||
|
||||
Rust / Wasm 活動チームによって開発されている CLI ツールで、WebAssembly をパッケージ化することができます。
|
||||
Webpack には[`wasm-pack-plugin`](https://github.com/wasm-tool/wasm-pack-plugin)が最もよく使われています。
|
||||
|
||||
[`wasm-pack`で始める](project-setup/using-wasm-pack.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`wasm-bindgen`**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/)
|
||||
|
||||
Rust/Wasm 活動チームによって開発されているライブラリと CLI ツールで、JS / WebAssembly の互換性を持たせるための低レベルなツールです
|
||||
(`wasm-pack`で内部的に使われています)。
|
||||
`wasm-bindgen`は手書きの JavaScript で WebAssembly のバイナリを使う必要があるため、直接使うのは非推奨です。
|
||||
しかし、詳細な情報については[**`wasm-bindgen` ガイド**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/)から得られます。
|
||||
|
||||
[`wasm-bindgen`で始める。](project-setup/using-wasm-bindgen.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`cargo-web`**](https://github.com/koute/cargo-web)
|
||||
|
||||
`wasm-pack`と`wasm-bindgen`を導入する前は好まれた Web ワークフローツールです。
|
||||
`wasm-pack`がサポートされていないサンプルを動かすのにインストールする価値があり、依然として**最もお手軽に**始められる方法です。
|
||||
|
||||
[`cargo web`で始める](project-setup/using-cargo-web.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### 比較
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}></th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>wasm-pack</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>wasm-bindgen</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>cargo-web</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>プロジェクトの進行状況</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/">Rust / Wasm活動チーム</a>
|
||||
により活発にメンテナンス
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/">Rust / Wasm 活動チーム</a>
|
||||
により活発にメンテナンス
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
6ヶ月間GitHubでの活発な活動無し
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>開発体験</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
ほぼ大丈夫! <code>webpack</code>があればなお良い。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
だいたい大丈夫。開発においては少し流れを書かないといけない。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
しっかり動く!完結していて、外部ライブラリに頼る必要無し。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>ローカルサーバー</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>webpack</code>プラグインによるサポートあり
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポート無し</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポートあり</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
ローカル環境での変更による自動再ビルド
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>webpack</code>プラグインによるサポートあり
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポート無し</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポートあり</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>ヘッドレスブラウザテスト</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/commands/test.html">
|
||||
サポートあり
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/wasm-bindgen-test/index.html">
|
||||
サポートあり
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/koute/cargo-web#features">
|
||||
サポートあり
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポートされているターゲット</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>asmjs-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>web-sys</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性無し</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>stdweb</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>使用例</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/yewstack/yew-wasm-pack-minimal">
|
||||
入門用テンプレート
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Yewで
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/yewstack/yew/blob/master/examples/build.sh">
|
||||
作る例
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Yewで
|
||||
<a href="https://www.github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/master/packages/yew-stdweb/examples">
|
||||
作る例
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
@ -1,188 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Introduction
|
||||
description: Set yourself up for success
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 始める
|
||||
|
||||
## Rust
|
||||
|
||||
まずはじめに Rust が必要です。Rust とビルドツールの`cargo`をインストールするために、以下の[公式サイト](https://www.rust-lang.org/tools/install)
|
||||
を見てください。
|
||||
|
||||
## **Wasm ビルドツール**
|
||||
|
||||
WebAssembly と JavaScript の互換を持たせるために他にツールが必要です。さらに、選んだツールに応じてブラウザでアプリから`.wasm`ファイルを実行するのに
|
||||
必要な JavaScript ラッパーのコードを生成し、これによってデプロイやパッケージ化での頭痛の種を軽減させるのに役立ちます。
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`wasm-pack`**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/)
|
||||
|
||||
Rust / Wasm 活動チームによって開発されている CLI ツールで、WebAssembly をパッケージ化することができます。
|
||||
Webpack には[`wasm-pack-plugin`](https://github.com/wasm-tool/wasm-pack-plugin)が最もよく使われています。
|
||||
|
||||
[`wasm-pack`で始める](project-setup/using-wasm-pack.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`wasm-bindgen`**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/)
|
||||
|
||||
Rust/Wasm 活動チームによって開発されているライブラリと CLI ツールで、JS / WebAssembly の互換性を持たせるための低レベルなツールです
|
||||
(`wasm-pack`で内部的に使われています)。
|
||||
`wasm-bindgen`は手書きの JavaScript で WebAssembly のバイナリを使う必要があるため、直接使うのは非推奨です。
|
||||
しかし、詳細な情報については[**`wasm-bindgen` ガイド**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/)から得られます。
|
||||
|
||||
[`wasm-bindgen`で始める。](project-setup/using-wasm-bindgen.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`cargo-web`**](https://github.com/koute/cargo-web)
|
||||
|
||||
`wasm-pack`と`wasm-bindgen`を導入する前は好まれた Web ワークフローツールです。
|
||||
`wasm-pack`がサポートされていないサンプルを動かすのにインストールする価値があり、依然として**最もお手軽に**始められる方法です。
|
||||
|
||||
[`cargo web`で始める](project-setup/using-cargo-web.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### 比較
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}></th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>wasm-pack</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>wasm-bindgen</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>cargo-web</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>プロジェクトの進行状況</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/">Rust / Wasm活動チーム</a>
|
||||
により活発にメンテナンス
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/">Rust / Wasm 活動チーム</a>
|
||||
により活発にメンテナンス
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
6ヶ月間GitHubでの活発な活動無し
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>開発体験</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
ほぼ大丈夫! <code>webpack</code>があればなお良い。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
だいたい大丈夫。開発においては少し流れを書かないといけない。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
しっかり動く!完結していて、外部ライブラリに頼る必要無し。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>ローカルサーバー</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>webpack</code>プラグインによるサポートあり
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポート無し</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポートあり</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
ローカル環境での変更による自動再ビルド
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>webpack</code>プラグインによるサポートあり
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポート無し</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポートあり</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>ヘッドレスブラウザテスト</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/commands/test.html">
|
||||
サポートあり
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/wasm-bindgen-test/index.html">
|
||||
サポートあり
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/koute/cargo-web#features">
|
||||
サポートあり
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>サポートされているターゲット</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>asmjs-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>web-sys</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性無し</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>stdweb</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>互換性あり</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>使用例</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/yewstack/yew-wasm-pack-minimal">
|
||||
入門用テンプレート
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Yewで
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/yewstack/yew/blob/master/examples/build.sh">
|
||||
作る例
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Yewで
|
||||
<a href="https://www.github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/master/packages/yew-stdweb/examples">
|
||||
作る例
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Using cargo-web
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Cargo web はクライアント Web アプリを作るための Cargo サブコマンドです。
|
||||
これにより Web アプリのビルドとデプロイを驚くほど簡単にできます。
|
||||
そして同時に Emscripten がターゲットなのを唯一サポートしているツールチェーンです。
|
||||
詳しくは[こちら](https://github.com/koute/cargo-web)。
|
||||
|
||||
**インストール**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo install cargo-web
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## ビルド
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo web build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 動かす
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo web start
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## サポートされているターゲット
|
||||
|
||||
- `wasm32-unknown-unknown`
|
||||
- `wasm32-unknown-emscripten`
|
||||
- `asmjs-unknown-emscripten`
|
||||
|
||||
:::注意
|
||||
`*-emscripten`をターゲットにする場合、Emscripten SDK をインストールする必要があります。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@ -1,51 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Using wasm-bindgen
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## インストール
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo install wasm-bindgen-cli
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## ビルド
|
||||
|
||||
はじめに、Wasm ファイルを生成するアプリをビルドしましょう。
|
||||
[サンプルアプリをビルド](../build-a-sample-app.mdx)のアプリをビルドしたいとします。
|
||||
生成されたファイルのパスは`target/wasm32-unknown-unknown/debug/yew-app.wasm`にあるはずです。
|
||||
もしクレートに何か別の名前をつけた場合、Wasm ファイルの名前は`yew-app.wasm`ではなく、`Cargo.toml`ファイルに
|
||||
`package.name`として名前をつけたものになるでしょう。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo build --target wasm32-unknown-unknown
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
次に、wasm-bindgen の CLI を動かしましょう。
|
||||
このコマンドは`--out-dir`のディレクトリにいくつかのファイルを生成し、その中には Wasm バイナリを読み込んで動かすための
|
||||
コンパイルされた WebAssembly と JavaScript のラッパーが入っています。
|
||||
現在のブラウザは直接 WebAssembly ファイルを読み込むことができないため、代わりに JavaScript 経由で読み込まれるなければならず、
|
||||
そのためにこれらのラッパーが必要となります。
|
||||
[サンプルアプリを作る(../build-a-sample-app.mdx)の例では`static`フォルダにファイルが生成されるようにしており
|
||||
(そのために`wasm-bindgen`へ`--out-dir static`と渡す必要があります)、
|
||||
`wasm.js`と`wasm_bg.wasm`という名前になります(`wasm-bindgen`へ`--out-name wasm`と渡すことで実現できます)
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
wasm-bindgen --target web --out-dir static --out-name wasm target/wasm32-unknown-unknown/debug/appname.wasm --no-typescript
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## アプリをサーブする
|
||||
|
||||
好きなサーバーを使ってください。
|
||||
ここではシンプルな Python のサーバーを使います。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m http.server 8000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## サポートされているターゲット
|
||||
|
||||
- `wasm32-unknown-unknown`
|
||||
|
||||
## 参考ドキュメント
|
||||
|
||||
- [The `wasm-bindgen` docs](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/)
|
||||
@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Using wasm-pack
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
このツールは Rust / Wasm 活動チームによって開発され、WebAssembly のアプリを作るのに使われれるツールで最も活発に開発されているものです。
|
||||
コードを`npm`モジュールへパッケージ化するのをサポートし、既存の JavaScript のアプリと簡単に統合できる
|
||||
[Webpack plugin](https://github.com/wasm-tool/wasm-pack-plugin)がついています。
|
||||
詳しい情報は[the `wasm-pack` documentation](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/introduction.html)にあります。
|
||||
|
||||
:::注意
|
||||
`wasm-pack`を使う際は`Cargo.toml`の crate-type は`cdylib`である必要があります。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## インストール
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo install wasm-pack
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## ビルド
|
||||
|
||||
このコマンドは JavaScript ラッパーとアプリの WebAssembly をまとめたものを`./pkg`ディレクトリに生成し、アプリをスタートすることができます。
|
||||
This command will produce a bundle in the `./pkg` directory with your app's compiled WebAssembly
|
||||
along with a JavaScript wrapper which can be used to start your application.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
wasm-pack build --target web
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## バンドル
|
||||
|
||||
ロールアップにについては詳しくは[ガイド](https://rollupjs.org/guide/en/#quick-start)をご覧ください。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
rollup ./main.js --format iife --file ./pkg/bundle.js
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## サーブ
|
||||
|
||||
好きなサーバーを使ってください。
|
||||
ここではシンプルな Python のサーバーを使ってアプリをサーブします。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m http.server 8000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## サポートされているターゲット
|
||||
|
||||
- `wasm32-unknown-unknown`
|
||||
@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Starter templates
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## `wasm-pack`
|
||||
|
||||
- [ミニマルテンプレート](https://github.com/yewstack/yew-wasm-pack-minimal) - アプリをビルドするのに `wasm-pack`と
|
||||
|
||||
`rollup`を使い、サーバーはアプリをサーブします. ベルや笛はここにはありません。
|
||||
|
||||
- [Webpack テンプレート](https://github.com/yewstack/yew-wasm-pack-template) - `wasm-pack`と
|
||||
|
||||
[`wasm-pack-plugin`](https://github.com/wasm-tool/wasm-pack-plugin)を使い、Webpack が開発を滑らかにします。
|
||||
|
||||
これらのテンプレートを使うのと`cargo-web`を使用するのと重要な違いは、このアプローチは`bin`クレートではなく`lib`クレートを用いて
|
||||
`#[wasm_bindgen]`によってエントリーポイントを指定できる点です。
|
||||
|
||||
また、`Cargo.toml`はクレートの種類が"cdylib"であると特定できるようにしましょう。
|
||||
|
||||
```text title="Cargo.toml"
|
||||
[package]
|
||||
name = "yew-app"
|
||||
version = "0.1.0"
|
||||
authors = ["Yew App Developer <name@example.com>"]
|
||||
edition = "2018"
|
||||
|
||||
[lib]
|
||||
crate-type = ["cdylib"]
|
||||
|
||||
[dependencies]
|
||||
# for web_sys
|
||||
yew = "0.17"
|
||||
# or for stdweb
|
||||
# yew = { version = "0.17", package = "yew-stdweb" }
|
||||
wasm-bindgen = "0.2"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## その他のテンプレート
|
||||
|
||||
- [Parcel Template](https://github.com/spielrs/yew-parcel-template) - コミュニティのメンバーによって開発され、
|
||||
Parcel](https://parceljs.org/)を使っています。
|
||||
@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: External libraries
|
||||
description: Libraries that can help with yew development
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 外部ライブラリ
|
||||
|
||||
### Yewtil
|
||||
|
||||
Yewtil は Yew のプログラムを書きやすくするユーティリティ集です。
|
||||
含まれているのは:
|
||||
|
||||
- NeqAssign - 先述の通り、再レンダリングを最小化するよう props を割り当てる方法です
|
||||
- PureComponents - 状態を更新しないコンポーネント。NeqAssign を使用するとマクロの中から通常のコンポーネントのように呼び出される関数がメモ化されます。
|
||||
|
||||
- Lrc - リンクされたリストは、`Rc`のようにカウントされたスマートポインタ関数を参照しますが、新しいデータ更新パターンを可能にします。
|
||||
- Mrc/Irc - Mutable/Immutable 参照カウントのスマートポインタは `Rc` のように機能しますが、`Mrc` に対して `DerefMut` と `BorrowMut` を実装しているため、Yew の中でより使いやすくなっています。これにより、`Mrc` を `NeqAssign` と一緒に使うことができます。`Irc` はデータに対する不変のビューとして機能するので、表示のみのタスクで使用されるデータを保持するのに理想的です。
|
||||
|
||||
- History - `VecDeque` を用いて、表示した過去の値を保持する履歴追跡ラッパーです。
|
||||
- Futures - コンポーネントの更新ループにメッセージを送信するのをサポートします。
|
||||
- Fetch - `web_sys` と前述の futures の機能を用いたフェッチリクエストを処理するための抽象化です。
|
||||
|
||||
## お探しのものは
|
||||
|
||||
エコシステムが必要なライブラリですが、まだありません。
|
||||
|
||||
Bootstrap/MaterialUi/arbitrary といった CSS フレームワークのコンポーネントのラッパー。
|
||||
@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Table of contents
|
||||
|
||||
- [はじめに](index.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 始める
|
||||
|
||||
- [プロジェクトの準備](getting-started/project-setup.mdx)
|
||||
- [trunk を使う](getting-started/project-setup/using-trunk.mdx)
|
||||
- [wasm-pack を使う](getting-started/project-setup/using-wasm-pack.mdx)
|
||||
- [cargo-web を使う](getting-started/project-setup/using-cargo-web.mdx)
|
||||
- [入門用テンプレート](getting-started/starter-templates.mdx)
|
||||
- [サンプルアプリを作る](getting-started/build-a-sample-app.mdx)
|
||||
- [web-sys か stdweb 選ぶ](getting-started/choose-web-library.mdx)
|
||||
- [例から学ぶ](getting-started/examples.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 基本となる概念 <a id="concepts"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
- [html!を使う](concepts/html.mdx)
|
||||
- [リスト](concepts/html/lists.mdx)
|
||||
- [要素](concepts/html/elements.mdx)
|
||||
- [リテラルと式](concepts/html/literals-and-expressions.mdx)
|
||||
- [コンポーネント](concepts/html/components.mdx)
|
||||
- [コンポーネント (Components)](concepts/components.mdx)
|
||||
- [属性 (Properties)](concepts/components/properties.mdx)
|
||||
- [コールバック (Callbacks)](concepts/components/callbacks.mdx)
|
||||
- [参照 (Refs)](concepts/components/refs.mdx)
|
||||
- [Agents](concepts/agents.mdx)
|
||||
- [Services](concepts/services.mdx)
|
||||
- [Format](concepts/services/format.mdx)
|
||||
- [ルータ](concepts/router.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 高度な内容
|
||||
|
||||
- [最適化とベストプラクティス](advanced-topics/optimizations.mdx)
|
||||
- [低レベルなライブラリの中身](advanced-topics/how-it-works.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 更なる内容
|
||||
|
||||
- [CSS](more/css.mdx)
|
||||
- [ロードマップ](more/roadmap.mdx)
|
||||
- [テスト](more/testing.mdx)
|
||||
- [デバッグ](more/debugging.mdx)
|
||||
- [外部ライブラリ](more/external-libs.mdx)
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Callbacks
|
||||
description: ComponentLink and Callbacks
|
||||
title: 'Callbacks'
|
||||
description: 'ComponentLink and Callbacks'
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
”リンク”コンポーネントはコンポーネントがコールバックを登録できて自身を更新することができるメカニズムです。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ slug: /
|
||||
|
||||
以下のリンクをクリックして初めての Yew アプリの作り方を学び、コミュニティのプロジェクト例を見てみましょう。
|
||||
|
||||
[始める](getting-started/project-setup.mdx)
|
||||
[始める](docs/getting-started/introduction)
|
||||
|
||||
### まだ満足していませんか?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,10 +11,6 @@
|
||||
"message": "More",
|
||||
"description": "The title of the footer links column with title=More in the footer"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"link.item.label.Fund Issues": {
|
||||
"message": "Fund Issues",
|
||||
"description": "The label of footer link with label=Fund Issues linking to https://issuehunt.io/r/yewstack/yew"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"link.item.label.Sponsor Project": {
|
||||
"message": "Sponsor Project",
|
||||
"description": "The label of footer link with label=Sponsor Project linking to https://opencollective.com/yew"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,88 +3,12 @@
|
||||
"message": "Next",
|
||||
"description": "The label for version current"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Getting Started": {
|
||||
"message": "Getting Started",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Getting Started in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Concepts": {
|
||||
"message": "Concepts",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Concepts in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Concepts.link.generated-index.title": {
|
||||
"message": "Yew concepts",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page title for category Concepts in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Concepts.link.generated-index.description": {
|
||||
"message": "Learn about the important Yew concepts!",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page description for category Concepts in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Components": {
|
||||
"message": "Components",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Components in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.HTML": {
|
||||
"message": "HTML",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category HTML in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Function Components": {
|
||||
"message": "Function Components",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Function Components in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.wasm-bindgen": {
|
||||
"message": "wasm-bindgen",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category wasm-bindgen in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.wasm-bindgen.link.generated-index.title": {
|
||||
"message": "wasm-bindgen",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page title for category wasm-bindgen in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.wasm-bindgen.link.generated-index.description": {
|
||||
"message": "Learn about wasm-bindgen",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page description for category wasm-bindgen in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Advanced topics": {
|
||||
"message": "Advanced topics",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Advanced topics in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Advanced topics.link.generated-index.title": {
|
||||
"message": "Advanced topics",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page title for category Advanced topics in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Advanced topics.link.generated-index.description": {
|
||||
"message": "Learn about the advanced topics and inner workings of Yew!",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page description for category Advanced topics in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.More": {
|
||||
"message": "More",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category More in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.More.link.generated-index.title": {
|
||||
"message": "Miscellaneous",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page title for category More in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.Migration guides": {
|
||||
"message": "Migration guides",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Migration guides in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.yew": {
|
||||
"message": "yew",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category yew in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.yew-agent": {
|
||||
"message": "yew-agent",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category yew-agent in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.sidebar.category.yew-router": {
|
||||
"message": "yew-router",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category yew-router in sidebar sidebar"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.Getting Started": {
|
||||
"message": "Getting Started",
|
||||
"message": "从零开始",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Getting Started in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.Concepts": {
|
||||
"message": "Concepts",
|
||||
"message": "核心概念",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Concepts in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.Concepts.link.generated-index.title": {
|
||||
@ -95,10 +19,6 @@
|
||||
"message": "Learn about the important Yew concepts!",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page description for category Concepts in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.Components": {
|
||||
"message": "Components",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Components in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.HTML": {
|
||||
"message": "HTML",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category HTML in sidebar docs"
|
||||
@ -107,24 +27,12 @@
|
||||
"message": "Function Components",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Function Components in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.wasm-bindgen": {
|
||||
"message": "wasm-bindgen",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category wasm-bindgen in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.wasm-bindgen.link.generated-index.title": {
|
||||
"message": "wasm-bindgen",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page title for category wasm-bindgen in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.wasm-bindgen.link.generated-index.description": {
|
||||
"message": "Learn about wasm-bindgen",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page description for category wasm-bindgen in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.Advanced topics": {
|
||||
"message": "Advanced topics",
|
||||
"message": "高级主题",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category Advanced topics in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.Advanced topics.link.generated-index.title": {
|
||||
"message": "Advanced topics",
|
||||
"message": "高级主题",
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page title for category Advanced topics in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.Advanced topics.link.generated-index.description": {
|
||||
@ -132,7 +40,7 @@
|
||||
"description": "The generated-index page description for category Advanced topics in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.More": {
|
||||
"message": "More",
|
||||
"message": "更多",
|
||||
"description": "The label for category More in sidebar docs"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sidebar.docs.category.More.link.generated-index.title": {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Table of contents
|
||||
|
||||
- [简介](README.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 从零开始 <a id="getting-started"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
- [项目设置](getting-started/project-setup.mdx)
|
||||
- [使用 wasm-pack](getting-started/project-setup/using-wasm-pack.mdx)
|
||||
- [使用 wasm-bindgen](getting-started/project-setup/using-wasm-bindgen.mdx)
|
||||
- [使用 cargo-web](getting-started/project-setup/using-cargo-web.mdx)
|
||||
- [新手模板](getting-started/starter-templates.mdx)
|
||||
- [第一个简单的 App](getting-started/build-a-sample-app.mdx)
|
||||
- [选择 web-sys 还是 stdweb](getting-started/choose-web-library.mdx)
|
||||
- [通过例子学习](getting-started/examples.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 核心概念 <a id="concepts"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
- [使用 html! 宏](concepts/html.mdx)
|
||||
- [列表](concepts/html/lists.mdx)
|
||||
- [元素](concepts/html/elements.mdx)
|
||||
- [常量和表达式](concepts/html/literals-and-expressions.mdx)
|
||||
- [组件](concepts/html/components.mdx)
|
||||
- [组件(Components)](concepts/components.mdx)
|
||||
- [属性(Properties)](concepts/components/properties.mdx)
|
||||
- [回调(Callbacks)](concepts/components/callbacks.mdx)
|
||||
- [Refs](concepts/components/refs.mdx)
|
||||
- [Agents](concepts/agents.mdx)
|
||||
- [Services](concepts/services.mdx)
|
||||
- [Format](concepts/services/format.mdx)
|
||||
- [Router](concepts/router.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 高级主题 <a id="advanced-topics"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
- [性能优化与最佳实践](advanced-topics/optimizations.mdx)
|
||||
- [底层库的内部细节](advanced-topics/how-it-works.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 更多 <a id="more"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
- [CSS](more/css.mdx)
|
||||
- [路线图](more/roadmap.mdx)
|
||||
- [测试](more/testing.mdx)
|
||||
- [Debugging](more/debugging.mdx)
|
||||
- [外部库](more/external-libs.mdx)
|
||||
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
有关用法的详细信息,请查看 [`html!` 宏指南](html.md)]
|
||||
有关用法的详细信息,请查看 [`html!` 宏指南](concepts/html/introduction.mdx)]
|
||||
|
||||
### Mounted
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,170 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
description: 组件及其生命周期钩子
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 组件(Components)
|
||||
|
||||
## 组件是什么?
|
||||
|
||||
组件是 Yew 的基石。它们管理自己的状态,并可以渲染为 DOM。组件是通过实现描述组件生命周期的 `Component` trait 来创建的。
|
||||
|
||||
## 生命周期
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
`为我们的文档做出贡献:`[添加组件的生命周期图示](https://github.com/yewstack/docs/issues/22)
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 生命周期方法
|
||||
|
||||
### Create
|
||||
|
||||
当一个组件被创建时,它会从其父组件以及一个 `ComponentLink` 接收属性(properties)。属性(properties)可用于初始化组件的状态,“link”可用于注册回调或向组件发送消息。
|
||||
|
||||
通常将 props 和 link 存储在组件的结构体中,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub struct MyComponent {
|
||||
props: Props,
|
||||
link: ComponentLink<Self>,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Properties = Props;
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn create(props: Self::Properties, link: ComponentLink<Self>) -> Self {
|
||||
MyComponent { props, link }
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### View
|
||||
|
||||
组件在 `view()` 方法中声明它的布局。Yew 提供了 `html!` 宏来声明 HTML 和 SVG 节点和它们的监听器及其子组件。这个宏的行为很像 React 中的 JSX,但是使用的是 Rust 表达式而不是 JavaScript。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
let onclick = self.link.callback(|_| Msg::Click);
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<button {onclick}>{ self.props.button_text }</button>
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
有关用法的详细信息,请查看 [`html!` 宏指南](html.mdx)]
|
||||
|
||||
### Mounted
|
||||
|
||||
`mounted()` 组件生命周期方法调用是在 `view()` 被处理并且 Yew 已经把组件挂载到 DOM 上之后,浏览器刷新页面之前。组件通常希望实现此方法以执行只能在组件渲染元素之后才能执行的操作。如果你想在做出一些更改后重新渲染组件,返回 `true` 就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
use stdweb::web::html_element::InputElement;
|
||||
use stdweb::web::IHtmlElement;
|
||||
use yew::prelude::*;
|
||||
|
||||
pub struct MyComponent {
|
||||
node_ref: NodeRef,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<input ref={self.node_ref.clone()} type="text" />
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn mounted(&mut self) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
if let Some(input) = self.node_ref.cast::<InputElement>() {
|
||||
input.focus();
|
||||
}
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
请注意,此生命周期方法不要求必须实现,默认情况下不会执行任何操作。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Update
|
||||
|
||||
组件是动态的,可以注册以接收异步信息。`update()` 生命周期方法对于每个消息都会被调用。这使得组件可以根据消息的内容来更新自身,并决定是否需要重新渲染自己。消息可以由 HTML 元素监听器触发,或者由子组件,Agents,Services 或 Futures 发送。
|
||||
|
||||
`update()` 可能看起来像下面这个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub enum Msg {
|
||||
SetInputEnabled(bool)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Message = Msg;
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn update(&mut self, msg: Self::Message) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
match msg {
|
||||
Msg::SetInputEnabled(enabled) => {
|
||||
if self.input_enabled != enabled {
|
||||
self.input_enabled = enabled;
|
||||
true // 重新渲染
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Change
|
||||
|
||||
组件可能被其父节点重新渲染。发生这种情况时,它们可以接收新的属性(properties)并选择重新渲染。这种设计通过更改属性(properties)来促进父子组件之间的通信。你不是必须实现 `change()`,但是如果想在组件被创建后通过 props 来更新组件,则可能要这么做。
|
||||
|
||||
一个原始的实现可能看起来像:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn change(&mut self, props: Self::Properties) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
self.props = props;
|
||||
true // 当提供了新的 props 将始终重新渲染。
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Destroy
|
||||
|
||||
组件从 DOM 上被卸载后,Yew 调用 `destroy()` 生命周期方法来支持任何必要的清理操作。这个方法是可选的,默认情况下不执行任何操作。
|
||||
|
||||
## 关联类型
|
||||
|
||||
`Component` trait 有两个关联类型:`Message` 和 `Properties`。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Message = Msg;
|
||||
type Properties = Props;
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`Message` 表示组件可以处理以触发某些副作用的各种消息。例如,你可能有一条 `Click` 消息,该消息触发 API 请求或者切换 UI 组件的外观。通常的做法是在组件模块中创建一个叫做 `Msg` 的枚举并将其用作组件中的消息类型。通常将“message”缩写为“msg”。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
enum Msg {
|
||||
Click,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`Properties` 表示从父级传递到组件的信息。此类型必须实现 `Properties` trait(通常通过派生),并且可以指定某些属性(properties)是必需的还是可选的。创建和更新组件时使用此类型。通常的做法是在组件模块中创建一个叫做 `Props` 的结构体并将其用作组件的 `Properties` 类型。通常将“properties”缩写为“props”。由于 props 是从父组件传递下来的,因此应用程序的根组件通常有一个类型为 `()` 的 `Properties`。如果你希望为根组件指定属性(properties),请使用 `App::mount_with_props` 方法。
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 函数式组件
|
||||
sidebar_label: 简介
|
||||
description: 介绍函数式组件
|
||||
slug: /concepts/function-components
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
函数式组件是普通组件的简化版本。它们由一个接收 props 的函数组成,并通过返回`Html`来确定应该呈现什么。基本上,它是一个简化为`view`方法的组件。就其本身而言,这将是相当有限的,因为您只能创建纯组件,而这就是 Hook 大展身手的地方。Hook 允许函数组件无需实现`Component` trait,就可以使用状态(state)和其他 Yew 功能。
|
||||
|
||||
## 创建函数式组件
|
||||
|
||||
创建函数式组件的最简单方法是在函数前添加`#[function_component]`属性。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
#[function_component(HelloWorld)]
|
||||
fn hello_world() -> Html {
|
||||
html! { "Hello world" }
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 更多细节
|
||||
|
||||
函数式组件由两部分组成。首先, `FunctionProvider` trait 与`Component` trait 差不多,但它只有一个名为`run`方法。之后是`FunctionComponent`结构体,它封装了`FunctionProvider`类型并将其转换为实际的`Component` 。 `#[function_component]`属性本质上只是`FunctionProvider`并将其暴露在`FunctionComponent` 。
|
||||
|
||||
### 钩子(Hooks)
|
||||
|
||||
钩子(Hooks)就是让您“钩住”组件的状态(state)和/或生命周期并执行操作的函数。 除了 Yew 自带的一些预定义的 Hook。您也可以创建自己的。
|
||||
@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
description: 用于生成 HTML 和 SVG 的宏程序
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 使用 html! 宏
|
||||
|
||||
`html!` 宏允许你为组件编写声明式的 HTML 和 SVG。如果你使用过 React 的 JSX,将会感觉到非常熟悉。
|
||||
|
||||
**重要提示**
|
||||
|
||||
1. `html!` 宏调用中只能有一个根节点
|
||||
2. 空的 `html! {}` 宏调用是有效的但不会渲染任何内容
|
||||
3. 常量必须始终被引号括起来并被包含在大括号里:`html! { "Hello, World" }`
|
||||
@ -1,5 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
description: Yew's glue to browser APIs.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Services
|
||||
@ -1,5 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Format
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
`Contribute to our docs:` [Explain the format module in depth](https://github.com/yewstack/docs/issues/24)
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@ -1,162 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# 选择 web-sys 还是 stdweb
|
||||
|
||||
## 简介
|
||||
|
||||
Yew 应用程序可以通过 [`web-sys`](https://docs.rs/web-sys) 或者 [`stdweb`](https://docs.rs/stdweb) 来构建。这两个 crates 提供了 Rust 和 Web API 之间的绑定。当把 `yew` 添加到你的 cargo 依赖时,你需要选择它们其中之一:
|
||||
|
||||
{% code title="Cargo.toml" %}
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
# 选择 `web-sys`
|
||||
yew = { version = "0.13", features = ["web_sys"] }
|
||||
|
||||
# 选择 `stdweb`
|
||||
yew = { version = "0.13", features = ["std_web"] }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% endcode %}
|
||||
|
||||
我们建议选择 `web-sys`,因为它是由 [Rust / Wasm 工作组](https://rustwasm.github.io/) 提供支持。
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例用法
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// web-sys
|
||||
let window: web_sys::Window = web_sys::window().expect("window not available");
|
||||
window.alert_with_message("hello from wasm!").expect("alert failed");
|
||||
|
||||
// stdweb
|
||||
let window: stdweb::web::Window = stdweb::web::window();
|
||||
window.alert("hello from wasm!");
|
||||
|
||||
// stdweb 搭配 js! 宏
|
||||
use stdweb::js;
|
||||
use stdweb::unstable::TryFrom;
|
||||
use stdweb::web::Window;
|
||||
|
||||
let window_val: stdweb::Value = js!{ return window; }; // <- 里面使用 JS 语法
|
||||
let window = Window::try_from(window_val).expect("conversion to window failed");
|
||||
window.alert("hello from wasm!");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
两个 crate 的 API 略有不用,但他们的目标大致相同,功能相似。
|
||||
|
||||
## 选择其中之一
|
||||
|
||||
当为你的应用程序选择使用 `web-sys` 还是 `stdweb` 时,有几个不同的角度需要考虑。注意,可以在一个应用程序中同时使用两者,但是为了最小化编译的 `.wasm` 二进制体积,最好选择其中之一。
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}></th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>web-sys</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>stdweb</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
项目状态
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
由
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/">
|
||||
Rust / Wasm 工作组
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
积极维护
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
超过四个月没有 Github
|
||||
活动
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Web API 覆盖率
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Rust API 是从 Web IDL
|
||||
规范自动生成,因此理论上有
|
||||
100% 的覆盖率。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
浏览器 API
|
||||
是根据需求由社区添加
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>Rust API 设计</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
采取保守的方法,为大多数
|
||||
API 调用返回 <code>Result</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
通常拒绝返回{' '}
|
||||
<code>Result</code>{' '}
|
||||
而更倾向于使用
|
||||
panic。例如,在 worker
|
||||
中调用 <code>stdweb::web::window()</code>{' '}
|
||||
将 panic。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
支持的构建工具
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm-bindgen</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm-pack</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>cargo-web</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm-bindgen</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm-pack</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
支持生成的目标代码
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>asmjs-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
有关更多挑选构建工具的信息,请参阅 [Wasm 构建工具](project-setup/#wasm-build-tools)
|
||||
指南。
|
||||
@ -1,203 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
description: 为成功做好准备
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 项目设置
|
||||
|
||||
## Rust
|
||||
|
||||
首先 ,你需要安装 Rust 。如何安装 Rust 和 `cargo` 构建工具,请参考[官方说明](https://www.rust-lang.org/tools/install)。
|
||||
|
||||
## **Wasm 构建工具**
|
||||
|
||||
需要安装额外的工具以方便 WebAssembly 与 JavaScript 间的相互操作。此外,根据你选择的工具,他们可以生成所有必需的 JavaScript 包装代码来让你的应用程序中的 `.wasm` 文件运行在浏览器中,从而帮助减轻部署和打包的麻烦。
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`wasm-pack`**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/)
|
||||
|
||||
一个由 Rust / Wasm 工作组开发的用于打包 WebAssembly 的 CLI 工具。与 Webpack 的 [`wasm-pack-plugin`](https://github.com/wasm-tool/wasm-pack-plugin) 插件搭配使用最佳。
|
||||
|
||||
[开始使用 wasm-pack](project-setup/using-wasm-pack.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`wasm-bindgen`**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/)
|
||||
|
||||
同时是一个库和一个 CLI 工具,也是由 Rust / Wasm 工作组开发。它是一个促进 JS 和 WebAssembly 之间互操作性的底层工具(在 `wasm-pack` 内部被用到)。我们不建议直接使用 `wasm-bindgen` 因为它需要手写一些 JavaScript 代码来引导你的 WebAssembly 二进制程序。但是,直接使用它也是可能的并且可以在 [**`wasm-bindgen` 指南**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/) 上找到更多信息。
|
||||
|
||||
[开始使用 wasm-bindgen](project-setup/using-wasm-bindgen.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`cargo-web`**](https://github.com/koute/cargo-web)
|
||||
|
||||
在 `wasm-pack` 和 `wasm-bindgen` 被介绍前的首选 web 工作流工具。它仍然是**最快捷**的启动和运行方式,值得安装以运行尚未迁移到支持 `wasm-pack` 的示例程序。
|
||||
|
||||
[开始使用 cargo-web](project-setup/using-cargo-web.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
### 对比
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}></th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>wasm-pack</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>wasm-bindgen</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>cargo-web</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
项目状态
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
由{' '}
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/">
|
||||
Rust / Wasm 工作组
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
积极维护
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
由{' '}
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/">
|
||||
Rust / Wasm 工作组
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
积极维护
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
超过六个月没有 Github
|
||||
活动
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
开发体验
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
接近完美!需要{' '}
|
||||
<code>webpack</code>{' '}
|
||||
以获得最佳体验。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
比较基础。你需要编写一些脚本来简化你的开发体验。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
管用!自带“电池”,不需要外部依赖。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
本地服务器
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
通过 <code>webpack</code>{' '}
|
||||
插件支持
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>不支持</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>支持</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
根据本地更改自动重新构建
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
通过 <code>webpack</code>{' '}
|
||||
插件支持
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>不支持</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>支持</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
无头浏览器测试
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/commands/test.html">
|
||||
支持
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/wasm-bindgen-test/index.html">
|
||||
支持
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/koute/cargo-web#features">
|
||||
支持
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
支持生成的目标代码
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>asmjs-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>web-sys</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>兼容</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>兼容</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>不兼容</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>stdweb</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>兼容</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>兼容</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>兼容</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
示例用法
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/yewstack/yew-wasm-pack-minimal">
|
||||
新手模板
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Yew 示例程序的
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/yewstack/yew/blob/master/examples/build_all.sh">
|
||||
构建脚本
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Yew 示例程序的
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/yewstack/yew/blob/master/examples/build_all.sh">
|
||||
构建脚本
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
@ -1,203 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
description: 为成功做好准备
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 项目设置
|
||||
|
||||
## Rust
|
||||
|
||||
首先 ,你需要安装 Rust 。如何安装 Rust 和 `cargo` 构建工具,请参考[官方说明](https://www.rust-lang.org/tools/install)。
|
||||
|
||||
## **Wasm 构建工具**
|
||||
|
||||
需要安装额外的工具以方便 WebAssembly 与 JavaScript 间的相互操作。此外,根据你选择的工具,他们可以生成所有必需的 JavaScript 包装代码来让你的应用程序中的 `.wasm` 文件运行在浏览器中,从而帮助减轻部署和打包的麻烦。
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`wasm-pack`**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/)
|
||||
|
||||
一个由 Rust / Wasm 工作组开发的用于打包 WebAssembly 的 CLI 工具。与 Webpack 的 [`wasm-pack-plugin`](https://github.com/wasm-tool/wasm-pack-plugin) 插件搭配使用最佳。
|
||||
|
||||
[开始使用 wasm-pack](project-setup/using-wasm-pack.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`wasm-bindgen`**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/)
|
||||
|
||||
同时是一个库和一个 CLI 工具,也是由 Rust / Wasm 工作组开发。它是一个促进 JS 和 WebAssembly 之间互操作性的底层工具(在 `wasm-pack` 内部被用到)。我们不建议直接使用 `wasm-bindgen` 因为它需要手写一些 JavaScript 代码来引导你的 WebAssembly 二进制程序。但是,直接使用它也是可能的并且可以在 [**`wasm-bindgen` 指南**](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/) 上找到更多信息。
|
||||
|
||||
[开始使用 wasm-bindgen](project-setup/using-wasm-bindgen.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### [**`cargo-web`**](https://github.com/koute/cargo-web)
|
||||
|
||||
在 `wasm-pack` 和 `wasm-bindgen` 被介绍前的首选 web 工作流工具。它仍然是**最快捷**的启动和运行方式,值得安装以运行尚未迁移到支持 `wasm-pack` 的示例程序。
|
||||
|
||||
[开始使用 cargo-web](project-setup/using-cargo-web.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### 对比
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}></th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>wasm-pack</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>wasm-bindgen</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
<th style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>cargo-web</code>
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
项目状态
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
由{' '}
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/">
|
||||
Rust / Wasm 工作组
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
积极维护
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
由{' '}
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/">
|
||||
Rust / Wasm 工作组
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
积极维护
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
超过六个月没有 Github
|
||||
活动
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
开发体验
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
接近完美!需要{' '}
|
||||
<code>webpack</code>{' '}
|
||||
以获得最佳体验。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
比较基础。你需要编写一些脚本来简化你的开发体验。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
管用!自带“电池”,不需要外部依赖。
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
本地服务器
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
通过 <code>webpack</code>{' '}
|
||||
插件支持
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>不支持</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>支持</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
根据本地更改自动重新构建
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
通过 <code>webpack</code>{' '}
|
||||
插件支持
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>不支持</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>支持</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
无头浏览器测试
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/commands/test.html">
|
||||
支持
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-bindgen/wasm-bindgen-test/index.html">
|
||||
支持
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/koute/cargo-web#features">
|
||||
支持
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
支持生成的目标代码
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-unknown</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>wasm32-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<code>asmjs-unknown-emscripten</code>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>web-sys</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>兼容</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>兼容</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>不兼容</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<code>stdweb</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>兼容</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>兼容</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>兼容</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
示例用法
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/yewstack/yew-wasm-pack-minimal">
|
||||
新手模板
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Yew 示例程序的
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/yewstack/yew/blob/master/examples/build_all.sh">
|
||||
构建脚本
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td style={{ textAlign: 'left' }}>
|
||||
Yew 示例程序的
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/yewstack/yew/blob/master/examples/build_all.sh">
|
||||
构建脚本
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# 使用 cargo-web
|
||||
|
||||
Cargo web 是一个用来构建 web 客户端应用的 Cargo 子命令,它让构建和部署 web 应用变得非常的简单。它同样也是唯一一个支持生成 Emscripten 目标代码的工具链。点击[这里](https://github.com/koute/cargo-web)了解更多。
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo install cargo-web
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 构建
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo web build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 运行
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo web start
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 支持生成的目标代码
|
||||
|
||||
- `wasm32-unknown-unknown`
|
||||
- `wasm32-unknown-emscripten`
|
||||
- `asmjs-unknown-emscripten`
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
对于 `*-emscripten` 的目标代码, 你需要安装 Emscripten SDK。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 使用trunk
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo install --locked trunk
|
||||
cargo install wasm-bindgen-cli
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 用法
|
||||
|
||||
请查看[“构建示例应用程序”](../build-a-sample-app.md),以获取有关如何使用 Trunk 构建 Yew 应用程序的简短指南。
|
||||
|
||||
您还可以通过查看我们的[示例](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/master/examples)来查看实际情况,所有示例都是使用 Trunk 构建的。
|
||||
|
||||
Trunk 基于`index.html`文件构建您的应用,并将其作为配置文件。与`wasm-pack`不同,此工具实际上是为构建应用而设计的。这意味着您不需要添加`cdylib`库,并且可以使用`main`函数作为入口点。
|
||||
|
||||
要构建一个简单的 Yew 应用程序,您只需要在项目的根目录下创建`index.html`:
|
||||
|
||||
```html
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html>
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="utf-8" />
|
||||
<title>Yew App</title>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Trunk CLI 提供了一些有用的命令,但是在开发过程中, `trunk serve`无疑是最有用的命令。它为您运行本地服务器,并在检测到更改时自动重建应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
当您准备发布应用程序时,只需运行`trunk build --release` 。
|
||||
|
||||
当前摘要仅介绍了 Trunk 的部分功能,请务必查看[README](https://github.com/thedodd/trunk) !
|
||||
@ -1,5 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# 使用 wasm-bindgen
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
`Contribute to our docs:` [Explain how to use wasm-bindgen to build an app](https://github.com/yewstack/docs/issues/34)
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# 使用 wasm-pack
|
||||
|
||||
这个工具由 Rust / Wasm 工作组开发维护,并且是现在最为活跃的 WebAssembly 应用开发工具。 它支持将代码打包成 `npm` 模块,并且随附了 [Webpack 插件](https://github.com/wasm-tool/wasm-pack-plugin),可以轻松的与已有的 JavaScript 应用结合。可以点击[这里](https://rustwasm.github.io/docs/wasm-pack/introduction.html)了解更多。
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
注:如果使用 `wasm-pack`作为开发工具,`Cargo.toml` 中的 `crate-type` 需要为 `cdylib`
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cargo install wasm-pack
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 构建
|
||||
|
||||
这条命令将在工程根目录下的 `./pkg` 目录中生成打包后的应用,其中包含应用的 WebAssembly 文件以及用来启动应用的 JavaScript 包装器。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
wasm-pack build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 打包
|
||||
|
||||
关于 Rollup 的更多信息,请查看这篇[指南](https://rollupjs.org/guide/en/#quick-start)
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
rollup ./main.js --format iife --file ./pkg/bundle.js
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 部署
|
||||
|
||||
选取你喜爱的服务器。这里我们使用一个简单的 Python 服务器来将项目部署到:[http://\[::1\]:8000](http://[::1]:8000)。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 8080
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 支持生成的目标代码
|
||||
|
||||
- `wasm32-unknown-unknown`
|
||||
@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# 新手模板
|
||||
|
||||
## `wasm-pack`
|
||||
|
||||
- [Minimal Template](https://github.com/yewstack/yew-wasm-pack-minimal) - 使用 `wasm-pack` 和 `rollup` 来构建你的应用, 并使用你自己的服务器来部署它,No bells or whistles here.
|
||||
- [Webpack Template](https://github.com/yewstack/yew-wasm-pack-template) - 使用 `wasm-pack` 和 wasm-pack 的插件 [`wasm-pack-plugin`](https://github.com/wasm-tool/wasm-pack-plugin) 来简化开发。
|
||||
|
||||
使用这些例子和使用 `cargo-web` 的最重要的区别是 它们 使用了 `lib` 类型 而非 `bin` 类型的工程,同时你的应用的入口应该使用 `#[wasm_bindgen]` 标记出来。
|
||||
|
||||
你的 `Cargo.toml` 同样应该指明你的工程的 crate-type 是 "cdylib" 。
|
||||
|
||||
{% code title="Cargo.toml" %}
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
[package]
|
||||
name = "yew-app"
|
||||
version = "0.1.0"
|
||||
authors = ["Yew App Developer <name@example.com>"]
|
||||
edition = "2018"
|
||||
|
||||
[lib]
|
||||
crate-type = ["cdylib"]
|
||||
|
||||
[dependencies]
|
||||
yew = { version = "0.13.0", features = ["web_sys" OR "std_web"] }
|
||||
wasm-bindgen = "0.2"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% endcode %}
|
||||
|
||||
## Parcel
|
||||
|
||||
- [Parcel Template](https://github.com/spielrs/yew-parcel-template) - 由一位社区成员建立并使用了 [Parcel](https://parceljs.org/) 。
|
||||
@ -1,47 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Introduction
|
||||
slug: /
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Yew 是什么?
|
||||
|
||||
**Yew** 是一个设计先进的 [Rust](https://www.rust-lang.org/) 框架,目的是使用 [WebAssembly](https://webassembly.org/) 来创建多线程的前端 web 应用。
|
||||
|
||||
- **基于组件的框架**,可以轻松的创建交互式 UI。拥有 [React](https://reactjs.org/) 或 [Elm](https://elm-lang.org/) 等框架经验的开发人员在使用 Yew 时会感到得心应手。
|
||||
- **高性能** ,前端开发者可以轻易的将工作分流至后端来减少 DOM API 的调用,从而达到异常出色的性能。
|
||||
- **支持与 JavaScript 交互** ,允许开发者使用 NPM 包,并与现有的 JavaScript 应用程序结合。
|
||||
|
||||
### 加入我们 😊
|
||||
|
||||
- 你可以在这里 [GitHub issues page](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/issues) 报告 Bugs 或者是提出新的想法。
|
||||
- 我们欢迎 pull requests 。 如果你想要帮助我们,先参考下 [good first issues](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22) 吧!
|
||||
- 我们的 [Discord chat](https://discord.gg/VQck8X4) 非常的热闹,也是一个问问题和解决问题的好地方!
|
||||
|
||||
### 准备好开始了吗?
|
||||
|
||||
点击下面的链接,来学习并编写你的第一个 Yew 前端 App , 并通过丰富的社区示例项目来学习。
|
||||
|
||||
[项目设置](getting-started/project-setup.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
### 还没有完全信服?
|
||||
|
||||
Yew 项目基于划时代的新技术,非常适合那些希望开发未来基础项目的开发者。接下来是一些我们相信 Yew 这样的框架将为成为未来 Web 开发的主流。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 等等,为什么选用 WebAssembly?
|
||||
|
||||
WebAssembly _(Wasm)_ 是一种可移植的底层语言,并且可以由 Rust 编译而来。它在浏览器中可以以原生速度运行,还同时支持和 JavaScript 交互。这些在所有的主流浏览器中都已经提供。希望了解更多关于 WebAssembly 是如何为前端应用提速的,可以查看官方[用例](https://webassembly.org/docs/use-cases/).
|
||||
|
||||
值得注意的是,Wasm(目前还)并不是提高 Web 应用性能的万金油(原文:A Silver Bullet)就目前来说,在 WebAssembly 中使用 DOM API 仍然比从 JavaScript 中调用要慢。但只是暂时性问题的,[WebAssembly Interface Types](https://github.com/WebAssembly/interface-types/blob/master/proposals/interface-types/Explainer.md) 计划将解决这个问题。如果你想要了解更多关于这方面的信息,可以查看 Mozilla 的这篇[佳作](https://hacks.mozilla.org/2019/08/webassembly-interface-types/) 。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 好的,那为什么选用 Rust 呢?
|
||||
|
||||
Rust 是一门运行速度超快,并且以他丰富的类型系统和可信赖的所有权模型而闻名的语言。尽管它的学习曲线非常的陡峭,但是带来的回报完全成正比!Rust 已经连续四年在 Stack Overflow 开发者调查报告中被评选为最受喜爱的编程语言:[2016](https://insights.stackoverflow.com/survey/2016#technology-most-loved-dreaded-and-wanted),[2017](https://insights.stackoverflow.com/survey/2017#most-loved-dreaded-and-wanted),[2018](https://insights.stackoverflow.com/survey/2018#technology-_-most-loved-dreaded-and-wanted-languages) 和 [2019](https://insights.stackoverflow.com/survey/2019#technology-_-most-loved-dreaded-and-wanted-languages)。
|
||||
|
||||
Rust 同样可以用它丰富的类型系统和可信赖的所有权模型来帮助开发者编写出更加安全的代码。和那些在 JavaScript 中难以定位的竞争条件 Bug 们说再见吧! 事实上,通过 Rust ,大部分的 Bugs 都将在项目上线之前的编写阶段被编译器发现。同时不用担心,当你的应用出现错误的时候,你仍然可以在浏览器的调试控制台中获得你 Rust 代码的完整的错误栈追踪。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 同类的项目?
|
||||
|
||||
我们非常愿意和其他的类似项目交流想法,并且相信通过这种方式,我们可以互相扶持进步来发挥出这个新技术的潜力。如果你对 Yew 没有兴趣,你可能会喜欢这些项目。
|
||||
|
||||
- [Percy](https://github.com/chinedufn/percy) - _"A modular toolkit for building isomorphic web apps with Rust + WebAssembly"_
|
||||
- [Seed](https://github.com/seed-rs/seed) - _"A Rust framework for creating web apps"_
|
||||
@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
description: 可以帮助 Yew 开发的库
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 外部库
|
||||
|
||||
### Yewtil
|
||||
|
||||
Yewtil 是一个帮助你编写 Yew 程序的通用工具集合。它包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- NeqAssign - 如前所述,这是给 props 赋值以保证最小化重新渲染的最佳方式。
|
||||
- PureComponents - 不更新任何状态的组件。它们在内部使用 NeqAssign,表现得像记忆化函数并像普通组件一样在 `html!` 宏内部被调用。
|
||||
- Lrc - 链表引用计数智能指针,功能类似于 `Rc`,但是允许新颖的数据更新模式。
|
||||
- Mrc/Irc - 可变/不可变引用计数智能指针,功能类似于 `Rc`,但由于为 `Mrc` 实现了 `DerefMut` 和 `BorrowMut`,因此在 Yew 中对用户更友好。这允许 `Mrc` 与 `NeqAssign` 一起使用。`Irc` 充当数据的不可变视图,这使其成为保存仅用于显示的数据的理想选择。
|
||||
- History - 历史记录追踪包装器,它使用 `VecDeque` 来保存其展示过的历史值。
|
||||
- Futures - 支持运行将消息发送到组件更新循环的 futures。
|
||||
- Fetch - 用于处理使用 `web-sys` 和前面提到的 Futures 功能发请求的抽象。
|
||||
|
||||
## 寻求
|
||||
|
||||
生态需要但目前还没有的库。
|
||||
|
||||
Bootstrap/MaterialUi/任意 css 框架的组件封装。
|
||||
@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Table of contents
|
||||
|
||||
- [简介](README.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 从零开始 <a id="getting-started"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
- [项目设置](getting-started/project-setup.mdx)
|
||||
- [使用 wasm-pack](getting-started/project-setup/using-wasm-pack.mdx)
|
||||
- [使用 wasm-bindgen](getting-started/project-setup/using-wasm-bindgen.mdx)
|
||||
- [使用 cargo-web](getting-started/project-setup/using-cargo-web.mdx)
|
||||
- [新手模板](getting-started/starter-templates.mdx)
|
||||
- [第一个简单的 App](getting-started/build-a-sample-app.mdx)
|
||||
- [选择 web-sys 还是 stdweb](getting-started/choose-web-library.mdx)
|
||||
- [通过例子学习](getting-started/examples.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 核心概念 <a id="concepts"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
- [使用 html! 宏](concepts/html.mdx)
|
||||
- [列表](concepts/html/lists.mdx)
|
||||
- [元素](concepts/html/elements.mdx)
|
||||
- [常量和表达式](concepts/html/literals-and-expressions.mdx)
|
||||
- [组件](concepts/html/components.mdx)
|
||||
- [组件(Components)](concepts/components.mdx)
|
||||
- [属性(Properties)](concepts/components/properties.mdx)
|
||||
- [回调(Callbacks)](concepts/components/callbacks.mdx)
|
||||
- [Refs](concepts/components/refs.mdx)
|
||||
- [Agents](concepts/agents.mdx)
|
||||
- [Services](concepts/services.mdx)
|
||||
- [Format](concepts/services/format.mdx)
|
||||
- [Router](concepts/router.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 高级主题 <a id="advanced-topics"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
- [性能优化与最佳实践](advanced-topics/optimizations.mdx)
|
||||
- [底层库的内部细节](advanced-topics/how-it-works.mdx)
|
||||
|
||||
## 更多 <a id="more"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
- [CSS](more/css.mdx)
|
||||
- [路线图](more/roadmap.mdx)
|
||||
- [测试](more/testing.mdx)
|
||||
- [Debugging](more/debugging.mdx)
|
||||
- [外部库](more/external-libs.mdx)
|
||||
@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
description: 有关框架的底层细节
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 底层库的内部细节
|
||||
|
||||
组件生命周期状态机,虚拟 dom diff 算法。
|
||||
@ -1,105 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
description: 加速你的应用程序
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 性能优化与最佳实践
|
||||
|
||||
## neq_assign
|
||||
|
||||
当组件从它的父组件接收 props 时,`change` 方法将被调用。除了允许你更新组件的状态,还允许你返回一个布尔类型的值 `ShouldRender` 来指示组件是否应该响应 props 的更改而重新渲染自身。
|
||||
|
||||
重新渲染的开销很大,你应该尽量避免。一个通用的法则是,你只应该在 props 实际更改时重新渲染。以下代码块展示了此法则,如果 props 和先前的 props 不同,则返回 `true`:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
fn change(&mut self, props: Self::Properties) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
if self.props != &props {
|
||||
*self.props = props;
|
||||
true
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
但是我们可以更进一步!对于任何实现了 `PartialEq` 的项,可以使用一个 trait 和一个 blanket implementation 将这六行样板代码减少到一行。
|
||||
|
||||
{% code title="neq\_assign.rs" %}
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub trait NeqAssign {
|
||||
fn neq_assign(&mut self, new: Self) -> ShouldRender;
|
||||
}
|
||||
impl<T: PartialEq> NeqAssign for T {
|
||||
fn neq_assign(&mut self, new: T) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
if self != &new {
|
||||
*self = new;
|
||||
true
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
fn change(&mut self, props: Self::Properties) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
self.props.neq_assign(props)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{% endcode %}
|
||||
|
||||
该 trait 称为 `NeqAssign` 是因为如果目标值和新值不相等,它将赋为新值。
|
||||
|
||||
这比简单的实现还要短:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// 不要这样做,除非你无法避免。
|
||||
fn change(&mut self, props: Self::Properties) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
self.props = props;
|
||||
true
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你不仅限在 `change` 函数中使用它。通常,在 `update` 函数中执行此操作也是有意义的,尽管性能提升在那里不太明显。
|
||||
|
||||
## wee_alloc
|
||||
|
||||
[wee_alloc](https://github.com/rustwasm/wee_alloc) 是一个比 Rust 二进制文件中通常使用的分配器还小得多的微型分配器。用这个分配器来替代默认的分配器将使 Wasm 文件体积更小,但会牺牲速度和内存开销。
|
||||
|
||||
对比不包含默认分配器换取的体积大小,牺牲的速度和内存开销是微不足道的。较小的文件体积意味着你的页面将加载更快,因此通常建议使用此分配器而不是默认分配器,除非你的应用程序会执行一些繁重的内存分配任务。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// 将 `wee_alloc` 作为全局分配器
|
||||
#[global_allocator]
|
||||
static ALLOC: wee_alloc::WeeAlloc = wee_alloc::WeeAlloc::INIT;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## RC
|
||||
|
||||
为了避免在重新渲染时为了创建 props 而克隆大块数据,我们可以使用智能指针来只克隆指针。如果在 props 和子组件中使用 `Rc<_>` 而不是普通未装箱的值,则可以延迟克隆直到需要修改子组件中的数据为止,在该组件中可以使用 `Rc::make_mut` 来对要更改数据进行克隆和获取可变引用。通过在要修改前不进行克隆,子组件可以在几乎没有性能成本的情况下拒绝与它们在 `Component::change` 中拥有状态的 props 相同的 props,这与数据本身需要先复制到父级 props 结构体中,然后在子级中进行比较和拒绝的情况相反。
|
||||
|
||||
对于不是 `Copy` 类型的数据,这种优化是最有用的。如果你能轻松地拷贝数据,那么将其放入智能指针中可能是不值得的。对于可以包含大量数据的结构,例如 `Vec`,`HashMap` 和 `String`,这种优化应该是值得的。
|
||||
|
||||
如果子组件从不更新组件的值,则这种优化效果最好,如果父组件很少更新组件的值,则效果更好。这使得 `Rc<_>s` 是包装纯组件属性值的不错选择。
|
||||
|
||||
## 视图函数
|
||||
|
||||
出于代码可读性的原因,将 `html!` 各个部分的代码迁移到他们自己的函数中通常是有意义的,这样就可以避免在深层嵌套的 HTML 中出现代码块向右偏移。
|
||||
|
||||
## 纯组件 / 函数式组件
|
||||
|
||||
纯组件是不会修改它们状态的组件,它们仅展示内容和向普通可变组件传递消息。它们与视图函数不同之处在于他们可以使用组件语法(`<SomePureComponent />`)而不是表达式语法(`{some_view_function()}`)来在 `html!` 宏中使用,并且根据它们的实现,它们可以被记忆化 - 使用前面提到的 `neq_assign` 逻辑来防止因为相同的 props 而重新渲染。
|
||||
|
||||
Yew 没有原生支持纯组件或者函数式组件,但是可以通过外部库获取它们。
|
||||
|
||||
函数式组件尚不存在,但是从理论上来讲,可以通过使用 proc 宏和标注函数生成纯组件。
|
||||
|
||||
## Keyed DOM nodes when they arrive
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用 Cargo Workspaces 进行编译速度优化
|
||||
|
||||
可以说,使用 Yew 的最大缺点是编译时间长。编译时间似乎与 `html!` 宏块中的代码量相关。对于较小的项目,这通常不是什么大问题,但是对于跨多个页面的 web 应用程序,将代码拆分为多个 crates 以最大程度地减少编译器要做的工作通常是有意义的。
|
||||
|
||||
你应该尝试让主 crate 处理路由和页面选择,将所有公用的代码移动到另一个 crate,然后为每一个页面创建一个不同的 crate,其中每个页面可能是一个不同的组件,或者只是一个产生 `Html` 的大函数。在最好的情况下,你将从重新构建所有代码到只重新构建主 crate 和一个页面的 crate。在最糟糕的情况下,当你在“公共” crate 中编辑内容时,你将回到起点:编译所有依赖此公用 crate 的代码,这可能就是除此之外的所有代码。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的主 crate 过于庞大,或者你想在深层嵌套的页面(例如,在另一个页面顶部渲染的页面)中快速迭代,则可以使用一个示例 crate 创建一个更简单的主页面实现并在之上渲染你正在开发的组件。
|
||||
@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Agents
|
||||
description: Yew 的 Actor 系统
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Agents 和 Angular 的 [Services](https://angular.io/guide/architecture-services) 相似(但没有依赖注入),给 Yew 提供了 [Actor 模型](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Actor_model)。Agents 可以用于在组件之间路由消息,而与它们在组件层次结构中的位置无关,或者可以用于协调全局状态,或者可以用于从主 UI 线程上卸载计算密集型任务,或者在不同的标签页间通信(在未来)。
|
||||
|
||||
Agents 使用 [web-workers](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Web_Workers_API/Using_web_workers) 同时运行来实现并发。
|
||||
|
||||
## 生命周期
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Agents 的类型
|
||||
|
||||
#### Reaches
|
||||
|
||||
- Job - 在 UI 线程上为每个新的 Bridge 生成一个新的 Agent。这对于将与浏览器通信的共享但独立的行为移出组件是很有用的。(待验证)任务完成后,Agent 将消失。
|
||||
- Context - Bridges 将生成或连接到 UI 线程上的 agent。这可用于在组件和其它 Agents 之间协调状态。当没有 Bridge 连接到该 Agent 时,Agent 将消失。
|
||||
- Private - 与 Job 相同,但运行在自己的 web worker 中。
|
||||
- Public - 与 Context 相同,但运行在自己的 web worker 中。
|
||||
- Global \(WIP\)
|
||||
|
||||
## Agent 通信
|
||||
|
||||
### Bridges
|
||||
|
||||
Bridges 将连接到一个 Agent 并且允许双向通信。
|
||||
|
||||
### Dispatchers
|
||||
|
||||
Dispatchers 和 Bridges 类似,但是他们只能发送消息给 Agents。
|
||||
|
||||
## 开销
|
||||
|
||||
Agents 通过使用二进制码 bincode 序列化其消息来进行通信。因此,存在比仅调用函数相比更高的性能消耗。除非计算成本或者在任意组件间协调的需求超过消息传递的成本,否则你应该尽可能地在函数中包含你的应用逻辑。
|
||||
|
||||
## Further reading
|
||||
|
||||
- The [pub_sub](https://github.com/yewstack/yew/tree/master/examples/pub_sub) example shows how components can use agents to communicate with each other.
|
||||
@ -1,170 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
description: 组件及其生命周期钩子
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 组件(Components)
|
||||
|
||||
## 组件是什么?
|
||||
|
||||
组件是 Yew 的基石。它们管理自己的状态,并可以渲染为 DOM。组件是通过实现描述组件生命周期的 `Component` trait 来创建的。
|
||||
|
||||
## 生命周期
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
`为我们的文档做出贡献:`[添加组件的生命周期图示](https://github.com/yewstack/docs/issues/22)
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## 生命周期方法
|
||||
|
||||
### Create
|
||||
|
||||
当一个组件被创建时,它会从其父组件以及一个 `ComponentLink` 接收属性(properties)。属性(properties)可用于初始化组件的状态,“link”可用于注册回调或向组件发送消息。
|
||||
|
||||
通常将 props 和 link 存储在组件的结构体中,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub struct MyComponent {
|
||||
props: Props,
|
||||
link: ComponentLink<Self>,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Properties = Props;
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn create(props: Self::Properties, link: ComponentLink<Self>) -> Self {
|
||||
MyComponent { props, link }
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### View
|
||||
|
||||
组件在 `view()` 方法中声明它的布局。Yew 提供了 `html!` 宏来声明 HTML 和 SVG 节点和它们的监听器及其子组件。这个宏的行为很像 React 中的 JSX,但是使用的是 Rust 表达式而不是 JavaScript。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
let onclick = self.link.callback(|_| Msg::Click);
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<button onclick=onclick>{ self.props.button_text }</button>
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
有关用法的详细信息,请查看 [`html!` 宏指南](html.mdx)]
|
||||
|
||||
### Mounted
|
||||
|
||||
`mounted()` 组件生命周期方法调用是在 `view()` 被处理并且 Yew 已经把组件挂载到 DOM 上之后,浏览器刷新页面之前。组件通常希望实现此方法以执行只能在组件渲染元素之后才能执行的操作。如果你想在做出一些更改后重新渲染组件,返回 `true` 就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
use stdweb::web::html_element::InputElement;
|
||||
use stdweb::web::IHtmlElement;
|
||||
use yew::prelude::*;
|
||||
|
||||
pub struct MyComponent {
|
||||
node_ref: NodeRef,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html {
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<input ref=self.node_ref.clone() type="text" />
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fn mounted(&mut self) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
if let Some(input) = self.node_ref.cast::<InputElement>() {
|
||||
input.focus();
|
||||
}
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
请注意,此生命周期方法不要求必须实现,默认情况下不会执行任何操作。
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Update
|
||||
|
||||
组件是动态的,可以注册以接收异步信息。`update()` 生命周期方法对于每个消息都会被调用。这使得组件可以根据消息的内容来更新自身,并决定是否需要重新渲染自己。消息可以由 HTML 元素监听器触发,或者由子组件,Agents,Services 或 Futures 发送。
|
||||
|
||||
`update()` 可能看起来像下面这个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub enum Msg {
|
||||
SetInputEnabled(bool)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Message = Msg;
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn update(&mut self, msg: Self::Message) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
match msg {
|
||||
Msg::SetInputEnabled(enabled) => {
|
||||
if self.input_enabled != enabled {
|
||||
self.input_enabled = enabled;
|
||||
true // 重新渲染
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Change
|
||||
|
||||
组件可能被其父节点重新渲染。发生这种情况时,它们可以接收新的属性(properties)并选择重新渲染。这种设计通过更改属性(properties)来促进父子组件之间的通信。你不是必须实现 `change()`,但是如果想在组件被创建后通过 props 来更新组件,则可能要这么做。
|
||||
|
||||
一个原始的实现可能看起来像:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
|
||||
fn change(&mut self, props: Self::Properties) -> ShouldRender {
|
||||
self.props = props;
|
||||
true // 当提供了新的 props 将始终重新渲染。
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Destroy
|
||||
|
||||
组件从 DOM 上被卸载后,Yew 调用 `destroy()` 生命周期方法来支持任何必要的清理操作。这个方法是可选的,默认情况下不执行任何操作。
|
||||
|
||||
## 关联类型
|
||||
|
||||
`Component` trait 有两个关联类型:`Message` 和 `Properties`。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
impl Component for MyComponent {
|
||||
type Message = Msg;
|
||||
type Properties = Props;
|
||||
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`Message` 表示组件可以处理以触发某些副作用的各种消息。例如,你可能有一条 `Click` 消息,该消息触发 API 请求或者切换 UI 组件的外观。通常的做法是在组件模块中创建一个叫做 `Msg` 的枚举并将其用作组件中的消息类型。通常将“message”缩写为“msg”。
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
enum Msg {
|
||||
Click,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`Properties` 表示从父级传递到组件的信息。此类型必须实现 `Properties` trait(通常通过派生),并且可以指定某些属性(properties)是必需的还是可选的。创建和更新组件时使用此类型。通常的做法是在组件模块中创建一个叫做 `Props` 的结构体并将其用作组件的 `Properties` 类型。通常将“properties”缩写为“props”。由于 props 是从父组件传递下来的,因此应用程序的根组件通常有一个类型为 `()` 的 `Properties`。如果你希望为根组件指定属性(properties),请使用 `App::mount_with_props` 方法。
|
||||
@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
description: ComponentLink 和 Callbacks.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 回调(Callbacks)
|
||||
|
||||
组件“link”是一种机制,通过该机制,组件可以注册回调并自行更新。
|
||||
|
||||
## ComponentLink API
|
||||
|
||||
### callback
|
||||
|
||||
注册一个回调,该回调将在执行时将消息发送到组件的更新机制。在内部,它将使用提供的闭包返回的消息调用 `send_self`。提供 `Fn(IN) -> Vec<COMP::Message>`,返回 `Callback<IN>`。
|
||||
|
||||
### send_message
|
||||
|
||||
当前循环结束后立即向组件发送消息,导致另一个更新循环启动。
|
||||
|
||||
### send_message_batch
|
||||
|
||||
注册一个回调,该回调在执行时立即发送一批消息。如果其中任何一个消息将导致组件重新渲染,那么组件会在该批次所有消息被处理后重新渲染。提供 `Fn(IN) -> COMP::Message`,返回 `Callback<IN>`。
|
||||
|
||||
## Callbacks
|
||||
|
||||
Callbacks 用于与 Yew 中的 services,agents 和父组件进行通信。它们仅仅是个 `Fn`,并由 `Rc` 包裹以允许被克隆。
|
||||
|
||||
它们有一个 `emit` 函数,该函数将它的 `<IN>` 类型作为参数并将其转换为目标所期望的消息。如果一个回调从父组件中通过 props 提供给子组件,则子组件可以在其 `update` 生命周期钩子中对该回调调用 `emit`,以将消息发送回父组件。在 `html!` 宏内被提供作为 props 的闭包或函数会自动转换为 Callbacks。
|
||||
@ -1,72 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
description: 父组件到子组件的通信
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 属性(Properties)
|
||||
|
||||
如“组件(Components)”页面所述,Properties 用于父级到子组件的通信。
|
||||
|
||||
## 派生宏
|
||||
|
||||
不要尝试自己去实现 `Properties`,而是通过使用 `#[derive(Properties)]` 来派生它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 必需属性
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,实现了 `Properties` 的结构体中的字段是必需的。当缺少了该字段并且在 `html!` 宏中创建了组件时,将返回编译错误。对于具有可选属性的字段,使用 `#[prop_or_default]` 来使用该类型的默认值。要指定一个值,请使用 `#[prop_or_else(value)]`,其中 value 是该属性的默认值。例如,要将一个布尔值的默认值设置为 `true`,请使用属性 `#[prop_or_else(true)]`。可选属性通常使用 `Option`,其默认值为 `None`。
|
||||
|
||||
### PartialEq
|
||||
|
||||
如果可以的话,在你的 props 上派生 `PartialEq` 通常是很有意义的。这使用了一个**性能优化与最佳实践**部分解释了的技巧,可以更轻松地避免重新渲染。
|
||||
|
||||
## Properties 的内存/速度开销
|
||||
|
||||
记住组件的 `view` 函数签名:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
fn view(&self) -> Html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你对组件的状态取了一个引用,并用来创建 `Html`。但是 properties 是有所有权的值(owned values)。这意味着为了创造它们并且将它们传递给子组件,我们需要获取 `view` 函数里提供的引用的所有权。这是在将引用传递给组件时隐式克隆引用完成的,以获得构成其 props 的有所有权的值。
|
||||
|
||||
这意味着每个组件都有从其父级传递来的状态的独特副本,而且,每当你重新渲染一个组件时,该重新渲染组件的所有子组件的 props 都将被克隆。
|
||||
|
||||
这意味着如果你将 _大量_ 数据作为 props(大小为 10 KB 的字符串)向下传递,则可能需要考虑将子组件转换为在父级运行返回 `Html` 的函数,因为这样就不会被强制克隆你的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,如果你不需要修改作为 props 传递的大数据,而只需要显示它,则可以将其包装在 `Rc` 中,以便仅克隆一个引用计数的指针,而不是数据本身。
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
pub struct LinkColor {
|
||||
Blue,
|
||||
Red,
|
||||
Green,
|
||||
Black,
|
||||
Purple,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
impl Default for LinkColor {
|
||||
fn default() -> Self {
|
||||
// 除非另有说明,否则链接的颜色将为蓝色
|
||||
LinkColor::Blue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#[derive(Properties, PartialEq)]
|
||||
pub struct LinkProps {
|
||||
/// 链接必须有一个目标地址
|
||||
href: String,
|
||||
/// 如果链接文本很大,这将使得复制字符串开销更小
|
||||
/// 除非有性能问题,否则通常不建议这么做
|
||||
text: Rc<String>,
|
||||
/// 链接的颜色
|
||||
#[prop_or_default]
|
||||
color: LinkColor,
|
||||
/// 如果为 None,则 view 函数将不指定大小
|
||||
#[prop_or_default]
|
||||
size: Option<u32>
|
||||
/// 当 view 函数没有指定 active,其默认为 true
|
||||
#[prop_or_else(true)]
|
||||
active: bool,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Refs
|
||||
description: 超出界限的 DOM 访问
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
`ref` 关键词可被用在任何 HTML 元素或组件内部以获得该项所附加到的 DOM 元素。这可被用于在 `view` 生命周期方法之外来对 DOM 进行更改。
|
||||
|
||||
这对于获取 canvas 元素或者滚动到页面的不同部分是有用的。
|
||||
|
||||
语法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```rust
|
||||
// 在 create 中
|
||||
self.node_ref = NodeRef::default();
|
||||
|
||||
// 在 view 中
|
||||
html! {
|
||||
<div ref=self.node_ref.clone()></div>
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 在 update 中
|
||||
let has_attributes = self.node_ref.cast::<Element>().unwrap().has_attributes();
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
description: 用于生成 HTML 和 SVG 的宏程序
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 使用 html! 宏
|
||||
|
||||
`html!` 宏允许你为组件编写声明式的 HTML 和 SVG。如果你使用过 React 的 JSX,将会感觉到非常熟悉。
|
||||
|
||||
**重要提示**
|
||||
|
||||
1. `html!` 宏调用中只能有一个根节点
|
||||
2. 空的 `html! {}` 宏调用是有效的但不会渲染任何内容
|
||||
3. 常量必须始终被引号括起来并被包含在大括号里:`html! { "Hello, World" }`
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
x
Reference in New Issue
Block a user