* Update README.pt-BR.md * TRIE README.pt-BR typo * TREE README.pt-BR typo * Stack README.pt-BR typo * Priority Queue README.pt-BR typo * hash-table README.pt-BR typo * doubly-linked-list README.pt-BR typo * disjoint-set README.pt-BR typo * bloom-filter README.pt-BR typo * merge-sort pt-BR translation * merge-sort README added pt-BR option * insertion sort pt-BR translation * insertion sort README added pt-br option * heap-sort pt-BR translation * heap-sort READMED added pt-BR option * bubble sort pt-BR typo * pt-BR translation for sorting algorithms Fixed typos and translated all the missing algorithms * Update README.pt-BR.md * linked list pt-BR translation * ml pt-BR translation * fix typo in README Co-authored-by: Oleksii Trekhleb <trehleb@gmail.com>
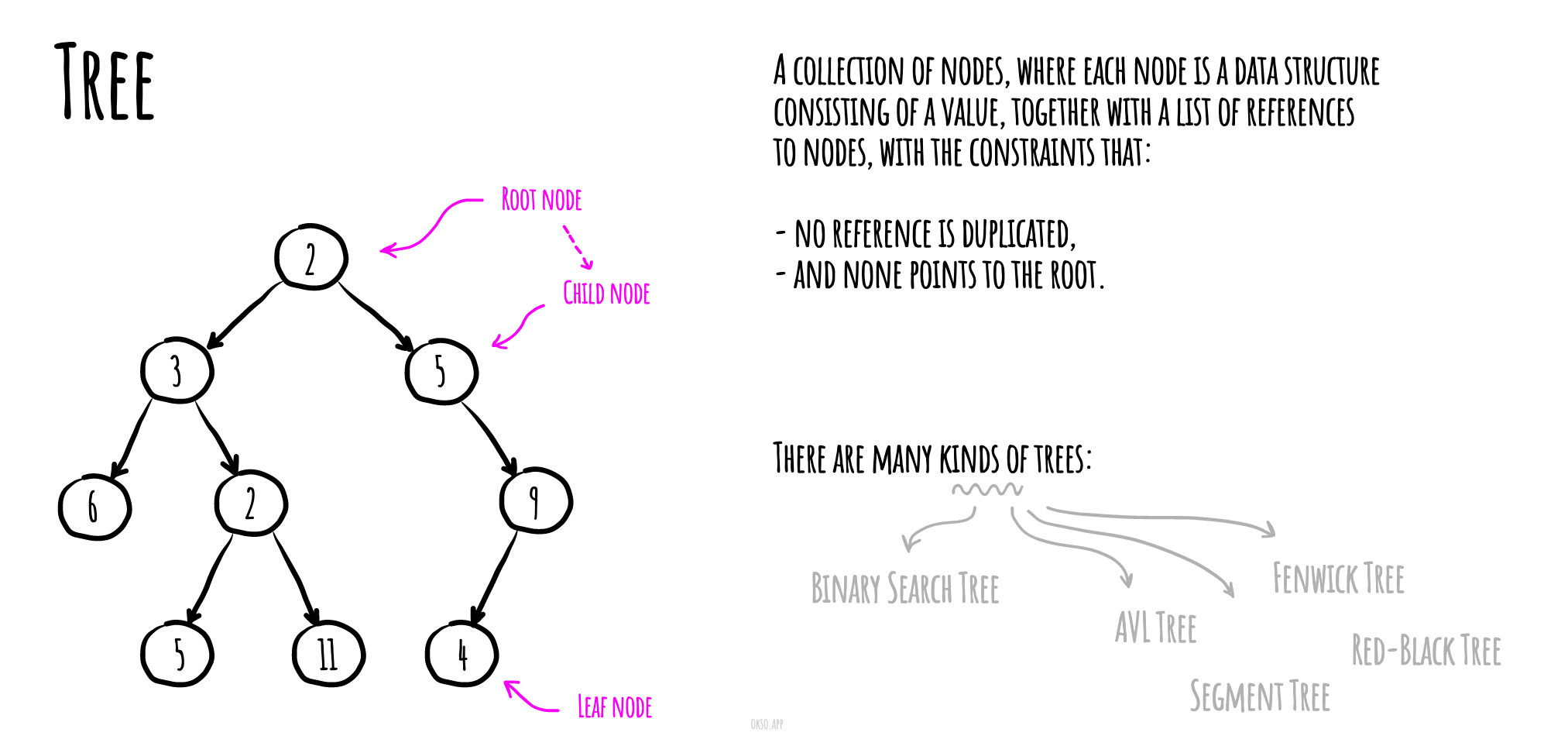
Tree
Read this in other languages: 简体中文, Português
- Binary Search Tree
- AVL Tree
- Red-Black Tree
- Segment Tree - with min/max/sum range queries examples
- Fenwick Tree (Binary Indexed Tree)
In computer science, a tree is a widely used abstract data type (ADT) — or data structure implementing this ADT—that simulates a hierarchical tree structure, with a root value and subtrees of children with a parent node, represented as a set of linked nodes.
A tree data structure can be defined recursively (locally) as a collection of nodes (starting at a root node), where each node is a data structure consisting of a value, together with a list of references to nodes (the "children"), with the constraints that no reference is duplicated, and none points to the root.
A simple unordered tree; in this diagram, the node labeled 7 has two children, labeled 2 and 6, and one parent, labeled 2. The root node, at the top, has no parent.
Made with okso.app